Whooping cough is a highly contagious respiratory tract infection. The name of the disease comes from the whooping noise you might make when you try to breathe in after coughing. Whooping cough is very contagious and can affect anyone. But it can be especially serious in babies who did not yet get the vaccine. About half of babies under age one who get whooping cough need care in the hospital.
What Causes Whooping Cough?
A type of bacteria called Bordetella pertussis causes whooping cough. If a person with whooping cough sneezes, coughs, or laughs, small droplets that have the bacteria may fly through the air. If you breathe in the droplets, you may get sick.
When the bacteria get into your airways, they attack the tiny hairs in the lining of the lungs. The bacteria then causes swelling and inflammation which may lead to a long-lasting cough and other cold-like symptoms.

What Are The Symptoms Of Whooping Cough?
When you are infected with whooping cough, it may take 7-10 days for the symptoms to appear. They’re usually mild at first and resemble those of a common cold:
- Runny nose
- Nasal congestion
- Red, watery eyes
- Fever
- Cough
After a week or two, symptoms worsen. Thick mucus accumulates inside your airways which may cause uncontrollable coughing. Severe and prolonged coughing attacks may:
- Result in a red or blue face
- Provoke vomiting
- Cause extreme fatigue
- End with a high-pitched whoop sound during the next breath of air
How to Diagnose Whooping Cough?
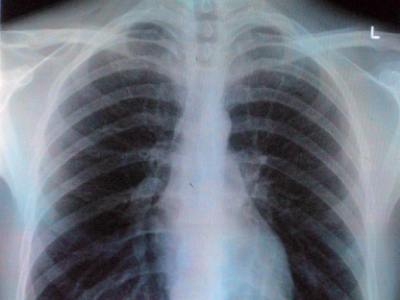
Whooping Cough diagnosis in the early stages can be difficult because the symptoms resemble those of other common respiratory illnesses. Sometimes, doctors diagnose this condition simply by asking about the symptoms and listening to the cough. Medical tests may be needed to confirm the diagnosis including:
- A nose or throat culture and test. Your doctor takes a swab or suction sample from the area where the nose and throat meet.
- A chest X-ray. Your doctor may order an X-ray to check for the presence of inflammation or fluid in the lungs.
- Blood tests. A blood sample is to check your white blood cell count because white blood cells help the body fight infections.
Treatment and Medication for Whooping Cough
Infants are usually hospitalized for treatment because whooping cough is more dangerous for that age group. If your child can’t keep down liquids or food, intravenous fluids may be needed. Your child will also be isolated from others to prevent the infection from spreading. Treatment for older children and adults usually can be managed at home.
Medications that can be used for whooping cough:
Antibiotics kill the bacteria causing whooping cough and help speed recovery. Exposed family members may be given preventive antibiotics.