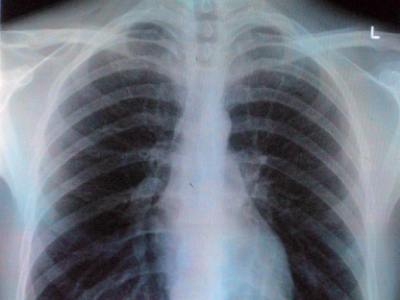
Measles is a childhood infection caused by a virus that can now almost always be prevented with a vaccine. This infection is also called rubeola. Measles can be serious and even fatal for small children. For more than a decade, the infection hasn’t been widespread in the U.S. as they have a high vaccination rate in general.
Most of the measles cases originated outside the country and occurred in people who were unvaccinated or who didn’t know whether or not they had been vaccinated.
What Causes Measles?
Measles is caused by an extremely contagious virus called morbillivirus. If 10 people weren’t vaccinated in a room with someone with measles, 9 of them would get measles. This infection is spread by:
- Sharing drinks or food with someone with measles.
- Contaminated droplets are spread through the air when you sneeze, cough, or talk.
- Kissing someone who has measles.
- Shaking hands or holding hands or hugging someone with measles.
- From pregnant people to their babies either during the pregnancy, delivery, or while nursing.

What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Measles?
The signs and symptoms of measles appear around 10 to 14 days after exposure to the virus. The signs and symptoms usually may include:
- Fever
- Runny nose
- Sore throat
- Dry cough
- Inflamed eyes
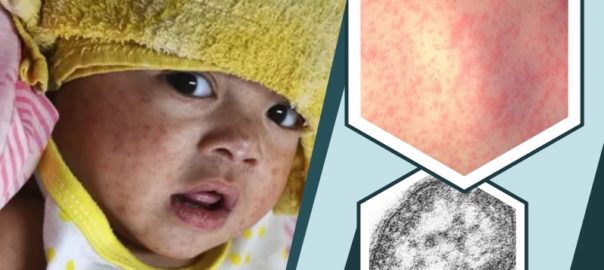
- A skin rash made up of large, flat blotches that often flow into one another
- Tiny white spots with bluish-white centers on a red background are found inside the mouth on the inner lining of the cheek
How to Diagnose Measles?
Your doctor can usually diagnose measles depending on the characteristics of the disease. However, many doctors have never seen measles, and the rash can be confused with several other illnesses. If needed, a blood test can confirm whether the rash is truly measles. The measles virus can also be established with a test that usually uses a throat swab or urine sample.
Treatment for Measles
There’s no exact treatment for established measles infection. However, some measures can be taken to protect vulnerable individuals who have been exposed to the virus.
- Immune serum globulin – infants, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems who are exposed to the virus may receive an injection of antibodies called immune serum globulin. These antibodies can prevent measles or make symptoms less severe when given within six days of exposure to the virus.
- Post-exposure vaccination – Non-immunized people, including infants, may be given the measles vaccination within 72 hours of exposure to the measles virus to protect against the disease.

Medications used for measles:
You should not give aspirin to children or teenagers who have measles symptoms. Though aspirin is approved for use in children older than age 3, children and teenagers recovering from chickenpox or flu-like symptoms must never take aspirin. Aspirin has been linked to Reye’s syndrome, a rare but potentially life-threatening condition, in such children.