Laryngitis is caused by an inflammation of the voice box (larynx). Swelling of the voice box can be triggered by an infection, such as bronchitis, cold, or flu. The problem could also be something as simple as overuse.
With proper treatment, Laryngitis should go away in no more than 3 weeks. Sometimes, this condition lasts longer and becomes chronic, but there are ways to help yourself feel better.
What Are The Symptoms Of Laryngitis?
In most cases, the symptoms of laryngitis last less than a couple of weeks and are caused by something minor. Less often, laryngitis symptoms are caused by something more serious or long-lasting. Laryngitis symptoms can include:
- Weak voice or voice loss
- Hoarseness
- Sore throat
- Dry throat
- Dry cough
- Tickling sensation and rawness in your throat
What Causes Laryngitis?
There are two types of Laryngitis with different causes:
Acute Laryngitis
Most cases of laryngitis are temporary and improve after the underlying cause gets better. Causes of acute laryngitis include:
- A vocal strain that is caused by yelling or overusing your voice
- Viral infections similar to those that cause a cold
- Bacterial infections, even though these are less common

Chronic Laryngitis
Chronic laryngitis lasts longer than three weeks. This type of laryngitis is generally caused by exposure to irritants over time. Chronic laryngitis can cause vocal cord strain and injuries or growths on the vocal cords. Chronic laryngitis can be caused by:
- Chronic sinusitis
- Excessive alcohol use
- Inhaled irritants, such as chemical fumes, allergens, or smoke
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Habitual overuse of your voice (such as in singers or cheerleaders)
- Smoking
Less common causes of chronic laryngitis include:
- Infections with certain parasites
- Bacterial or fungal infections
Other causes of chronic hoarseness include:
- Cancer
- Bowing of the vocal cords
- Vocal cord paralysis can cause nerve injury due to surgery, cancer, injury to the chest or neck, nerve disorders, or other health conditions
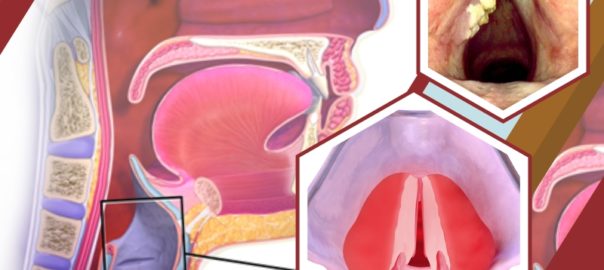
Diagnosis for Laryngitis
Laryngitis is characterized primarily by hoarseness. Voice changes can range from mild hoarseness to almost complete voice loss, depending on the severity of infection or irritation. Symptoms and medical history may be reviewed by your doctor if you have chronic hoarseness. Your doctor may listen to your voice and examine your vocal cords, and you may be referred to an ear, nose, and throat specialist.
These techniques sometimes are used to help diagnose laryngitis:
- Biopsy – if there are any suspicious areas, your doctor may use this technique
- Laryngoscopy – your doctor can visually examine your vocal cords by using a light and a tiny mirror to look into the back of your throat
Treatment for Laryngitis
Laryngitis often gets better on its own within a week. Self-care measures, such as voice rest, drinking fluids, and humidifying your air, also can help improve symptoms.
Medication used for this condition:
- Azithromycin – this is proven to be effective to treat Laryngitis. Azithromycin is in a class of medications called macrolide antibiotics. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria.