Venous Ulcers: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Causes, and Treatment
What is a Venous Ulcer?
A venous ulcer is a wound that takes longer than usual to heal. It is due to vein and blood flow issues and often occurs on your legs near your ankle. This condition can sometimes lead to severe problems if left untreated. However, there are also several ways to prevent them from happening.
The Signs and Symptoms of Venous Ulcer
- Brownish discoloration
- A foul-smelling fluid oozing from the sore
- A rash or dry skin
Worsening symptoms include:
- Worsening pain
- A fever
- A redness or swelling of the surrounding skin
- Pus
Call your doctor if you experience:
- Bleeding
- Odor
- Fever or chills
- Redness, increased warmth, or swelling around the wound
- More drainage than before or drainage that is yellowish or cloudy
- Increased pain
Risk Factors Of Venous Ulcers

- Obesity
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Sitting for long periods with legs positioned below heart level
- Family history of ulcers.
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Lymphedema
- Standing for long periods
- Uncontrolled swelling
- Older age
- Personal history of venous ulcers
- Trauma, such as a fracture or burn
What Causes Venous Ulcers?
Your veins contain tiny valves that keep blood circulating throughout your body. These valves snap open and shut to move blood against the force of gravity back to your heart. In some people, venous diseases affect valve functioning. Other medical conditions, like diabetes, can also put you at risk for leg and foot ulcers.
The veins in the leg, which should send blood back to the heart, might not be doing their job all that well. That is often because the valves that stop the flow of blood back into the veins are not. The backflow of blood means increased pressure at the end of the limb. Over time, it can weaken the skin and make it harder for a cut or scrape to heal.
Other causes are:
- High blood pressure, which damages blood vessel walls.
- Venous obstruction is a vein blockage that’s sometimes due to blood clots.
- Venous reflux is when blood flows backward through weak or damaged valves.
If left untreated, this condition may cause the following complications:
- Infection. Bacteria, viruses, or fungi can lead to infection of the wound. Some severe infections, such as osteomyelitis or septicemia, can occur and require antibiotics.
- Worsening or nonhealing ulcer. An untreated ulcer or underlying
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Venous Ulcers
Venous ulcers don’t heal on their own. The longer you live with them, the greater the likelihood of permanent tissue damage. The damage can spread or cause infections that can become life- or limb-threatening. To prevent this condition, you can:

- Use compression stockings especially if you experience this condition before. Compression stockings may be recommended by your doctors to squeeze your legs and improve your circulation.
- Weight loss. Maintaining a healthy weight loss is essential for people who have obesity or are overweight. It can help treat and prevent venous leg ulcers. Excess weight leads to high pressure in the veins in your legs, which can damage your skin. To help you lose weight, regular exercise and a healthy, balanced diet are recommended.
- Treating underlying problems. Varicose veins are a common condition that may worsen venous ulcers. Treating underlying conditions involves inserting a flexible tube into the affected veins, with high-frequency radio waves or lasers used to seal them.
Venous ulcers that are severe or not responding to standard therapies may require additional treatments such as:
- Growth factor therapy. It uses injectable substances that attract healthy cells to ulcers.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy. It is a treatment in which you sit in a special, pressurized chamber and inhale pure oxygen.
- Lymphedema therapy. Massage, skincare, and bandaging techniques that clear fluid buildup.
- Skin graft, replacing diseased skin with healthy skin from another part of your body.
- Stem cell therapy, injections of bone to generate healthy tissue.
- Venous disease treatment to correct blood pooling problems and improve circulation.
Fungal Nail Infection: Symptoms, Types, Risk Factors, Causes, and Treatment
Fungal nail infection is one of the most common infections of the nail. It begins as a yellow-brown or white spot that appears under the tip of your nail. As time passes, the nail might change color, thicken, and then break near the edge. Nail fungus can affect several nails. Fungi may be found in soil, air, plants, and our bodies. Fungi can be beneficial or harmful, like other microbes.
Types Of Fungal Nail Infection
- The subungual onychomycosis can be lateral or distal. It is the most prevalent type. It’s caused by a fungus known as a dermatophyte. It can be found on your toenails or fingernails. It starts inside the nail bed, beneath the nail. It’s a yellowish area that extends across the edges of your nail towards the center and the places it breaks away from the nail bed.
- White, superficial onychomycosis. It is not as common and only affects the nail’s surface, mostly around your fingernails. The first signs are white spots that turn dry and cause the nail to crack.
- Proximal subungual onychomycosis. It is first seen as white spots in the middle of the nail bed, near the cuticle. They expand as the toenail or finger expands. It’s not common and typically is seen in people with issues with their immune system, such as HIV infection.
- Candidal onychomycosis. The yeast that causes this infection generally affects the fingernails. The nail area is usually inflamed and swollen, and the nails could disappear completely. It is common for nails to be damaged due to an injury or a different infection.
Signs and Symptoms of Fungal Nail Infection
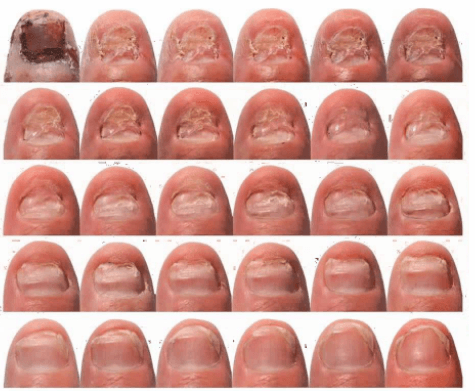
- Nails with thickened nails
- Nails with discoloration
- Crumbly, crumbly, or rough
- Misshapen nails
- Separated from the nail bed
- Smelly
See your doctor if you experience:
- If you have diabetes, you may be developing a nail fungal infection
- Nail bleeding
- Pain or swelling around the nails
- Walking is difficult.
Risk Factors Of Fungal Nail Infection
A serious nail fungus condition could be painful and result in permanent nail damage. Factors that could increase the risk of developing nail fungus are:
- Older age
- Shoes that cause your feet to sweat very much
- A history of an athlete’s foot in the past
- Untidy walking in areas with damp conditions, such as fitness centers, pools, and shower rooms.
- A minor skin or nail injury
- Being afflicted with a skin disease that affects your nails, like psoriasis,
- Being diagnosed with issues with blood flow or a deficient immune system
What Causes Fungal Nail Infection?
The cause of the infection is different organisms. The most prevalent is known as Dermatophyte. Bacteria, yeast, and mold can also result in nail infection. The discoloration caused by an infection caused by bacteria tends to be black or green. It may be spread to the nail, and fungal infections of the nail may spread to the feet. It is also possible to get the infection by touching areas where fungi thrive, such as the floor tiles in a gym shower or inside sweaty, dark, and moist shoes.
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Fungal Nail Infection

- Clean your feet and hands frequently. Wash your hands immediately after touching a nail that is infected. Dry them well, and apply antifungal foot powder and moisturizer to your nails.
- Try applying a nail softener that can assist in strengthening the cuticles and nails.
- Straighten nails, smooth out the edges using a file, and then file the thickened areas. Make sure to clean your nail clippers following every use. Allowing your nails to grow long gives more opportunities for fungus to thrive.
- Change your socks with absorbent socks, or wear absorbent ones. Your socks during the day.
- Select shoes made of substances that allow air to circulate.
- Please remove old shoes, or treat them with antifungal or disinfectant powders.
- Pick a salon that employs sterilized manicure equipment for each client. Also, disinfect the tools you use to do your manicures at home.
- If you suffer from an athlete’s foot, treat it using an antifungal medication.
Medication Used for Fungal Nail Infection
Terbinafine tablet. This tablet treats fungal diseases of nails and fingernails. Terbinafine is part of a group of drugs known as antifungals. It stops the growth of the fungi.
Insulin Resistance: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Causes, and Treatment
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance is when cells in your muscles, fat, and liver don’t respond well to insulin and can’t use glucose from your blood for energy. It may also include conditions like obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes. Insulin is a hormone released by the pancreas that tells your cells to open up to that sugar and convert it into energy.
When you eat food, your body converts that food into dietary sugars. The cells do not react with resistance, resulting in excessive sugar in the blood. Over time, the pancreas keeps trying to regulate the blood sugar, producing more and more insulin until it wears out and may not produce large amounts of insulin anymore. As a result, blood sugar levels increase to the point of being in the diabetic range.
Signs and Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
- A fasting triglyceride level over 150 mg/dL
- A HDL cholesterol level under 40 mg/dL in men and 50 mg/dL in women
- Skin tags
- A waistline over 40 inches in men and 35 inches in women
- Blood pressure readings of 130/80 or higher
- A fasting glucose level over 100 mg/dL
- Patches of dark, velvety skin
What are the Risk Factors of Insulin Resistance?
Anyone can develop insulin resistance temporarily or chronically. Over time, chronic insulin resistance can lead to pre-diabetes and then Type 2 diabetes if it’s not treated or can be treated. You are at risk if:

- You have obesity, or you are overweight, especially when the extra body weight is around the midriff
- You have a sedentary lifestyle
- You smoke or drink excessive amounts of alcoholic beverages
- You consume large amounts of alcohol, which can impact the liver
- You have sleep issues
- Having high cholesterol levels
- Having high blood pressure
How Common is Insulin Resistance?
The best way to measure the prevalence of insulin resistance is through the number of prediabetes cases. More than 84 million adults in the United States have prediabetes. That’s about 1 out of every 3 adults.
This condition may progress to type 2 diabetes if you do not change how you eat and exercise. Your blood sugar levels will rise until you have prediabetes. It causes your pancreas to use extra insulin to make up for it. It will work for a while, and your blood sugar levels will stay normal.
How is Insulin Resistance Diagnosed?
Doctors usually request more than one of these tests to ensure an accurate diagnosis. Several tests can help diagnose prediabetes and diabetes:
- An A1C test measures a person’s average blood sugar level over the previous 3 months.
- Fasting blood glucose test: A doctor checks glucose levels after an individual refrains from eating or drinking for 8 hours.
- Random glucose test involves a medical professional checking blood glucose levels at some point during the day.
How to Prevent Insulin Resistance?

- Factors such as genetic and family history are not preventable. Ensure to visit your doctor for further recommendations. Here are some tips to prevent the condition:
- Manage your weight or quit smoking to prevent heart disease and stroke. Experts say that up to 50% of people with prediabetes can prevent the onset of diabetes through such measures.
- According to the CDC, if a person with overweight or obesity loses 5 to 7% of their body weight, this can significantly reduce their risk of developing diabetes.
- Exercise can also help. Muscles become more sensitive to insulin after exercise, helping the body reverse insulin resistance.
Medication Used For Insulin Resistance
Pioglitazone. It enhances the transcription of insulin-responsive genes and improves the entry of glucose into muscles and fats. It can also be used as monotherapy along with diet and exercise in mild cases and to supplement insulin in advanced cases.
Esophageal Ulcers: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
An esophageal ulcer is a type of peptic ulcer that develops in the lining of the esophagus. It occurs when the layer of mucus, which lines and protects the gastrointestinal tract, wears away. The condition results from an infection with a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori. It can also be caused by destruction from stomach acid moving up into the esophagus.
Signs and Symptoms of Esophageal Ulcers
- Difficult or painful swallowing
- Pain that is lessened by eating, drinking, or taking antacids
- Nausea or vomiting
- Acid reflux or indigestion
- Sour taste in the mouth
- Dry cough
- Bloating
- Vomiting
- Lack of appetite
What Causes Esophageal Ulcers?
Most of the time, this problem can be caused by a bacterium called H. Pylori. The bacterium damages the mucosal lining of the esophagus. It makes the esophagus vulnerable to damage caused by stomach acid.
A chronic condition called GERD can cause an ulcer in the esophageal tract. People suffering from GERD suffer from frequent acid reflux. Patients who suffer from GERD suffer from acid reflux at least every two weeks.
Acid reflux happens in the stomach when contents travel backward towards the stomach and into the esophagus. It can occur when the lower esophageal sphinx is damaged or weak, so it can’t close properly.
Alcohol consumption, smoking, and the frequent consumption of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications may also cause damage to the mucosal linings of the esophagus. It can lead to an ulcer. Genetics also plays a part.
Several pills could cause ulcers and irritation of the esophagus if not taken with enough water or lying down right after taking. If you take any type of pill, you must swallow it with plenty of water.
For those with compromised immune systems, the problem could be caused by other fungal, bacterial, or viral infections, such as:
- HIV
- Candida overgrowth
- Herpes simplex virus
- Cytomegalovirus
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Esophageal Ulcers
The treatment for ulcers of the esophageal tract is dependent on the reason. Most ulcers are treated with proton pump inhibitors, an acid-blocking drug. If you’ve been diagnosed with esophageal ossification on endoscopy, ongoing treatment using PPI medication could be necessary.
If an ulcer has begun to bleed, a doctor may treat the bleeding through an endoscopy. It can be done by injecting the region with medication or heating the site to stop bleeding. They may also advise avoiding NSAIDs, particularly when those drugs cause the ulcer. When the ulcer appears to be related to an infection, doctors may also recommend medication.
If you’ve had the typical signs of esophagitis due to a pill following a prescription and are unsure what to do, it’s unlikely to need an endoscopy. In these cases, if there’s a strong connection, the injury usually requires the time needed to recover.
Homecare Management and Recovery Tips

- Avoid and drink more water
- Avoid smoking and lose some weight if you have excess pounds
- Find ways to reduce stress, such as by exercising or taking a yoga class
- Eat smaller meals more frequently
- Chew some gum after meals to help increase saliva and keep acid out of the esophagus
- Stand for a couple of hours after eating
- Get adequate sleep
- Eat a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains and low in processed or sugary foods
To prevent the condition from coming or worsening, it would be helpful if you will incorporate a diet. During a treatment plan, your doctor might suggest dietary adjustments. Contrary to what many believe, having a bland food plan or avoiding all spices is unnecessary. Instead, you should eat a balanced diet of fruits, fiber, and vegetables.
Also, avoid anything that can make the symptoms worse. The symptoms are aggravated by food items that relax the esophageal muscle. Keep a food journal to keep track of the foods that cause your symptoms. It can aid in eliminating problematic foods.
Diabetic Nephropathy: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Stages, Causes, and Treatment
Diabetic nephropathy affects the kidneys’ ability to do their usual work of removing waste products and extra fluid from your body. The best way to prevent or delay diabetic nephropathy is by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and adequately managing your diabetes and high blood pressure. Over many years, the condition slowly damages your kidneys’ delicate filtering system. Early treatment may prevent or slow the disease’s progress and reduce the chance of complications.
What is Diabetic Nephropathy?
Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. It’s also called diabetic kidney disease. In the United States, about 1 in 3 people with diabetes have diabetic nephropathy. There are five stages of diabetic nephropathy. The fifth stage is ESRD. Progress from one stage to the next can take many years.
Signs and Symptoms of Diabetic Nephropathy
In the early stages of diabetic nephropathy, you would likely not notice any signs or symptoms. In later stages, signs and symptoms may include:

- Worsening blood pressure control
- Protein in the urine
- Swelling of feet, ankles, hands, or eyes
- Increased need to urinate
- Reduced need for insulin or diabetes medicine
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- Shortness of breath
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Persistent itching
- Fatigue
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs or symptoms of kidney disease. If you are living with diabetes, visit your doctor yearly or as recommended for kidney function tests.
Risk Factors of Diabetic Nephropathy
If you’re living with diabetes, factors that can increase your risk of diabetic nephropathy include:
- Uncontrolled high blood sugar (hyperglycemia)
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure (hypertension)
- Being a smoker
- High blood cholesterol
- Obesity
- A family history of diabetes and kidney disease
Stages of Diabetic Nephropathy
The stages of any kidney disease, including diabetes-related nephropathy, include:
- Stage I. Your GFR is 90 or higher. At this stage, your kidneys have mild damage but still function normally.
- Stage II. Your GFR may be as low as 60 or as high as 89. You have more damage to your kidneys than in stage I, but they still function well.
- Stage III. Your GFR may be as low as 30 or as high as 59. You may have mild or severe loss of kidney function.
- Stage IV. Your GFR may be as low as 15 or as high as 29. You have severe loss of kidney function.
- Stage V., Your GFR, is below 15. Your kidneys are nearing or at complete failure.
What Causes Diabetic Nephropathy?
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a complication of diabetes that is believed to contribute most directly to diabetic nephropathy. Hypertension is believed to be a cause of diabetic nephropathy and a result of the damage created by the disease. As kidney disease progresses, physical changes in the kidneys often lead to increased blood pressure. Uncontrolled hypertension can make the progress toward stage five diabetic nephropathy occur more rapidly.
The high blood sugar associated with diabetes also causes damage to the kidney through many different and complicated pathways. Most of this damage is directed toward the blood vessels that filter the blood to make urine.
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Diabetic Nephropathy
The first step in treating diabetic nephropathy is to treat and control your diabetes and high blood pressure. It includes diet, lifestyle changes, exercise, and prescription medications. With good management of your blood sugar and hypertension, you may prevent or delay kidney dysfunction and other complications. If your disease progresses to kidney failure, your doctor will likely discuss options for care focused on either replacing the function of your kidneys or making you more comfortable.
If you have diabetes, you should schedule regular appointments with your healthcare provider every three to six months or as your healthcare provider recommends. If you have diabetes, your healthcare provider will recommend annual diabetes-related nephropathy testing five years after your initial diagnosis. Kidney damage usually doesn’t appear within the first 10 years of your diabetes diagnosis. If you’ve had diabetes for more than 25 years and don’t have kidney damage, you’re less likely to develop diabetes-related nephropathy.
The best way to prevent diabetes-related nephropathy is to manage your diabetes and lower your blood pressure. Be sure to follow your treatment plan as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
How Can Fungal Infections Affect The Lungs?
A fungus is a tiny type of germ that usually doesn’t cause any problems. They are all around us. You can only see them with a microscope. But fungi can infect your lungs in some situations, particularly if you have other serious illnesses. It can be very serious and requires specialist care.
What are Fungal Infections?
Fungi may cause lung disease through direct infection of pulmonary tissue, infection of pulmonary air spaces/lung cavities, or their ability to trigger an immunological reaction when fungal material is inhaled. The latter mechanism is involved in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, aspergillus-induced asthma, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis due to fungi.
Except for aspergillosis, these infections are usually not present to any significant degree in immunocompetent residents of the UK. They are more likely to affect those who have traveled abroad to areas where they are endemic or arise as opportunistic infections in patients who are immunocompromised due to oncological treatment due to immunomodulation following solid organ transplantation or HIV infection. Pulmonary infection occurs after inhalation of spores/conidia or by the reactivation of latent infection. Hematogenous dissemination of fungal infection leading to a systemic mycosis tends to occur chiefly in immunocompromised patients.
Types of Fungal Infections
- Fungal nail infections
- Vaginal candidiasis
- Ringworm
- Candida infections of the mouth, throat, and esophagus
- Blastomycosis
- Cryptococcus gattii infection
- Paracoccidioidomycosis
- Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever)
- Histoplasmosis
- Aspergillosis
- Canadida auris infection
- Invasive candidiasis
- Candidiasis
- Cryptococcus neoformans infection
- Mucormycosis
- Talaromycosis
- Fungal eye infections
- Sporotrichosis
- Mycetoma
Signs and Symptoms of Fungal Infections
Symptoms of fungal infections can range from mild to very serious. The exact symptoms depend on the type of fungus that has caused the infection. Some common symptoms include:

- Asthma-like symptoms
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Muscle aches or joint pain
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Chest pain
- Itchy or scaly skin
Fungal infections can affect many parts of the body, including:
- Hair
- Skin
- Lungs
- Bloodstream
- Brain
- Gastrointestinal system
- Vagina
Symptoms of fungal infections can mimic other conditions, so it’s important to consult your physician for a complete exam and diagnosis.
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Fungal Infections
Antifungal medicines can kill a fungus. Or they may stop it from multiplying or growing. There are several classes of antifungal medications and different types of medicines. Your healthcare provider will select the best prescription medicine. Or they may guide you to an effective over-the-counter (OTC) treatment.
There are OTC and prescription antifungal medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider about what treatment to use.
Antifungals come in different forms, including:
- Injections (shots) or IV
- Oral pills or liquids
- Topical (skin) creams, ointments, gels and sprays
- Vaginal suppositories
Treatment length varies depending on the fungal infection. Some fungal skin infections like ringworm clear up in a few weeks. But clearing up some fungal nail, blood, and lung infections can take months or years.
Recommended medication used for fungal infection:
- Indinavir – the drug is in a class of medications called protease inhibitors. Indinavir inhibits the HIV viral protease enzyme, which prevents cleavage of the gag-pol polyprotein, resulting in noninfectious, immature viral particles.
Antifungal medications treat fungal infections affecting skin, nails, lungs, and other organs. Some fungal infections clear up in a few weeks. Others may need months of treatment. Taking antifungal medicines for an extended period or failing to complete the prescribed treatment may lead to antifungal resistance.
Medication safety depends on the antifungal drug. Breastfeeding infants who develop thrush can get antifungal mouth drops. Their moms also need treatment, typically with an antifungal skin cream. Your healthcare provider can determine whether it’s okay for you or your child to take an antifungal medicine.
Side effects from antifungals vary. Results depend on the type of drug, dosage (strength), and fungus. You may experience the following:
- Abdominal pain, upset stomach, and diarrhea
- Itchy skin, burning sensation, or skin rash
Rarely, an antifungal drug may cause serious problems like:
- Liver damage (jaundice)
- Severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis
- Severe allergic skin reactions, such as blisters and peeling skin
Getting To Know More About Antiepileptic Drug
Antiepileptic medications do not cure epilepsy but rather attempt to prevent seizures. The medications do not alter the underlying problem predisposing to seizures. People with epilepsy are prescribed antiepileptic medications to decrease seizures’ number, severity, and duration. While seizure freedom is the ideal treatment outcome, seizures can still occur while taking antiepileptic medication.
What is an Antiepileptic Drug?
Normal brain function involves communication between millions of nerve cells. At any one time, nerve cells are resting, exciting, or inhibiting other nerve cells. A nerve cell comprises a cell body and branches called axons and dendrites, which join other neurons at synapses. Electrical signals are sent from the cell body along the axon to the synapse, resulting from ion currents across channels in the nerve cell membrane. Chemical signals pass across synapses between neurons. Neurotransmitters cross the synaptic gap between neurons and fix to receptor points of the adjoining neuron. Some neurotransmitters excite the joining neuron to send a further electrical signal. Other neurotransmitters inhibit the joining neuron and electrical signals passing down that neuron. The millions of neurons within the brain communicate and function normally through these electrical and chemical pathways.
Seizures occur when there is an imbalance within these excitatory and inhibitory circuits in the brain, either throughout the brain or in a localized part of the brain, so neurons fire off in a bizarre fashion.
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) protect against seizures by modulation of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels, enhancing GABA receptor-mediated synaptic inhibition, and inhibiting ionotropic glutamate receptor-mediated synaptic excitation.
How Do Antiepileptic Drugs Work?
Antiepileptic medications work in different ways to prevent seizures, either by decreasing excitation or enhancing inhibition. Specifically, they act by either:
- Altering electrical activity in neurons by affecting ion channels in the cell membrane.
- Altering chemical transmission between neurons by affecting neurotransmitters in the synapse.
- For some drugs, the mode of action is unknown.
As the specific mechanisms that cause epilepsy are mostly unknown, drugs with specific mechanisms of an action directed at the underlying epileptic processes have not yet been developed.
List of Antiepileptic Drugs
Narrow-spectrum Antiepileptic Drugs:
- Phenytoin (Dilantin)
- Phenobarbital
- Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
- Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal)
- Gabapentin (Neurontin)
- Pregabalin (Lyrica)
- Lacosamide (Vimpat)
- Vigabatrin (Sabril)
Broad-spectrum Antiepileptic Drugs:
- Valproic acid (Depakote)
- Lamotrigine (Lamictal)
- Topiramate (Topamax)
- Zonisamide (Zonegran)
- Levetiracetam (Keppra)
- Clonazepam (Klonopin)
- Rufinamide (Banzel)
Recommended medication used for seizures:
- Levetiracetam – is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. It works by decreasing abnormal excitement in the brain.
Side Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs
Epilepsy is a common condition that affects the brain and causes frequent seizures. Seizures are bursts of electrical activity in the brain that temporarily affect how it works. They can cause a wide range of symptoms. Epilepsy can start at any age but usually in childhood or in people over 60. It’s often lifelong but can sometimes get slowly better over time.
Seizures can affect people differently, depending on which part of the brain is involved. Possible symptoms include:

- Uncontrollable jerking and shaking are called a “fit.”
- Losing awareness and staring blankly into space
- Becoming stiff
- Strange sensations, such as a “rising” feeling in the tummy, unusual smells or tastes, and a tingling feeling in your arms or legs
- Collapsing
Sometimes you might pass out and not remember what happened.
Treatment can help most people with epilepsy have fewer seizures or stop having seizures completely.
Treatments include:
- Medicines called antiepileptic drugs – are the main treatment
- Surgery to remove a small part of the brain that’s causing the seizures
- A procedure to put a small electrical device inside the body that can help control seizures
- A special diet that can help control seizures
Some people need treatment for life. But you might be able to stop treatment if your seizures disappear over time.
Side effects are common when starting treatment with Antiepileptic drugs. Some may appear soon after starting treatment and pass in a few days or weeks, while others may not appear for a few weeks.
The side effects you may get depend on the medicine you’re taking. Common side effects of Antiepileptic drugs include:
- Drowsiness
- A lack of energy
- Agitation
- Headaches
- Uncontrollable shaking (tremor)
- Hair loss or unwanted hair growth
- Swollen gums
- Rashes
Contact your doctor or specialist if you have symptoms like being drunk, such as instability, poor concentration, and being sick. It could mean your dose is too high.
Muscle Spasms: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
A muscle spasm is a sudden, involuntary movement in one or more muscles. People may also call it a charley horse, muscle cramp, or twitch. These movements can happen in any body muscle, and they are prevalent. Muscle spasms often occur due to stress, exercise, or dehydration. They are usually not a cause for concern.
What are Muscle Spasms?
A muscle spasm is a sudden, unexpected tightening of one or more muscles. Sometimes called a charley horse, a muscle cramp can be excruciating. Exercising or working hard, especially in the heat, can lead to muscle cramps. Some medicines and illnesses also might cause muscle cramps. Muscle cramps aren’t usually harmful. Self-care measures can treat most muscle cramps.

Factors that might increase the risk of muscle cramps include:
- Age. Older people lose muscle mass. Then the muscles can’t work as hard and can get stressed more easily.
- Poor conditioning. Not being in shape for activity causes muscles to tire more easily.
- Extreme sweating. Athletes who tire and sweat a lot while playing sports in warm weather get muscle cramps.
- Pregnancy. Muscle cramps are common during pregnancy.
- Medical issues. Having diabetes or illnesses that involve nerves, liver or thyroid can increase the risk of muscle cramps.
- Weight. Being overweight can increase the risk of muscle cramps.
Signs and Symptoms of Muscle Spasms
Muscle cramps occur mainly in leg muscles, most often in the calf. Cramps usually last for seconds to minutes. After the cramp eases, the area might be sore for hours or days.
Muscle cramps usually go away on their own. They don’t usually need medical care. However, see a healthcare provider for cramps that:
- Cause severe discomfort
- Have leg swelling, redness or skin changes
- Come with muscle weakness
- Happen often
- Don’t get better with self-care
What Causes Muscle Spasms?
A muscle cramp can happen after working a muscle too hard or straining it, losing body fluids through sweat or simply holding a position for a long time. Often, however, the cause isn’t known.
Most muscle cramps are harmless. But some might be related to a medical concern, such as:
- Not enough blood flow. A narrowing of the arteries that bring blood to the legs can cause cramping pain in the legs and feet during exercise. These cramps usually go away soon after exercise stops.
- Nerve compression. Pressure on the nerves in the spine also can cause cramping pain in the legs. The pain usually gets worse with walking. Walking bent slightly forward, such as when pushing a shopping cart, might ease cramping.
- Not enough minerals. Too little potassium, calcium or magnesium in the diet can cause leg cramps. Medicines often prescribed for high blood pressure can cause increased urination, which may drain the body of these minerals.
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Muscle Spasms

Self-care measures can usually treat muscle cramps. A healthcare provider can show you stretching exercises that reduce the chances of muscle cramps. Drinking plenty of fluids can also help prevent muscle cramps.
If you keep getting cramps that wake you from sleep, a care provider might prescribe medicine to relax muscles or help you sleep.
If you have a cramp, these actions might help:
- Stretch and massage. Stretch the cramped muscle and gently rub it. Keep the leg straight for a calf cramp while pulling the top of your foot on the side that’s cramped toward your face. Also, try standing with your weight on your cramped leg and pressing down firmly. It helps ease a cramp in the back of the thigh too.
- Try pulling the foot on that leg up toward your buttock for a front thigh cramp. Hold on to a chair to steady yourself.
- Apply heat or cold. Use a warm towel or heating pad on tense or tight muscles. Taking a warm bath or directing the stream of a hot shower onto the cramped muscle also can help. Rubbing the sore muscle with ice also might relieve pain.
The recommended medication you can use:
- Baclofen – is in a class of medications called skeletal muscle relaxants. Baclofen acts on the spinal cord nerves and decreases the number and severity of muscle spasms caused by multiple sclerosis or spinal cord conditions. It also relieves pain and improves muscle movement.
Dysuria: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Dysuria refers to pain when you urinate. Individuals with dysuria usually describe it as a burning sensation. It can affect anyone of any age, but it is most common in women. Treatment for dysuria depends on the underlying cause. If a bacterial infection causes dysuria, antibiotics are usually prescribed.
What is Dysuria?

Dysuria is pain or discomfort when you urinate. It isn’t about how often you go, though urinary frequency often happens together with dysuria. Dysuria is not a diagnosis. It’s a sign or symptom of an underlying health problem.
Men and women of any age can experience painful urination. It’s more common in women. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are commonly associated with dysuria. UTIs occur in more women than men.
Other people at a higher risk of dysuria include:
- Pregnant women
- Men and women with diabetes
- Men and women with any disease of the bladder
Signs and Symptoms of Dysuria
Symptoms of painful urination can vary between men and women, but both genders usually describe it as a burning, stinging, or itching. Burning is the most commonly reported symptom.
Pain can occur at the start of urination or after urination. Pain at the start of urination is often a symptom of a urinary tract infection. Pain after urination can be a sign of a problem with the bladder or prostate. In men, pain can also remain in your penis before and after urination.
Symptoms in women can be internal or external. Pain outside your vaginal area may be caused by inflammation or irritation of this sensitive skin. Internal pain can be a symptom of a urinary tract infection.
Dysuria is a symptom. It causes a burning sensation, pain, and discomfort. You will likely contact your healthcare provider because this symptom is uncomfortable. It’s essential to see your provider determine if your symptom relates to a urinary tract infection or another medical cause. In any case, the sooner you see your provider, the sooner a diagnosis can be made and treatment can be started.
What Causes Dysuria?
There are many causes of dysuria. Also, know that doctors can’t always identify the cause.
WOMEN: Painful urination for women can be the result of:

- Bladder infection (cystitis)
- Vaginal infection
- Urinary tract infection
- Endometritis and other causes outside the urinary tract, including diverticulosis and diverticulitis
- Inflammation of the bladder or urethra (urethritis)
- Sexual intercourse, douches, soaps, scented toilet paper, contraceptive sponges, or spermicides may also cause inflammation.
MEN: Painful urination for men may be the result of:
- Urinary tract infections and other infections outside the urinary tract include diverticulosis and diverticulitis.
- Prostate disease
- Cancer
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Dysuria
Treatment for dysuria depends on the cause of your pain/burning sensation. The first step in your treatment is to determine if infection, inflammation, dietary factors, or a problem with your bladder or prostate causes your painful urination.
- Urinary tract infections are most commonly treated with antibiotics. If your pain is severe, you may be prescribed phenazopyridine. Note: this medication turns your urine red-orange and stains undergarments.
- Inflammation caused by irritation to the skin is usually treated by avoiding the cause of the irritant.
- Dysuria caused by an underlying bladder or prostate condition is treated by addressing the underlying condition.
You can take several steps to reduce the discomfort of painful urination, including drinking more water or taking an over-the-counter aid to treat painful urination. Other treatments need prescription medications. If you have frequent urinary tract infections, your provider can help find the cause.
Recommended medication:
- Famciclovir – Famciclovir is in a class of medications called antivirals. It works by stopping the spread of the herpes virus in the body. Famciclovir does not cure herpes infections and may not stop the spread of the herpes virus to other people. However, it may decrease the symptoms of pain, burning, tingling, tenderness, and itching. It also help sores to heal and prevent new sores from forming.
Medical Tips For Nausea And Vomiting Caused By Cancer Treatment
One of the most common side effects of cancer treatment is nausea. It can be caused by chemotherapy, radiation therapy and even anaesthesia. Dehydration or constipation can play a part, too. Several medications are available now to help patients manage nausea.
What are Nausea and Vomiting?
Nausea and vomiting are common and sometimes serious side effects of cancer treatment. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and other cancer treatments can cause nausea and vomiting.
Nausea feels queasy, sick to your stomach, or like you might throw up. Vomiting is throwing up the food and liquid in your stomach.
It is important that your nausea and vomiting are controlled and managed. If these aren’t, these problems can affect your daily life, mental health, and physical health and even delay treatment. Relieving side effects, palliative care or supportive care, is an important part of cancer care and treatment.
What Causes Nausea and Vomiting When On Cancer Therapy?
When you have cancer, the causes of nausea and vomiting can include the following:
- Chemotherapy. Nausea and vomiting are common side effects of certain chemotherapy drugs. Your healthcare team may call it chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV). And a higher dosage of chemotherapy can make your side effects worse.
- Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy to large areas of the body, specifically the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, liver, or brain, can cause nausea and vomiting. A higher radiation therapy dosage is also more likely to cause these symptoms.
- Other medications used in cancer care. Other drugs used to treat cancer, including targeted therapy and immunotherapy, can cause nausea and vomiting. Some medications to help with side effects can also cause nausea and vomiting. For instance, pain medications commonly cause stomach problems.
Types of Nausea and Vomiting Caused By Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy
- Delayed nausea and vomiting usually start more than 24 hours after treatment and can last up to a few days after treatment ends.
- Anticipatory nausea and vomiting are learned or conditioned responses. It appears to result from previous experiences with treatment that led to nausea and vomiting, in which the brain pairs some parts of the treatment, such as the sights, sounds, and smells of the treatment area, with vomiting.
- Breakthrough nausea and vomiting happen even though treatment has been given to prevent it. When this happens, you may need more or different medicines to help prevent further nausea and vomiting.
- Refractory vomiting is when you’reyou get medicines to prevent or control nausea and vomiting, but the drugs are not working. Your nausea and vomiting have become refractory to the medicines you’reyou take to prevent it. You may need more or different medicines to stop nausea and vomiting.
Nausea and vomiting can be caused by radiation therapy based on the following:
- Total body irradiation is linked to a high risk of nausea and vomiting if treatment is not given to prevent it. Patients may also get high doses of chemo to prepare for the transplant, raising the chance of nausea and vomiting.
- The part of the body being treated. The risk is greatest when the brain is treated or the area of the body being treated includes a large part of the upper abdomen.
- The dose of radiation given. The bigger the radiation dose given, the higher the risk for nausea and vomiting.
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting

You can take steps to reduce your risk of nausea and vomiting. For example:
- Eat what appeals to you. It’s best, however, to avoid sweet, fried or fatty foods. In addition, cool foods may give off less bothersome odours.
- Eat small meals. Stagger small meals throughout the day rather than eating fewer, larger meals. If possible, don’t skip meals. Eating a light meal a few hours before treatment also may help.
- Drink lots of fluids. Try cool beverages, such as water, unsweetened fruit juices, tea or ginger ale that’s lost its carbonation. It may help to drink small amounts throughout the day rather than larger amounts less frequently.
- Cook and freeze meals before treatment to avoid cooking when you’re not feeling well. Or have someone else cook for you.
- Avoid unpleasant smells. Pay attention to what smells trigger nausea and limit your exposure to unpleasant smells. Fresh air may help.
- Use relaxation techniques. Examples include meditation and deep breathing.
- Make yourself comfortable. Rest after eating, but don’t lie flat for a couple of hours. Try wearing loose fitting clothing and distracting yourself with other activities.
- Consider complementary therapies. Complementary and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and aromatherapy, may help you feel better when combined with your doctor’s medications. Tell your doctor if you’re interested in trying these treatments. He or she may be able to recommend a practitioner who works with people undergoing cancer treatments.
A recommended prescription that can be used for nausea and vomiting:
- Ondansetron – this drug is in a class of medications called serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. It works by blocking the action of serotonin, a natural substance that may cause nausea and vomiting.
Urinary Incontinence: Symptoms, Types, Risk Factors, Causes and Treatment
Urinary incontinence is a common and often embarrassing problem. The severity ranges from occasionally leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having the urge to urinate that’s so sudden and strong you don’t get to a toilet in time.
Though it occurs more often as people get older, urinary incontinence isn’t an inevitable consequence of ageing. Don’t hesitate to see your doctor if urinary incontinence affects your daily activities. For most people, simple lifestyle and dietary changes or medical care can treat symptoms of urinary incontinence.
What is Urinary Incontinence?
Urinary incontinence is a condition that impacts many people’s lives. You may experience bladder control issues and leak urine when you have incontinence. This leakage is often uncontrollable and can negatively impact your life.
Your urinary system comprises the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. These parts do several jobs. They filter, store and remove waste from your body. Your kidneys are the filters of your body. Waste products are removed from your blood by the kidneys, creating urine. The urine then moves down through two thin tubes called ureters. The ureters connect to the bladder, where the urine will collect until it leaves the body. Your bladder is like a storage tank. Once the bladder is complete, the brain signals that it’s time to urinate. Urine then leaves the bladder when a muscle opens up, allowing the urine to flow freely out of the body through the urethra. When this system is working smoothly, you usually have time to get to a bathroom before urinating, and you don’t experience any urine leakage. Urinary incontinence can happen when these parts don’t operate as they should. It can happen for many different reasons throughout your life.
Many people think incontinence is a normal part of ageing that can’t be helped. While it is true that your risk of incontinence increases as you get older, there are also treatments available to help you manage this condition. Incontinence doesn’t have to disrupt your life and keep you from being active.
Types of Urinary Incontinence
There are several different types of incontinence. These types have different causes, characteristics and triggers for urine leakage. Knowing the type of incontinence is often an essential part of the diagnosis and treatment plan for incontinence.
The types of incontinence include:
- Urge incontinence
- Stress incontinence
- Overflow incontinence
- Mixed incontinence
Signs and Symptoms of Urinary Incontinence
The main symptom of incontinence is a leakage of urine. It could be a constant dripping of urine or an occasional leakage experience. If you have incontinence, you might have significant amounts or small amounts of leaked urine. You might experience leakage for various reasons, often depending on the type of incontinence you have.

You might leak urine when you:
- Exercise
- Cough
- Laugh
- Sneeze
- Have the urge to urinate but can’t make it to the toilet on time
- Have to get up in the middle of the night to urinate
Risk Factors of Urinary Incontinence
Incontinence can happen to anyone. However, it’s more common in certain groups and times in your life. Incontinence is much more common in women than in men. It is often related to pregnancy, childbirth and menopause. Each of these experiences can cause a woman’s pelvic support muscles to weaken over time.
You’re also more likely to experience incontinence as you get older. The muscles that support your pelvic organs can become weaker over time, causing you to experience leakage issues.
What Causes of Urinary Incontinence
There are many different reasons that you could experience incontinence. These causes can vary depending on if you’re a woman or a man. Some causes are temporary health conditions that usually go away once treated. In those cases, your incontinence also usually stops once the condition is treated. Long-term medical conditions can cause incontinence. When you experience leakage issues because of a chronic condition, it’s usually something you will have to manage over a more extended period. Even with treatment, chronic conditions usually don’t go away. Incontinence may have to be managed over time as a symptom of your chronic condition.
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Urinary Incontinence
There are many different factors that your healthcare provider will consider when creating a treatment plan for your incontinence. The type of incontinence and how it affects your life are significant considerations. Your provider will also talk to you about the type of treatment you are most comfortable with. You can explore three main treatment types for incontinence — medications, lifestyle changes and surgery. Each option has pros and cons that your provider will discuss with you.
5 Stages of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease affects people in various ways, and those who live with the condition may not experience all of the typical symptoms. Those who share similar or identical symptoms may not necessarily have them simultaneously or experience the same intensity. It’s a disease that progresses uniquely from person to person, and the uncertainty of what might happen next can be very difficult for patients and their loved ones.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease?

Parkinson’s disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra, leading to progressive damage to several areas of the brain over many years. The loss of nerves reduces dopamine in the brain, which plays a vital role in the body’s ability to move. This reduction of dopamine is responsible for several Parkinson’s symptoms, mainly motor symptoms, but the mechanism for losing nerve cells remains unclear. Most experts agree that it’s due to genetic and environmental factors.
The three typical movement symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are:
- Involuntary shaking or a ‘tremor’ of parts of the body
- Slow movement
- Stiff muscles and difficulties with flexibility
Additionally, people with Parkinson’s disease can also experience other physical and non-movement symptoms, such as:
- Depression and anxiety
- Balance issues
- Losing sense of smell
- Sleeping problems
- Memory difficulties
Many medical professionals who diagnose Parkinson’s disease use the Hoehn and Yahr scale to classify symptoms and their severity. This scale rates the condition and breaks it into five stages based on disease progression. The scale allows doctors to evaluate how far PD has advanced in patients and what treatments may be most effective for symptom management.
Stage 1
Changes in a Person’s Habits
At stage 1, there can be mild symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, but they’re often not severe enough at this point to impact daily tasks and general quality of life. However, this isn’t to say symptoms are not present. Family and friends may notice changes in a person’s movement, recognize poor posture, and see differences in facial expressions at this early stage.
Stage 2
Muscle Stiffness and Posture Problems
Stage 2 of Parkinson’s disease is considered a ‘moderate’ condition, with symptoms becoming more noticeable than in the previous stage. Examples include noticeable tremors, stiffness, and trembling. Also, changes to facial expressions can occur but are not always apparent to others.
Although stage 2 doesn’t usually cause balance-related issues, other movement symptoms, such as muscle stiffness, can make tasks more challenging. Additionally, the condition can hinder a person’s posture at this stage, leading to back and neck pain. At this point, the disease can impact both sides of the body, and difficulties with speech can also occur.
Progression from stage 1 to 2 can take months to years, and there are no reliable methods to predict how it will progress. People in stage 2 of Parkinson’s can generally live alone but tend to find everyday tasks more difficult.
Stage 3
Poor Reflexes and Balance Issues
The third stage of Parkinson’s is considered mid-stage Parkinson’s progression and a significant turning point in how the disease will progress from here on out. While many of the symptoms remain the same or similar to stage 2, stage 3 can also introduce poorer reflexes and loss of balance at times. For this reason, people in stage three experience more noticeable movement issues or appear to ‘slow down.’ Unfortunately, falls become more frequent at this stage due to balance and reflex problems.
Stage 4
Poor Motor Skills

The critical factor in separating people with stage 3 Parkinson’s and stage 4 is independence. Motor skills are heavily impacted at stage 4, and movement symptoms affect a person’s ability to retain their independence. Some people at stage 4 can stand confidently without assistance, and some can walk without the help of equipment or another person, but it’s common for a person to require assistive equipment such as a walker.
Stage 5
Severe Stiffness
Stage 5 of Parkinson’s disease is the final and most debilitating stage and reflects the most advanced progression. Severe stiffness can make it difficult, if not impossible, for a person to stand or walk. It is due to stiffness causing the legs to freeze when the patient attempts to stand essentially. These symptoms make daily tasks impossible and dangerous for someone to try without assistance. Therefore, it’s common for stage 5 sufferers to need a wheelchair because of an inability to stand without help — meaning they often require supervision to avoid falls.
Recommended medications for this type of disease may include:
These drugs are in a class of medications called dopamine agonists. It works by acting in place of dopamine, a natural substance in the brain needed to control movement.
Watery Eyes: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Watery eyes can be due to many factors and conditions. In infants, persistent watery eyes, often with some matter, are commonly the result of blocked tear ducts. In babies, the tear duct may not be fully open and functioning for the first several months of life.
What are Watery Eyes?
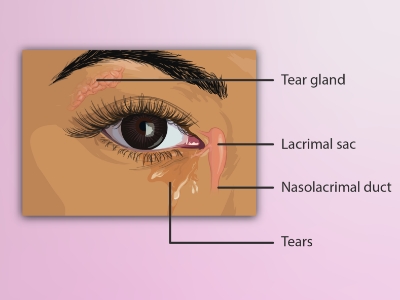
Epiphora is the medical term for having watery eyes. Usually, tears lubricate and protect your eyes. Epiphora happens when something causes you to make too many tears or stops them from draining away from your eyes as they should.
Epiphora can happen for lots of reasons, many of which don’t need any treatment. It can be a temporary condition, but it can also be a sign of a serious eye infection or a blockage in your tear ducts. Visit your healthcare provider if your eyes are constantly watering or you’re having trouble seeing. Anyone can be affected by epiphora. Most people experience watery eyes at some point throughout their life. Epiphora happens frequently and is more common in babies and adults older than 50.
Signs and Symptoms of Watery Eyes
Symptoms of watery eyes include:
- Eyes that feel too wet or watery
- Tears running down your face
- Tears build up in your eyes when you’re not crying or laughing
What Causes Watery Eyes?
Watery eyes are usually a sign of another issue or condition that’s affecting your eyes or tear system. Some of the most common causes of epiphora include:

- Allergies
- Blepharitis
- Blocked tear ducts
- Dry eyes
- Styes
- Chalazion
- Entropion
- Eye injuries can also cause epiphora, including:
- Environmental irritants like smoke or air pollution
- Scratched corneas
- Dirt, debris, chemicals, or any foreign object that touches your eye for too long
Infections like pink eye or sinus infections can cause watery eyes, as well.
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Watery Eyes
How your watery eyes are treated depends on what’s causing them. Many people experience temporary watery eyes that clear up on their own without any treatment.
Your provider will tell you which type of treatment you’ll need. The most common treatments include:
- Medications: You’ll need medication to treat your watery eyes if the epiphora is caused by allergies or an infection. If you have a condition like dry eye syndrome, your provider might prescribe artificial tears or prescription eye drops.
- Removing foreign objects: If there’s something in your eye or something hit your eye and damaged it, your provider will remove it or treat the damage. You might need surgery if a foreign object severely damaged your eye.
- Clearing blocked tear ducts: If you have blocked tear ducts, your provider will open them. They can flush them with a saline solution to rinse away the blockage. They can use a probe to open your tear ducts manually if they need to. If your tear ducts are damaged or blocked by something your provider can’t remove with either saline or a probe, you might need surgery to open them.
- Repairing your eyes or eyelids: If the physical shape of your eyes or eyelids is causing epiphora, your provider will repair the damage. You might need surgery to correct some issues.
Your provider will tell you how to manage your epiphora symptoms. If they prescribe a medication, make sure to take it or use it as often as they say. This is especially true if they give you antibiotics for an infection. You need to take antibiotics for as long as your provider prescribes, even if your symptoms improve. If you don’t take the full course of antibiotics, the infection might come back, get worse or spread to other parts of your body.
The recommended prescription used for the condition:
- Desloratadine – is an antihistamine that works by preventing the effects of a substance called histamine, which is produced by the body. Histamine can cause itching, sneezing, runny nose, and watery eyes.
Talk to your provider about ways you might be able to prevent watery eyes in the future.
Using Nasal Spray for the Treatment of Migraine
When creating a migraine treatment plan with your doctor, you have many medication options. A fast-acting, effective way to deliver relief, nasal sprays are one form of migraine treatment to consider. Different types of nasal sprays help with migraine care. Which one will work best for you may depend on your specific symptoms and the stage of your migraine? The other treatments you use matter as well.
How Migraine Nasal Spray Works?
Nasal sprays for migraine can offer more rapid relief than oral medications. A 2013 research review showed that nasal sprays could begin to ease the symptoms of an acute migraine attack as quickly as 15 minutes. Generally speaking, medications given intranasally can be absorbed more rapidly and effectively than oral medications.
Your nasal cavity contains a high amount of blood vessels. It provides a more direct route for the drug into your bloodstream. When a drug is directly absorbed into your bloodstream, it avoids being broken down by your digestive system or your liver during first-pass metabolism. It means more of the drug is readily available to counteract your migraine symptoms.
Types of Migraine Nasal Spray
Three classes of medications are available as nasal sprays for treating ongoing migraine.
- Nasal Triptans (cause blood vessel narrowing)
- Nasal dihydroergotamine or DHE (a formulation of ergotamine, which also constricts blood vessels)
- Nasal ketorolac (a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory to prevent pain)
Nasal triptans and ergotamines are specifically approved to treat migraine. Ketorolac is U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved to fight pain, but not specifically for migraine.
Recommended nasal spray that can be used for migraine:
- Sumatriptan Nasal Spray – this nasal spray is a triptan. When the blood vessels in your brain widen, it causes a headache. Sumatriptan works by tightening the blood vessels to relieve your migraine headache and stop pain signals from going to your brain.
How To Use Migraine Nasal Spray?
Like all acute treatments, nasal sprays work best when you take them as soon as you feel a migraine attack coming on. While you might be tempted to follow the advice the school nurse gave you when you got a nosebleed, you shouldn’t tip your head back. Doing so makes the medication drip down your throat and get absorbed by your stomach, which slows down the absorption process. For the same reason, try not to sniff too much while the spray is in your nose.
Since each user should administer a pre-measured amount of medication, you don’t need to worry much about dosage. Just be sure not to use the medication more often than directed.
Side Effects of Migraine Nasal Spray

Some people who use migraine nasal spray medications experience the following side effects:
- Unusual taste
- Dry mouth
- Pain, pressure, and tightness sensations (such as in the nose, throat, or chest)
- Tingling sensation, numbness, and skin sensitivity, especially around the nose
- Drowsiness, fatigue, or weakness
- Dizziness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stuffy or runny nose
These are not all the possible side effects of nasal sprays. Patients should check the specific class of nasal spray for an exhaustive list of side effects and talk to their doctor about what to expect with treatment with nasal sprays.
Most of these medications should not be taken if you are pregnant, may become pregnant, or are nursing. They are also unsafe to take if you have heart problems, high blood pressure, circulatory problems, or kidney problems. Some of these medicines have been linked to life-threatening conditions when combined with certain protease inhibitors, anti-fungal medications, and certain antibiotics.
It is always important to read the warnings on the drug label to learn if you should avoid taking the drug and what you should discuss with your doctor. It would be best to begin with no medication or supplement without first checking with your healthcare provider and let them know of any other prescriptions, OTCs, and herbals you are taking to ensure no interactions.
Actinic Keratosis: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Causes, and Treatment
Actinic keratosis (AK) is a skin disorder. AK is a type of pre-cancer, which means that if you don’t treat the condition, it could turn into cancer. Without treatment, AK can lead to a type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma. About 58 million Americans have one or more spots of actinic keratosis. AK is the most common type of skin pre-cancer.
What is Actinic Keratosis?
Actinic keratosis is a rough, scaly patch on the skin that develops from years of sun exposure. It’s often found on the face, lips, ears, forearms, scalp, neck, or back of the hands.
Also known as solar keratosis, actinic keratosis grows slowly and usually first appears in people over 40. You can reduce your risk of this skin condition by minimizing sun exposure and protecting your skin from ultraviolet (UV) rays.
Signs and Symptoms of Actinic Keratosis
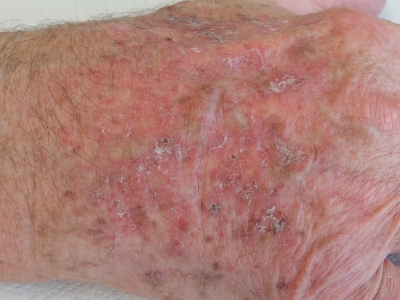
Usually, the first signs of actinic keratosis are rough, raised bumps on your skin. They can vary in color but often have a yellow or brown crust on top. These bumps may be:
- Gray
- Pink
- Red
- The same color as your skin
Symptoms may also include:
- Bleeding
- Burning, stinging, or itching
- Dry, scaly lips
- Hornlike skin growths that stick out (like an animal’s horn)
- Loss of color in the lips
- Pain or tenderness
It can be challenging to distinguish between noncancerous spots and cancerous ones. So it’s best to have new skin changes evaluated by a healthcare provider, especially if a scaly spot or patch persists, grows, or bleeds.
What Causes Actinic Keratosis?
The most common cause of actinic keratosis is too much exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. UV light comes from the sun or indoor tanning equipment like beds. UV light can damage your outer layer of skin cells, called keratinocytes.
Risk Factors for Actinic Keratosis
UV rays from the sun and tanning beds cause almost all actinic keratosis. Damage to the skin from UV rays builds up over time. It means that even short-term exposure to the sun regularly can build up over a lifetime and increase the risk of actinic keratosis.
Some people are more at risk than others, including:
- People with pale skin, blonde or red hair, and blue, green, or gray eyes
- People with darker skin, hair, and eyes who have been exposed to UV rays without protection
- Older adults
- People with suppressed immune systems (due to chemotherapy, AIDS, organ transplant, or other causes)
- People with rare conditions that make the skin very sensitive to UV rays, such as albinism or xeroderma pigmentosum (XP)
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Actinic Keratosis
Your healthcare provider will likely determine whether you have an actinic keratosis simply by looking at your skin. If there’s any doubt, your healthcare provider may do other tests, such as a skin biopsy. During a skin biopsy, a small skin sample is taken for analysis in a lab. A biopsy can usually be done in a clinic after a numbing injection. Even after treatment for actinic keratosis, your healthcare provider might suggest you have your skin checked at least once a year for signs of skin cancer.

An actinic keratosis sometimes disappears but might return after more sun exposure. It’s hard to tell which actinic keratosis will develop into skin cancer, so they’re usually removed as a precaution.
Many methods are used to remove actinic keratosis, including:
- Freezing (cryotherapy)
- Scraping (curettage)
- Laser therapy
- Photodynamic therapy
If you have several actinic keratoses, your healthcare provider might prescribe a medicated cream or gel to remove them, such as:
- Imiquimod Cream – is in a class of medications called immune response modifiers. Imiquimod works on the immune system to help the body fight viruses that cause warts. It does not destroy the viruses directly. This medicine is for use on the skin only. Do not get it in your eyes, nose, mouth, vagina, or anus. Please do not use it on skin areas with cuts, scrapes, or burns. If it does get on these areas, rinse it immediately with water.
What is the Best Treatment for Actinic Keratosis?
What is Actinic Keratosis?
Actinic keratosis is a rough, scaly patch on the skin that develops from years of sun exposure. It grows slowly and usually first appears in people over 40. If left untreated, this condition may lead to squamous cell carcinoma is about 5% to 10%. The lesions frequently arise on sun-exposed areas of the face, lips, ears, scalp, shoulders, neck, and the back of the hands and forearms.
What are the Symptoms?

- Bump on the top layer of skin or flat to slightly raised patch
- Scaly patch of skin or rough dry, usually less than 1 inch
- Color variations, including red, brown, or pink
- In some cases, a hard, wart-like surface
- New patches or bumps on sun-exposed areas of the head, neck, hands, and forearms
- Burning, Itching, crusting, or bleeding
- New patches or bumps on sun-exposed areas of the head, neck, hands, and forearms
- Itching, burning, bleeding, or crusting
What Causes Actinic Keratosis?
AKs result from long-term exposure to UV rays. This means that if you already have an AK, you are likely to develop more in the future. This puts you at a higher risk for skin cancer which sometimes can be an invasive form of the disease.
Risk Factors of Actinic Keratosis
- Are older than 40
- You work outdoors most of the time
- Have blond hair or blue and red or light-colored eyes
- Tend to freckle or burn when exposed to sunlight
- Have a history of a lot of sun exposure or sunburn
- You have a weakened immune system
How to Prevent Actinic Keratosis?

- Use sunscreen if possible. Apply a broad-spectrum water-resistant sunscreen with a sun protection factor of at least 30. Use a lip balm with sunscreen on your lips. Apply sunscreen at least 15 minutes before going outside and reapply it every two hours.
- Dress properly. For extra protection from the sun, wear tightly woven clothing that covers your arms and legs.
- Limit your sun exposure. Avoid time in the sun between 10 in the morning and 2 in the afternoon. You also have to avoid staying in the sun so long that you get sunburned.
- Avoid tanning beds. The UV exposure from a tanning bed can cause just as much skin damage as a tan from the sun.
- Check your skin regularly. Examine your skin regularly, looking for the development of new skin growths or changes in existing moles, freckles, bumps, and birthmarks.
Treatment for Actinic Keratosis
In some cases, this condition will disappear on its own without the need for medication. If you have several AKs your healthcare provider might prescribe a medicated cream or gel to remove them.
Imiquimod cream is often recommended to treat skin infections such as AK. It is generally known as an immune response modifier and is sometimes indicated for other types of skin infections too. This also improves the immune response of the cells when applied. The activated immune cells travel to areas of infection and eliminate the infected cells.
Surgical and Other Treatment Procedures
- Laser therapy. This technique is increasingly used to treat this condition. Your healthcare provider uses an ablative laser device to destroy the patch, allowing new skin to appear. Side effects may include scarring and staining of the affected skin.
- Freezing. The condition can be removed by freezing them with liquid nitrogen. As your skin heals, the damaged cells slough off, allowing new skin to appear. Cryotherapy is the most common treatment.
- Photodynamic therapy. Your healthcare provider might apply a light-sensitive chemical solution to the affected skin and then expose it to a special light that will destroy the condition.
- Curettage. In this procedure, your healthcare provider uses a device called a curet to scrape off damaged cells. Side effects of this procedure may include infection, scarring, and changes in the skin color of the affected area.
Do Smokers’ Lungs Heal After Quitting?
Your lungs are responsible for delivering oxygen to your entire body. Oxygen is essential for all your organs and cells. Without clean or enough oxygen, you face a higher risk of illness and disease, including cancer. Oxygen is needed for optimal brain function, good mood, and energy. It can also improve your strength, boost your immune system, and reduce stress and anxiety. Quitting smoking is one of the most imaginative things you can do to improve your overall health. The time it takes for the lungs to heal is different for everyone.
Do Smokers’ Lungs Heal After Quitting?
Within two weeks to 3 months after quitting, you may start to notice improved lung function as your lungs start the self-cleaning process.
In the first year after quitting, symptoms like coughing and shortness of breath decrease. During this time, your lungs clean themselves better to reduce infection risk. As your lungs continue to self-clean and heal over time, you’ll continue to reap the health benefits of smoking cessation.
How Many Cigarettes Does It Take Damage The Lungs?

Researchers say that people who smoke five cigarettes a day are doing almost as much damage to their lungs as people who smoke 30 cigarettes daily. They say it takes “light” smokers about one year to develop as much lung damage as “heavy” smoking does in 9 months.
They note that a lighted cigarette releases 7,000 chemicals, 69 of which are considered cancer-causing substances.
Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of preventable disease and death in the United States. About 480,000 people die every year due to smoking. Experts estimate 34 million adults smoke, and more than 16 million live with a smoking-related disease. Whether a person smokes five cigarettes a day or two packs a day, the negative impact on the body is significant. When cigarettes burn, more than 7,000 chemicals are released. At least 69 of those chemicals are known to cause cancer.
These chemicals cause injury to the cells inside the lungs. When the injured cells become inflamed and swollen, the body attempts to repair the damage. During that process, normal, healthy lung tissue can be broken down as the body tries to fix the damage caused by smoking.
The average smoker takes ten puffs of a cigarette over 5 minutes. A person who smokes 25 cigarettes daily will receive a hit of nicotine 250 times. Nicotine is just one of the toxic chemicals found in cigarettes.
How Fast Do Your Lungs Heal After Quitting?
20 minutes after quitting:
- Your heart rate drops to an average level.
12 to 24 hours after quitting:
- The carbon monoxide level in your blood drops to normal.
- The risk of heart attack is significantly reduced.
Two weeks to 3 months after quitting:
- Your risk of having a heart attack begins to drop.
- Your lung function begins to improve.
1 to 9 months after quitting:
- Your coughing and shortness of breath decrease.
One year after quitting:
- Your added risk of coronary heart disease is half that of a smoker.
5 to 15 years after quitting:
- Your stroke risk is reduced to that of a nonsmoker.
- Your chance of getting mouth, throat, or oesophagus cancer is half that of a smoker.
Ten years after quitting:
- Your risk of lung cancer is about half that of a smoker.
- Your chance of getting bladder cancer is half that of a smoker.
- Your chance of getting cervical cancer or cancer of the larynx, kidney or pancreas decreases.
15 years after quitting:
- Your risk of coronary heart disease is the same as that of a nonsmoker.
Medication used to help people stop smoking:
- Bupropion – the drug is in a class of medications called antidepressants. It works by increasing certain types of activity in the brain. Bupropion is a tablet and a sustained-release or extended-release (long-acting) tablet to take by mouth.
What Causes Social Anxiety?
Social anxiety is also known as social phobia. It affects about 5.3 million people in the United States. The average age it begins is between ages 11 and 19 or the teenage years. In this condition, the fear is limited to one or two particular situations, like speaking in public or initiating a conversation. Others are very anxious and afraid of any social situation. The tough part is being able to ask for help.

People who have this condition may have trouble with any of the following:
- Talking to strangers
- Eating in front of other people
- Going to school or work
- Speaking in public
- Going to parties
- Dating
- Making eye contact
- Starting conversations
- Entering rooms
- Using public restrooms
What are the Causes of Social Anxiety Disorder?
- Genetic traits. You’re more likely to develop social anxiety disorder if your biological parents or siblings have the condition. However, it isn’t entirely clear how much of this may be due to genetics and how much is due to learned behavior.
- Negative experiences. There is a greater risk of social anxiety disorder for children who have experienced teasing, bullying, rejection, ridicule, or humiliation. In addition, other negative events in life, such as family conflict, trauma, or abuse, may be associated with this disorder.
- Having a condition that draws attention. Social anxiety disorder can be triggered by facial disfigurement, stuttering, or tremors caused by Parkinson’s disease.
- Brain structure. A structure in the brain may play a role in controlling the fear response. It may cause other people to have a heightened fear response, causing increased anxiety in social situations.
- Environment. It can also be a learned trait as some people may develop significant anxiety after an unpleasant or embarrassing social situation.

Symptoms of Social Anxiety
- Trembling
- Sweating
- Upset stomach or nausea
- Trouble catching your breath
- Fear of situations in which you may be judged negatively
- Worry about embarrassing or humiliating yourself
- Avoidance doing things or speaking to people
- Blushing
- Fast heartbeat
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Intense fear of interacting or talking with strangers
- Feeling that your mind has gone blank
- Muscle tension
- Avoidance of situations where you might be the center of attention
- Anxiety in expectation of a feared activity or event
- Intense fear or anxiety during social situations
- Fear that others will notice that you look anxious
Does Social Anxiety Affect Your Life?
It prevents you from living your life as you avoid situations that most people consider normal. You might even have a hard time understanding how others can handle them so easily. It also affects your personal relationships. It leads to low self-esteem, negative thoughts, low social skills, depression, and sensitivity to criticism.
If this condition keeps you from doing things you want or need to do, or from making or keeping friends, you may need treatment. Talk about your fears and worries with a doctor or therapist who has experience treating such conditions.
Why Should You Talk to a Professional?
Note that getting help from doctors does not mean that you are not normal. Your feelings are valid and you are not alone. Many people also experience the condition and experts can help you get through it. Talk to a professional to help you find solutions. Talk openly with your doctor about treatment to avoid depression, drug or alcohol problems, school or work problems, and a poor quality of life.
Treatment for Social Anxiety
The treatment depends on what causes the condition. A combination of medication and therapy would be a great help for your recovery. Psychotherapy improves symptoms and helps you learn how to recognize and change negative thoughts about yourself and develop skills to help you gain confidence in social situations.
Your doctor may also prescribe medcations such as anti anxiety, antidepressants, and beta blockers. Though several types of medications are available, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are often the first type of drug tried for persistent symptoms of social anxiety. To reduce the side effects, you may be instructed to start with a lower dosage.
Depression in Children: Symptoms and How to Treat It?
Depression in children is an uncommon case. However, many children have fears and worries and may feel sad and hopeless from time to time. Strong fears may appear at different times during growth. Although fears and worries are typical in children, persistent or extreme forms of fear and sadness could be due to anxiety or depression.
Symptoms of Depression in Children

- Crankiness or anger
- Continuous feelings of sadness and hopelessness
- Social withdrawal
- Feelings of worthlessness or guilt
- Impaired thinking or concentration
- Thoughts of death or suicide
- Physical complaints such as stomachaches
- Frequent headache
- Changes in appetite
- Excessive sleepiness or lack of sleep
- Sensitive to rejection
- Changes in appetite, either increased or decreased
- Trouble concentrating
- Fatigue and low energy
- Trouble during events and activities
- Loss of hobbies and interest
What Causes Depression in Children?
Up to 3% of children and 8% of adolescents in the U.S. have depression. The condition is more common in boys under the age of 10. But by age 16, girls have a greater incidence of depression. It can be caused by any combination of things that relate to physical health, family history, life events, environmental influence, genetic vulnerability, and biochemical disturbance.
How Common is Depression in Children?
Depression is among the most common mental health disorders in children. About 3% have depression which tends to be higher in older children and teenagers between the ages of 12 and 17. An estimated 3.2 million adolescents aged 12 to 17 in the US had at least one major depressive episode. This number represented 13.3% of the U.S. population aged 12 to 17.
How to Diagnose Depression in Children?
If your child has been experiencing symptoms of depression for at least 2 weeks, schedule an appointment with their doctor to make sure there are no physical reasons for the symptoms and to ensure proper treatment is provided. A consultation with a mental health care professional who specializes in children is also recommended.
A mental health evaluation should include interviews with you and your child and any other psychological testing that is needed. It can be beneficial to get information from teachers, friends, and classmates to show that these symptoms are consistent during your child’s various activities and are a marked change from previous behavior. In addition to information about the child’s personal characteristics, questionnaires can be very helpful in helping diagnose depression in children.
Managing the Condition and Staying Healthy
It is not known exactly why some children develop this condition but factors may play a role, including biology and temperament. Life experiences such as trauma, maltreatment, bullying, rejection, and stress can trigger the condition. Here are ways you can do as a guardian or parent on managing this condition.
- Ensure that your child maintains a healthy eating plan centered on fruits, vegetables, lean protein sources, and nuts and seeds.
- Allow your child to participate in physical activities every day. You can also plan recreational activities at home to prevent them from isolating.
- Be a good listener to your child and be open-minded to understand that things are not the same for everybody.
- Let your child get the recommended amount of sleep each night.
- Ensure that you are always present especially during the hard times and help your child come up with healthy solutions to his/her problems.
- Practice mindfulness or relaxation techniques.
How to Treat Child Depression?
Treatment options for children with depression are like those for adults. Doctors may recommend medication, psychotherapy, and or a combination of both. During psychotherapy, your child will talk to a licensed and trained mental health care professional to identify and work through the factors that may be triggering the depression.
There is a wide range of available antidepressants and your doctor will choose the best treatment for your child. Note that there no single best antidepressant, and the best one for your child depends on the symptoms and individual needs.
How Do You Know If You Have Bipolar Disorder?
What is Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar disorder is a brain disorder that causes changes in a person’s mood, energy, and ability to function. It is previously called manic-depressive illness or manic depression is a mental illness which causes an unusual shift in mood, activity, energy, concentration, levels, and the ability to carry out tasks.
How Do You Know if You Have Bipolar Disorder?
In this condition, the dramatic episodes of high and low moods do not follow a set pattern. Someone may feel manic and depressed several times before switching to the opposite mood. These episodes can happen over a period of weeks, months, and or years.
Your symptoms during a period of depression may include:

- Lacking energy
- Irritable most of the time, feeling sad or hopeless
- Lost interest in everyday activities
- Difficulty remembering things and concentrating
- A feeling of despair and guilt
- A feeling of worthlessness or emptiness
- Lack of confidence
- Feeling pessimistic about everything
- Don’t have the desire to eat food
- Being delusional
- Waking up early
- Difficulty falling asleep at night
- Suicidal thoughts
The manic stage of bipolar disorder may include:
- Pressured speech
- Feeling very overjoyed, happy, or elated
- Feeling self-important
- Feeling full of energy
- Being easily distracted
- Feeling full of having important plans and great new ideas
- Being delusional
- Being easily agitated or irritated
- Doing things that often have tragic consequences such as spending large sums of money
- Making decisions or saying things that are out of character
- Not feeling like sleeping
Symptoms of a major depressive episode
- Unexplainable weight loss
- Either insomnia or excessive sleep
- Reduced or increased appetite (in children)
- Fatigue, restlessness, or slowed behavior
- Loss of energy
- Feeling sad, empty, hopeless, or tearful
- Loss of interest and pleasure in all things
- Excessive or inappropriate guilt
- Indecisiveness
- Suicide attempts
If you have any symptoms of depression or mania, see your doctor or mental health professional. This condition does not get better on its own. Treatment from a mental health professional with experience can help you get your symptoms under control.
Get emergency help or call 911 if you or someone you know have thoughts of suicide or ending your life. If you have a loved one who is in danger of suicide or has made a suicide attempt, make sure someone stays with that person.
What are the Causes of Bipolar Disorder?
- Biological differences. People with this condition appear to have physical changes in their brains. The significance of these changes is still uncertain but may eventually help pinpoint causes.
- Heredities. It is more common in people who have a first-degree relative, such as a sibling or parent, with the condition. Researchers are trying to find genes that may be involved in causing this condition.
Can You Prevent Bipolar Disorder?
There is no specific way to prevent this condition but treatments at the earliest sign may prevent the worsening of the disorder. If you have been diagnosed with this condition, some strategies can help prevent minor symptoms from becoming full-blown episodes of mania or depression:
- Pay attention to warning signs. Addressing symptoms early on can prevent episodes from getting worse. You may have identified a pattern to your bipolar episodes and what triggers them.
- Avoid drugs and alcohol. Using alcohol or recreational drugs can worsen your symptoms and make them more likely to come back.
- Take your medications. Take your prescriptions as instructed by doctors Stopping your medication or reducing your dose on your own may cause withdrawal effects or your symptoms may worsen or return.
How is it Treated?
The treatment for this condition involves medical specialists who are experts in dealing with mental health conditions. You may have a treatment team that also includes a psychologist, social worker, and psychiatric nurse. Treatment is directed at managing symptoms. This includes medications, day treatment programs, hospitalization, and substance abuse treatment.
Chlorpromazine. It is used by doctors to their patients to control agitation and mania in people who have bipolar disorder. It works by helping to restore the balance of certain natural substances in the brain and reduce aggressive behavior and the desire to hurt yourself or others. It may also help to decrease hallucinations.
Roundworms: Parasitic Infections, Symptoms & Treatment
What are Roundworms?
Roundworms are small organisms that can live in your intestine. It can live in the human intestine for a long time and can cause many problems including diarrhea, high fever, and abdominal pain. They have long and round bodies that can be of different types and sizes. The eggs and larvae of this worm live in the infected stool and soil.
What are its Symptoms?
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
- Abdominal pain
- Blood in the stool
- Diarrhea and Nausea
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Presence of the worm in stool or vomit
Are Roundworms Common?
Hundreds of millions of people around the world are infected with roundworms at any given time. However, these parasites are not common in the United States. People can acquire them when traveling to certain countries.
The Life Cycle of A Worm

- Ingestion. It can be infectious when it comes in contact with soil. People can ingest them through exposure to contaminated soil or through hand-to-mouth contact by eating uncooked fruits or vegetables that have been grown in contaminated soil.
- Migration. The larvae hatch in your small intestine and migrate through the intestine to travel to the heart and lungs via the bloodstream or lymphatic system. After maturing for about 10 to 14 days in your lungs, the larvae break into your airway and travel up the throat.
- Maturation of the worm. The parasites grow into male or female worms. Female worms can be more than 15 inches and male worms are generally smaller.
- Reproduction. Female worms can produce 200,000 eggs a day if there are both female and male worms in the intestines, and the eggs leave your body in feces.
What Causes the Spread of Roundworm Infection?
The causes of the spread of the infection are not directly from person to person. It starts with a person has to come into contact with soil mixed with human or animal feces that contain eggs or infected water. These are widespread in some developing countries where human feces are used for fertilizer, or poor sanitary facilities allow human waste to mix with soil in yards. People can also get it from eating uncooked meat products that are infected.
What are the Treatments for Roundworms?
Anti-parasite medications are the first line of treatment against this infection. In some cases, these parasites will go on their own without the need for treatment. Doctors often recommend the following anti-parasite medication:
Ivermectin. It treats conditions caused by roundworms. It works by paralyzing and inactivating the gut of parasites in humans. It stops the adult one from producing larvae. It kills the newly developed parasite and works to treat the infection. Medications for this condition often start to work in 3 days period. Ensure to take your prescription at the same time each day to get the utmost benefit.
Doctors may recommend surgery if the parasite causes heavy infestation. It may be necessary to remove worms and repair the damage they’ve caused. Intestinal blockage or holes, bile duct blockage, and appendicitis are complications that may require surgery.
Are Roundworms Life-threatening to Humans?
If humans ingest the larvae of cat or dog roundworms, they can become infected, and illness results from the larvae migrating through organs and tissues. In severe cases, the worms may partly or completely block your small intestine. You may get an inflamed pancreas. The infection can even be life-threatening.
How to Prevent Roundworm Infection?

- Avoid touching the soil as it might be contaminated with human feces.
- Wash your hands with soap and water before preparing food.
- Teach your children to do the proper handwashing and let them wash their hands frequently.
- Wash, peel, and cook fruits and vegetables especially if they grow from manure-fertilized soil.
- Avoid exposure to improper sewage disposal.
- Contact your doctor if you have stomach problems especially if you have traveled from developing countries where there is an outbreak of the infection.
What is Schizophrenia: Symptoms and Treatment
What is Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder in which individuals interpret reality abnormally and may result in some combination of delusions, hallucinations, and disordered thinking. This behavior damages daily functioning and inactivates a person’s daily dealings in life. This condition needs lifelong treatment.
What are the Symptoms of Schizophrenia?

- Abnormal motor behavior. This may show a number of ways, from silliness to unpredictable agitation without purpose. It can cause difficulties in the performance of daily life activities.
- Negative symptoms. Where people reduce or lack of ability to function normally. Take no interest in everyday social interactions, often appear emotionless, and lack the ability to experience pleasure.
- Disorganized thinking. People with disorganized thinking may speak inarticulately, respond to questions with unrelated answers, shift topics frequently, or say unreasoned things.
- Delusions. Is a belief that a person holds that is not based in reality and is not altered or modified when the person is presented with contradictory evidence.
- Hallucinations. It can be in any of the senses, but hearing voices is the most common one.
What are the Causes of Schizophrenia?
This condition has no specific cause but it is believed that a combination of genetics, brain chemistry, and environmental contributions can cause this disorder. Neuroimaging studies show differences in the brain structure and central nervous system of people with this condition. While researchers are not certain about the significance of these changes, they indicate that this is a brain disease. Common risk factors for this condition are:
- Having a family history of schizophrenia
- Some pregnancy and birth complications, such as malnutrition or exposure to toxins or viruses may impact brain development
- Taking mind-altering drugs during teen years and young adulthood
Treatment of Schizophrenia

This condition requires lifelong treatment, even when symptoms have subsided. Treatment with medications and psychosocial therapy can help manage the condition. However, some cases may also need hospitalization.
Medications are the foundation for treating this condition. A patient may be recommended to take antipsychotic drugs that control the symptoms by affecting the brain neurotransmitter dopamine. The goal of this treatment is to manage signs and symptoms at the lowest possible dose. Other medications also may help, such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs. It can take several weeks to notice an improvement in symptoms.
Chlorpromazine is a typically recommended prescription for this condition. It works by helping to restore the balance of certain natural substances in the brain and reduce aggressive behavior and the desire to hurt yourself or others. It may also help to decrease hallucinations.
Doctors may also give long-acting injectable antipsychotics as an option if someone has a preference for fewer pills which may help with adherence. They are usually given every two to four weeks, depending on the medication. Psychological interventions also play a very important role in treating this condition. This may include individual therapy, social skills training, and family therapy.
Coping and Homecare Support
- Learn about this condition. Education about the disorder can help the affected individual understand the importance of sticking to the treatment plan. It can help the people around to understand the disorder and be more compassionate with the person who has it.
- Focus on the goals. Keeping treatment goals in mind can help the person with this condition stay motivated. If a family member has this condition, ensure to help to remind them about taking medications.
- Avoid alcohol and drug use. Using alcohol and recreational drugs can make it difficult to treat this condition. get advice from a professional if a family member or someone you know is addicted because quitting can also be a challenge.
- Get help. These services may be able to assist with affordable housing, transportation, and other daily activities.
- Learn relaxation techniques. The person with this disorder and loved ones may benefit from stress-reduction techniques. Ask for help from professionals on how to incorporate healthy routines along with the recovery process.
What is Melancholia: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment?
What is Melancholia?
Melancholia is a term used to describe the feeling of being deeply sad and desperate since that time. Also known as melancholic depression is a type of depression. About 15%-30% of people have this type of depression. This condition may have more severe symptoms than other types of depression and it’s harder to treat.
It is a major mental health condition characterized by persistent and intense feelings of sadness and hopelessness. The disorder can affect many areas of life and may also impact mood and behavior as well as various physical functions. People with this condition often lose interest in activities they once enjoyed and have trouble getting through the day. Occasionally, they may also feel as if life isn’t worth living.
What are the Symptoms of Melancholia?

- Depression that is consistently worse in the morning
- A different quality of depressed mood characterized by profound despair, sadness, or emptiness
- Sleep badly and wale early in the morning
- Lose their appetite and lose weight
- Extreme or inappropriate guilt
- Think about suicide
What Causes Melancholia?
The typical causes of this condition are changes in the brain and hormonal pathways. This is due to the malfunction of the adrenal glands, hypothalamus, and pituitary glands. These glands release chemicals that regulate stress and appetite. With this condition, you may have high levels of steroids and cortisol. These are hormones that are made by your adrenal glands when you are stressed. This affects many different functions in your body, including your metabolism, appetite, and memory. You may also have changes in brain signals called neurons. These signals affect how you respond to your surroundings.
What is the Treatment for Melancholia?
Psychotherapy and medication are often part of the treatment plan for this condition because it is believed to have a biological root. Causes of melancholic depression appear to be mainly due to genetic makeup and brain function, necessitating a medication that works on biological causes like brain function. Types of antidepressants used for this condition are:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. These works by changing the way the neurotransmitter serotonin works in the brain, thereby improving mood
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. It affects the way both serotonin and norepinephrine work in the brain.
- Norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitors. It affects norepinephrine and dopamine.
- Atypical antidepressants. These medications affect brain chemicals that seem to improve mood.
In addition to medication, psychotherapy is also used to treat people who have MDD with melancholic symptoms. A combination of these two treatment methods is usually more effective than either approach on its own. This involves meeting with a therapist on a regular basis to discuss symptoms and related issues. It helps a patient in the:
- Adjusting to a crisis or other stressful event
- Managing or replacing negative beliefs and behaviors with positive, healthy ones
- Improving communication skills and producing healthy coping mechanisms to solve problems
- Regain a sense of satisfaction and control in life and boost self-esteem
Medication Used for Melancholia
Venlafaxine. It is an atypical antidepressant drug referred to as serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor. It works by increasing the levels of mood-enhancing chemicals called serotonin and noradrenaline in the brain. The side effects of this medication include feeling sick, headaches, sweating, and dry mouth are common. They are usually mild and go away after a couple of weeks.
Warnings and Precautions When Taking Venlafaxine

- It can make your heart beat faster or cause an irregular heartbeat, so your doctor may not think it is suitable if you are already taking medicine for your heart.
- Talk to your doctor if you have a history of blood pressure and heart problems before taking this medication.
- If you are pregnant or planning to get pregnant, avoid this medication or talk to your doctor about its risks and benefits.
- Take this medication as instructed by your physician and avoid inconsistent dosing.
OCD: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
What is OCD?
Obsessive-compulsive disorder or OCD is a common mental health disorder where a person has obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. This condition can affect anyone and some people start having symptoms early, often around puberty but it usually starts during early adulthood.
What are the Causes of OCD?
Some causes of this condition are:
- Biology. It may be a result of changes in your body’s natural chemistry or brain functions.
- Heredity. It may have a genetic component, but specific genes have yet to be identified.
- Learning. Obsessive fears and compulsive behaviors can be learned from watching family members or gradually learned over time.
Experts are not sure why people have this condition. Genetics, brain abnormalities, and environment are supposed to play a role. Also, stress can make symptoms worse. It often starts in teens or early adulthood but it can also start in childhood as well. Other anxiety depression, problems, substance abuse, or eating disorders may happen with OCD. Watch out for the factors that may increase your risk of the condition such as;
- A history of physical or sexual abuse as a child
- Physical differences in certain parts of your brain
- A parent, siblings, or child with OCD
- Experience trauma, depression, and anxiety
What are the Symptoms of OCD?

- Fear of contamination or dirt
- Doubting and having difficulty tolerating uncertainty
- Needing things orderly and symmetrical
- Aggressive thoughts about losing control and harming yourself or others
- Unwanted thoughts, including aggression, or sexual or religious subjects
Compulsion symptoms include:
As with obsessions, compulsions typically have themes, such as:
- Washing and cleaning
- Counting
- Following a strict routine
- Orderliness
- Checking
- Demanding reassurance
How is OCD Diagnosed?

It is sometimes difficult to diagnose this condition because symptoms can be similar to those of obsessive-compulsive personality disorder, anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, depression, or other mental health disorders. The steps for diagnosis are:
- Psychological evaluation. This includes talking about your thoughts, feelings, symptoms, and behavior patterns to determine if you have obsessions or compulsive behaviors that interfere with your quality of life.
- Using the criteria for OCD. Your doctor may use criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders published by the American Psychiatric Association.
- Physical exam. This may be done to help rule out other problems that could be causing your symptoms and to check for any related complications.
Treatment for OCD
The goal of the treatment is to help bring symptoms under control so that they don’t rule your daily life. Depending on the severity of the condition, some people may need long-term, ongoing, or more intensive treatment. Cognitive behavioral therapy, CBT therapy, and exposure and response prevention are typically recommended parts of the treatment. Doctors may also prescribe medications to control the obsessions and compulsions of this condition. Most commonly, antidepressants are tried first.
Paroxetine is a selective serotonin and reuptake inhibitor. It is used in the treatment of obsessive compulsion disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and posttraumatic stress disorder. Generally, the goal is to effectively control symptoms at the lowest possible dosage. It’s not unusual to try several drugs before finding one that works well. Your doctor might recommend more than one medication to effectively manage your symptoms.
Care and Support for OCD
- Learn about your condition to keep you motivated and empowered to follow the treatment plan.
- Stay focused on your goals in mind and remember that recovery is an ongoing process.
- Reaching out to others facing similar challenges can provide you with support and help you cope with challenges.
- Learn relaxation and stress management such as meditation, visualization, muscle relaxation, massage, deep breathing, and yoga may help ease stress and anxiety.
- Work with your mental health professional to identify techniques and skills that help manage symptoms, and practice these regularly.
Can Depression Affect Others?
What is Depression?
Depression is a mood condition that causes people persistent feelings of sadness and loss of interest in something. That is also called major clinical depression or depressive disorder. It affects the way you think, feels, and behave and leads to a change in emotional and physical problems. You may struggle to do normal day-to-day activities, and sometimes you may feel as if life is not worth living.
Does Depression Affect Other People?
This condition affects your relationships with family and friends. While a person is stressed by this symptom on their own, it also takes a toll on those around them. Relationships may also worsen symptoms of depression as it often increases feelings of loneliness, sadness, and isolation. This depression disorder, in a way, can push others away, leaving the way many people feeling more isolated and withdrawn than ever.
In some cases, this condition creates space for the person, but this often worsens their state of being. Instead of taking symptoms personally, it is necessary for family and friends to be determined in their care and support. Helping to guide someone towards treatment is critical and remaining supportive of someone with this condition is vital even though their symptoms have them attempting to push others away.
General Symptoms of Depression

- Feelings of sadness and hopelessness
- An angry outburst, frustration, and irritability
- Sleep disturbances such as insomnia or oversleeping
- Trouble thinking and concentrating
- Loss of interest or pleasure in most of your normal activities
- Lack of energy, even on small tasks
- Appetite loss and weight loss for some
- Weight gain and increased cravings
- A feeling of guilt, worthlessness, and self-blame
- Agitation and restlessness
- Frequent thoughts of death
- Suicide attempts and or suicidal thoughts
- Unexplained back pain and other physical problems
- Slowed thinking, slurred speech, and slow body movements
When to Get Immediate Help?
If you or someone have symptoms of this condition, talk to your doctor right away. Call 911 if someone is attempting suicide or other forms of self-harm.
Typical Causes of Depression
- Biological differences. People with this condition appear to have physical changes in their brains. The significance of these changes is still uncertain but may eventually help pinpoint causes.
- Hormones. An imbalance of hormones can be a cause of this condition. This includes hormonal changes during and after pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid problems.
- Brain chemistry. The naturally occurring chemicals in the brain may also trigger this condition. Changes in the function and effect of these neurotransmitters and how they interact with neurocircuits involved in maintaining mood stability may play a significant role in depression and its treatment.
- Inherited traits. This is more common in people whose blood relatives also have this condition. Researchers are trying to find genes that may be involved in causing this problem.
Treatment for Depression

A combination approach of psychotherapy and medication is helpful in treating clinical conditions. Your primary care doctor or psychiatrist can prescribe medications to relieve symptoms. If you have severe depression, you may need a hospital stay, or you may need to participate in an outpatient treatment program until your symptoms improve.
Medication Used for Depression
Fluvoxamine. It blocks the reuptake of serotonin and increases its amount in central synapses. It is used very effectively to treat symptoms associated with depression. Fluvoxamine also helps in relieving the imbalance in the neurons, which is believed to give rise to anxiety and depression.
Coping and Support for Depression
- Cut back on obligations that are far from your capacity.
- Try doing a journal to improve your mood and to healthily express your anger, fear, pain, and other emotions.
- Locate helpful groups such as assistance programs and religious groups that offer help for mental health concerns.
- Try to participate in social activities and get together with family or friends regularly.
- Learn ways to relax and manage your stress.
- Plan your day and learn time management to reduce stress and improve your organizational skills.
What are the Effects of Eczema on Children?
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a condition that causes dry, itchy, and swollen skin. This is common in young children but can happen at any age. This condition is long-lasting and tends to flare sometimes, and can be irritating, but it is not infectious. Persons with this condition are at risk of developing asthma, food allergies, and hay fever.
What are its Symptoms?
- Rash on swollen skin that varies in color depending on your skin color
- Dry, cracked skin, and Itchiness
- Oozing and crusting
- Small, raised bumps on brown or Black skin
- Darkening of the skin around the eyes
- Raw, sensitive skin from scratching
- Thickened skin
Talk to your doctor if your child has any of the following:
- Has symptoms of Eczema
- Has a skin infection look for new streaks
- Has pus and yellow scabs
- Has symptoms even after trying self-care steps
- An uncomfortable condition that affects sleep and daily activities
- If you or your child has a fever and the rash looks infected, seek immediate medical attention.
What is its Effect on Children?
In infants and toddlers, eczema looks and acts differently rather than it does in older children.
- For infants or the first six months. It appears on the cheeks, face, forehead, scalp, and chin. It can also spread to other areas of the body, but not usually in the diaper area, where moisture protects the skin. The skin during this period also tends to look red.
- For babies. It often appears on your baby’s elbows and knees places which are easy to rub or scratch as they are crawling. If this condition rash becomes infected, it may form a yellow crust or very small bumps on the skin.
- For toddlers. It affects the face of children and can appear as red patches with small bumps, as shown here. The condition is more likely to appear in the creases of the elbows and knees or on their hands, wrists, and ankle. It may also appear on the skin around your toddler’s mouth and eyelids.

How to Prevent Eczema in Children?
- Make sure that your child takes a bath daily. Use warm, rather than hot, water, and limit your bath or shower to about 10 minutes.
- Use a gentle cleanser. For young children, you usually need only warm water to get them clean. Soap can be especially irritating to the skin of young children, so as much as possible, use the safest products.
- Moisturize your child’s skin at least twice a day. Creams, ointments, shea butter, and lotions seal in moisture. Choose a product or products that work well for your child. Using petroleum jelly on your baby’s skin may help prevent the development of atopic dermatitis.
- Pat dry. After bathing, gently pat the skin with a soft towel. Apply moisturizer while your child’s skin is still damp.
Treatment for Eczema in Children
Start with regular moisturizing and a self-care routine for your child. If these do not help, your doctor might suggest medicated creams that control itching and help repair skin. These are sometimes combined with other treatments. This condition can be persistent, and your child may need to try various treatments over months or years to control it.
There are several options that will help control itching and repair the skin. Products are available in various strengths and as creams, gels and ointments. Talk with your child’s doctor about the options and your preferences. Whatever is prescribed, apply it as directed before you moisturize.
Recommended Medication for Eczema
Clobetasol. It is used to treat various types of skin disorders, such as eczema. It has properties that work by controlling the synthesis of inflammation-causing mediators such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Controlling the production of inflammation-causing substances can effectively reduce symptoms associated with allergic reactions in the skin.
What is Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression? Symptoms and Treatment
What is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland does not make enough hormones. It may not cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages, but if left untreated, it may trigger other health problems such as heart disease and high cholesterol.
What are its Symptoms?

- Tiredness
- Sensitivity to cold
- Weight gain
- Dry skin and constipation
- Hoarse voice
- Coarse hair and skin
- Muscle aches, tenderness, and stiffness
- Muscle weakness
- Puffy face
- Memory problem
- Depression
- Muscle weakness
- Hair thinning
- Irregular menstrual cycle for women
Symptoms in infants include:
- Poor growth and feeding problems
- Poor weight gain
- Jaundice or yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Poor muscle tone
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Hoarse crying
- Enlarges tongue
- A soft bulge or swelling near the belly button
Symptoms in children and teens
- Stature caused by poor growth
- Delayed development of permanent teeth
- Delayed puberty
- Poor mental development
What Causes Hypothyroidism?

It happens when the thyroid gland doesn’t make enough hormones. Conditions or problems that can lead to this condition include:
- Autoimmune disease. Hashimoto’s disease is a common autoimmune condition that triggers hypothyroidism. It happens when the immune system makes antibodies that attack healthy tissues. Sometimes that process involves the thyroid gland and affects its ability to make hormones.
- Problems at birth. Some babies are born with a thyroid gland that doesn’t work correctly. Often, infants born with hypothyroidism don’t have noticeable symptoms at first. That’s one reason why most states require newborn thyroid screening.
- Pituitary disorder. A relatively rare cause of hypothyroidism is the failure of the pituitary gland to make enough thyroid-stimulating hormone. This is usually because of a noncancerous tumor of the pituitary gland.
- Thyroid surgery. This medical procedure lowers the gland’s ability to make thyroid hormones or stop it completely.
- Radiation therapy. Using radiation to treat cancers of the head and neck can affect the thyroid gland and lead to hypothyroidism.
- Thyroiditis. It is an inflammation of the thyroid caused by an infection, or it can also result from an autoimmune disorder or another medical condition affecting the thyroid. It can trigger the thyroid to release all of its stored thyroid hormones at once.
- Medicine. A number of medicines may lead to hypothyroidism. One such medicine is lithium, which is used to treat some psychiatric disorders.
- Pregnancy. Some people develop hypothyroidism during or after pregnancy. If hypothyroidism happens during pregnancy and isn’t treated, it raises the risk of pregnancy loss, premature delivery, and preeclampsia. Preeclampsia causes a significant rise in blood pressure during the last three months of pregnancy.
How Diagnose Hypothyroidism?
The diagnosis of hypothyroidism doesn’t rely on symptoms alone. It’s usually based on the results of blood tests. The first blood test is typically done to diagnose hypothyroidism and measures the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood. If the second test shows high TSH, but T-4 and T-3 are in the standard range, then the diagnosis is a condition called a subclinical condition. It usually doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms.
Medication Used for Hypothyroidism
Thyroxine sodium. It is used for the treatment of hypothyroidism and pituitary TSH suppression. It binds to the thyroid hormone response element and results in gene transcription. This results in the expression of a predetermined genetically coded pattern of protein synthesis.
Most healthcare providers recommend taking the medicine levothyroxine to treat hypothyroidism. But an extract containing thyroid hormone derived from the thyroid glands of pigs is available. It is sometimes called desiccated thyroid extract. This medicine is taken by mouth. It returns hormone levels to a healthy range, eliminating symptoms of hypothyroidism.
You’ll likely start to feel better one or two weeks after you begin treatment. Treatment with this medication can be lifelong because the dosage you need may change. Visit your doctor from time to time for a regular check-up.
Systemic Mastocytosis: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Causes, and Treatment
What is Systemic Mastocytosis?
Systemic Mastocytosis is a rare condition that results in too many mast cells building up in your body. A mast cell is a type of white blood cell. These are found in connective tissues throughout your body. They help your immune system function properly and help protect you from disease.
Excess mast cells build up in your bone, skin, digestive tract, marrow, or other body organs when you have this condition. When triggered, these mast cells release substances that can cause signs and symptoms similar to an allergic reaction. This condition can also cause severe inflammation that may result in organ damage. Avoiding its typical triggers, such as spicy foods, alcohol, and certain medications, can help.
Five Main Types of Systemic Mastocytosis
- Indolent. This usually doesn’t include organ dysfunction. Skin symptoms are common, but other organs may be affected, and the disease may worsen slowly over time.
- Smoldering. It is linked with more-significant symptoms and may include organ dysfunction and worsening illness over time.
- Systemic type with another blood or bone marrow disorder. This is considered a severe type that develops rapidly and is often linked with organ dysfunction and damage.
- Aggressive. This is more severe and may show several symptoms that are usually associated with progressive organ dysfunction and damage.
- Mast cell leukemia. This is an extremely rare and aggressive form of this condition.

Signs and Symptoms of Systemic Mastocytosis
The signs and symptoms depend on the part of the body where it occurs. Most of the cells build up in the skin, spleen, bone marrow, and liver skin. Signs and symptoms of systemic Mastocytosis may include:
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting
- Flushing, itching, or hives
- Bone and muscle pain
- Anemia or bleeding disorders
- Enlarged liver, spleen, or lymph nodes
- Depression, mood changes, or problems concentrating
People have different triggers for this condition, but the most typical causes include the following:
- Skin irritation
- Alcohol
- Exercise
- Insect stings
- Spicy foods
- Certain medications
Talk to your doctor if you have problems with hives or flushing or if you have concerns about the signs or symptoms listed above.
What Causes Systemic Mastocytosis?
Most cases of this condition are caused by a mutation in the KIT gene. Too many mast cells are produced and build up in tissues and body organs, releasing substances such as histamine, leukotrienes, and cytokines that cause inflammation and symptoms. This condition can cause several complications, such as:
- Peptic ulcer disease. Chronic stomach irritation can lead to ulcers and bleeding in your digestive tract.
- Anaphylactic reaction. This severe allergic reaction includes signs and symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, fainting, loss of consciousness, and shock. If you have a severe allergic reaction, you may need an injection of epinephrine.
- Blood disorders. These can include anemia and poor blood clotting.
- Organ failure. A buildup of mast cells in body organs can cause inflammation and damage to the organ.
- Reduced bone density. Because systemic Mastocytosis can affect your bones and bone marrow, you may be at risk of bone problems, such as osteoporosis.
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Systemic Mastocytosis
The treatment for this condition varies depending on the type of condition, and part of the organ is affected. It focuses on managing the symptoms, regular monitoring, and managing the disease itself. To control the triggers, identify and avoid the common triggers such as foods.
Ranitidine is a prescription used in the treatment and management of this condition. It blocks all the phases of gastric secretion. The recommended dosage of this medicine in adults is 150 mg twice daily or 300mg once daily, given at bedtime. The recommended dose of Ranitidine in pediatric patients is 2 to 4 mg once daily.

Homecare and Lifestyle Support for Systemic Mastocytosis
- Identify and avoid your triggers.
- Treat allergic reactions and always carry your medications to avoid forgetting a dose.
- Follow your doctor’s recommended care and ongoing monitoring.
- Learn as much as you can about your disease and make the best choices.
- Find a team of trusted professionals. Medical centers with specialty teams can offer you information about the disease.
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Causes, and Treatment
What is Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome?
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome is a rare condition that causes tumors to grow in your intestine or pancreas. Tumors or gastrinomas release hormones that trigger your stomach to produce gastric acid. Too much production may lead to ulcers and other complications which may also include cancerous tumors.

Signs and Symptoms of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
- Diarrhea
- Stomach pain
- Aching and burning discomfort in the upper abdomen
- Heartburn
- Nausea and vomiting
- Burping
- Acid reflux
- Unexplained weight loss
- Bleeding in the digestive tract
- Loss of appetite
Seek immediate help if you have aching or burning pain in your upper belly that does not go away with medications. Conditions associated with nausea, vomiting, and persistent diarrhea may need immediate medical attention.
What Causes Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome?
The exact specific cause of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is unknown. But the pattern of events that occurs in this condition typically follows the same sequence. The syndrome begins when one or more tumors form in your pancreas or a part of the duodenum or the section connected to your stomach. Sometimes the tumors form at other sites, such as the lymph nodes next to your pancreas.
Your pancreas sits behind and below your stomach. It makes enzymes that are needed for digesting food. Digestive juices from the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder mix in the duodenum. This is where most of your digestion happens.
The tumors that occur with this condition are made up of cells that secrete large amounts of the hormone gastrin. High gastrin production causes the stomach to make far too much acid. The excess acid then leads to peptic ulcers and sometimes to diarrhea. Besides causing excess acid production, the tumors are often cancerous and may affect the liver and other nearby organs.
What are the Risk Factors of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome?
Anyone is at risk of this condition but people with the condition may have a genetic problem known as multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1). Children of adults with MEN1 are at a greater risk of getting the disease. This is common in men from 30 to 50 years old. Ensure to seek immediate help if you experience persistent symptoms of ZES.
How to Diagnose Zollinger Ellison Syndrome?
Your doctor will assess your symptoms and review your medical history. To diagnose ZES, your doctor will run some blood tests to see through your gastrin levels. Other diagnostic method includes:
- Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Tissue samples may be removed to examine gastrin-producing tumors. This test can determine whether the stomach is making high levels of gastric acid.
- Endoscopic ultrasound. This procedure uses an endoscope to spot tumors in your stomach, duodenum, and pancreas. This test also requires fasting after midnight and sedation.
- Imaging tests. One test is a nuclear scan called somatostatin receptor scintigraphy. This test uses radioactive tracers to help locate tumors. Other helpful imaging tests include ultrasound, computerized tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and Ga-DOTATATE PET-CT scanning.
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
The goal of the treatment is to focus on managing the hormone-secreting tumors as well as the ulcer they cause. The treatment of tumors includes an operation to remove the gastrinomas. If you have just one tumor, your provider may be able to remove it surgically. But surgery may not be an option if you have many tumors or tumors that have spread to your liver. Risks associated with surgery include infection, pain, and blood loss. Talk to your doctor to understand your risks.
Medication Used for Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Ranitidine. This drug blocks gastric secretion and treats conditions like hypersecretory conditions like ZES. Ranitidine counteracts the effects of gastrin. Medicines known as proton pump inhibitors are the first line of treatment. These are effective medicines for controlling acid production in ZES. Continue taking this medication throughout the treatment course to ensure recovery.
Insights on Musculoskeletal Disorders
What are Musculoskeletal Disorders?
Musculoskeletal disorders affect joints, bones, tendons, muscles, or ligaments. It is often characterized by persistent pain that affects mobility and dexterity. It reduces your ability to work and participate in any day-to-day activities.
What are the Different Types of Musculoskeletal Disorders?
- Muscle pain. Cramps, muscle spasms, and injuries can cause muscle pain. This may also include pain that is caused by tumors and other possible causes.
- Tendon and ligament pain. These are strong bonds of tissue that connects your joints. Overuse injuries, strains, and sprains can lead to pain.
- Bone pain. This is caused by injuries such s bone fractures or other causes that cause pain.
- Joint pain. Inflammation and stiffness often accompany the pain. For many people, this pain gets better however some conditions worsen with activity.
Muscle spasms range from mild to intense conditions. The spastic muscle may feel harder than normal to touch and some may appear visibly distorted. Spasms typically last from seconds to fifteen minutes, or longer. Some attacks may also reoccur before totally going away.
What are the Causes of Musculoskeletal Disorders?
There is usually no single cause of this condition. But it has various risk factors that often work in combination, including physical and organizational and psychosocial, and individual factors. Common causes of this condition include bone fracture, joint dislocation, overuse injuries, poor postures, and sprain. Direct blows to muscles and joints may also cause this condition.
What are the Symptoms of Musculoskeletal Pain?
- Stiffness and aching
- Burning sensations in the muscles
- Muscle twitches and fatigue
- Pain that worsens with movement
- Sleep disturbances
If the condition interferes with your daily activities or function, speak with your doctor. Seek immediate medical help if you have severe pain from a sudden injury.
What are the Risk Factors of Musculoskeletal Pain?
- Arthritis. It causes chronic joint inflammation. Many people experience this kind of condition.
- Fibromyalgia. It is a chronic illness that causes all musculoskeletal pain and fatigue.
Tunnel syndromes. This condition causes nerve compression. Examples of this condition include carpal tunnel syndrome, and cubital tunnel syndrome leads to these conditions.
How are Musculoskeletal Disorders Diagnosed?
Your doctor will start by assessing your signs, symptoms, and medical history. Symptoms such as fever or rash may help with the diagnosis to determine whether the pain is chronic or acute. Your healthcare provider will perform a hands-on exam to look for the source or cause of the pain by touching the affected area. Some testing methods may include:
- Blood test
- X-ray
- CT scan
- MRI
Treatment for Musculoskeletal Disorder
Typically, this condition improves with proper treatment. If an underlying condition causes pain, treating that condition can help relieve symptoms. Maintaining strong bones and joints is essential for preventing this condition. Along with proper exercise and medications, ensure that you are following a healthy lifestyle, especially during the treatment course. Use good posture and limit repetitive movements to successfully treat the pain.
Medication Used for Musculoskeletal pain
Ibuprofen. This is a tolerable pain reliever than using aspirin. It is used as a simple analgesic and antipyretic for muscle and bone pain. You can buy OTC ibuprofen but ensure to talk to your doctor about taking this medication especially if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
How to Manage and Prevent Musculoskeletal Pain?
- Regular strengthening exercises and stretching can help keep your bones, joints, and muscles strong.
- It’s crucial to develop healthy lifestyle habits now.
- Ask your doctor for more information about how you can maintain a healthy system and lower your risk of MSDs.
- Maintain a tall posture to prevent back pain, and be careful when picking up heavy objects.
- Keep repetitive motions to a minimum. Avoid prolonged work in poor postures
- By taking care of your body throughout adulthood, you can lower your risk of developing these disorders.
Managing GERD During Thanksgiving
Thanksgiving is probably the most anticipated meal of the year, but it can cause discomfort for people who have GERD. To minimize the attacks or this condition, ensure to plan ahead your menu to celebrate thanksgiving with gladness.
What is GERD?
GERD is a disease that can lead to damage and, eventually, complications to the esophagus over time. It occurs when stomach acid repeatedly flows back into the tube connecting your mouth and stomach. It can interfere with daily living, but most people can get relief from it through lifestyle changes, home remedies, and medical treatment.
Symptoms of GERD
A burning sensation in your chest, usually after eating, which might be worse at night or while lying down:
- Trouble swallowing
- The sensation of a lump in your throat
- The backwash of food or sour liquid
- Upper abdominal or chest pain
If you have nighttime acid reflux, you might also experience:
- An ongoing cough
- Inflammation of the vocal cords
- New or worsening asthma

What Not to Eat or Drink If You Have GERD?
- Chocolate
- Mint
- Carbonated drinks
- Alcohol
- Fatty foods
- Spicy foods
- Tomatoes
- Coffee
- Citrus fruits and juices
- Fried foods
Navigating GERD To Enjoy Thanksgiving
You can also make some strategic decisions about the Thanksgiving meal to prevent symptoms. Experts suggest eating earlier in the day to allow more time to digest the meal. Alcohol is a trigger for many people, so you may want to avoid alcohol or just have a small glass of wine with your early meal.
Tips to Avoid GERD Attacks on Thanksgiving
- Consider pre-medicating. If you have been taking medications with lifestyle modifications, ensure that you have OTC medication prepared to reduce the amount of acid your stomach produces as you digest.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Excess pounds put pressure on your abdomen, pushing up your stomach and causing acid to reflux into your esophagus.
- Skip the drinks. Both alcohol and caffeinated beverages relax the lower esophageal sphincter, the barrier between your stomach and esophagus that opens and closes to allow food to enter your stomach or acid to creep upward. It increases production and inflames the stomach lining, increasing the likelihood of symptoms.
- Practice portion control. Avoid overeating because it triggers attacks. Stop eating before you get extra full or eat way too much.
- Be cautious with alcohol. It can lower your inhibitions and makes you more likely to have that second helping of stuffing after all.
- Do not lie down after a meal. Wait at least three hours after eating before lying down or going to bed. Eat food slowly and chew thoroughly.
- Take a walk instead of sleeping. Lying down right after a meal perfectly positions your body for acid to sneak into your esophagus. A better plan is to go for a walk to aid your digestion and wait at least three hours after eating before crawling into bed.
- Identify the risk factors. Certain foods are more likely to worsen acid reflux and heartburn. These include fatty foods, spicy foods, onions, garlic, caffeine, chocolate, citrus fruits and juices, and mints. Avoid these triggers to enjoy the celebration.
Recipe That Doesn’t Trigger GERD

Whipped Sweet Potatoes
Ingredients:
- 4 large sweet potatoes
- 1 cup almond milk
- 1 tablespoon nutritional yeast
- 1 tablespoon maple syrup
- ½ teaspoon cinnamon
- 1 teaspoon garlic powder
- Salt and pepper to taste
- ½ cup of toasted pecans
Cooking Instructions:
- Heat oven to 395 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Pierce your sweet potatoes multiple times with a fork and wrap them in foil and bake them for about 30 minutes.
- Allow the potatoes to cool, then peel and transfer them to a blender or food processor.
- Add in almond milk, yeast, cinnamon, maple syrup, garlic powder, salt, and pepper.
- Blend or process until nicely whipped.
- Scoop into a serving dish and top with toasted pecans
Medication Used for GERD
Esomeprazole. It is a Proton Pump Inhibitor that reduces gastric secretion. It reduces the amount of acid your stomach makes and treats indigestion, heartburn and acid reflux, and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Class III Obesity: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Causes, and Treatment
What is Class III Obesity?
Class III obesity, previously known as morbid obesity, is a complex chronic condition that can lead to several serious health issues. When you resort to processed foods, it can increase the fat deposition in your body. Excessive weight is due to fat accumulation that links to health problems. When your BMI is over 30, you are obese. It is due to eating loads of calories and having an inactive lifestyle. Likewise, it is also due to genetic disorders.
Signs and Symptoms of Class III Obesity
- Difficulty in sleeping or sleep apnea
- Daytime drowsiness
- Woman with knee pain
- Back and or joint pains
- Heavy sweating
- Intolerance to heat
- Body with skin folds
- Infections in skin folds
- Fatigue
- Depression
- A feeling of shortness of breath
- Hyperpigmentation in the skin folds and armpits
- Stretch due to endocrinological alteration
- Swelling and varicose veins in the lower limbs.
- Body Mass Index greater than 30 kg/m2.
- Waist circumference greater than 94 cm in men and 88 cm in women.
- High blood pressure
Risk Factors of Class III Obesity
- Hormone imbalances. Your body makes hundreds of hormones that each have unique and important functions. Many of those hormones can affect how your body signals that you need food and how your body uses energy. Chronic stress can increase cortisol levels, which can lead to weight gain and increase cravings for sweet, fatty, and salty foods. Low thyroid hormone levels can slow down your metabolism and lead to weight gain.
- Genetic factors. It has been shown that obesity is an inherited trait and that multiple genes are involved in the process.
- Cultural factors. Increasing portion sizes and marketing of calorie-dense foods can contribute to obesity.
- Socioeconomic and geographical factors. Being low in socioeconomic status and having easier access to unhealthy fast foods than healthy whole foods can contribute to obesity. A lack of recreational facilities or parks and few safe or easy walking routes in your neighborhood can also contribute to obesity.
The Many Causes of Class III Obesity
When you eat, your body uses the calories you consume to run your body. The body also needs calories to pump your heart or digest food. If those calories are not used, the body stores them as fat. Your body will build up fat stores if you continue to eat more calories than your body can use during daily activities and exercise. Morbid conditions are due to chronic and uncontrolled weight gain caused by several factors.

Treatment and Management of Class III Obesity
Treatment for excessive weight gain is a combination of therapy and the help of professionals to increase your chances of success. These includes:
- Medication. If you are struggling with the desire to eat more than your allotted calories for the day, your doctor may suggest a medication that blocks fat absorption or acts as an appetite suppressant.
- Diet and exercise. You may start by eating fewer calories than you burn but do so with the guidance of a medical professional to make sure you’re still getting enough nutrition. You also want to add in physical activity every day but you have to start small to avoid compromising your body.
- Behavioral therapy. Sometimes old habits are so deeply set in the mind and are hard to overcome. Behavioral therapy focuses on changing your unhealthy habits and correcting your eating pattern or improving emotional coping mechanisms.
- Surgery. If none of these things help sufficiently, you may need surgery to lose enough weight. Bariatric surgery works by sealing off most of your stomach, so you feel fuller faster. However, surgery is expensive and sometimes life-threatening.
Medication Used for Class III Obesity
Orlistat. It is a drug that is prescribed to people suffering from morbid weight gain conditions. works by inhibiting the lipases that are required to break down the fatty acids, thereby preventing the absorption of fatty acids in the diet. Talk to your doctor about the risk, benefits, and further guidelines when taking orlistat for weight loss.
Use Cyproheptadine to Fight Allergies
What is Cyproheptadine?
Cyproheptadine is an antihistamine that reduces the effects of the natural chemical histamine in the body. It is used to treat a variety of allergic conditions. This medication comes in both tablet and syrup forms and can be used in people ages 2 and older. However, this is not commonly used because it causes more drowsiness and other side effects compared to other allergy medications.

Common Types of Allergies
- Pollen allergy. It is an airborne allergy caused by changes in season. It is one of the most common types of aversion.
- Pet allergy. It is an allergic reaction to proteins found in an animal’s skin cells, saliva, or urine.
- Food allergy. It is an immune system reaction that occurs soon after eating a certain food.
- Drug allergy. It is the reaction of the immune system to a medicine regardless if it is a prescription or non-prescription drug.
Usage, Dosage, and Storage
Cyproheptadine is used to treat sneezing, runny nose, itching, red or watery eyes, and other symptoms of seasonal allergies. This is also prescribed to treat other conditions such as eczema or skin reactions to insect bites and is sometimes used to treat certain types of headaches, including migraines.
The dosage of this medication depends on your condition or age. Your doctor may change your dosage to get the best results. Avoid taking this medication in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended. To get the proper amount for a liquid prescription, use the syringe provided, or a special dose-measuring spoon or medicine cup.
If you miss a dose, take the missed dose as soon as you remember but skip it if is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up for the missed dose. Avoid drinking alcohol with this medicine because it can interfere with recovery and may cause other health risks.
Storage of Cyproheptadine
Store Cyproheptadine in a cool dry place or away from direct sunlight and moisture. Avoid putting this in the freezer or hot temperature to prevent the solution from spoiling. Keep away from the reach of children and pets.
Dosage Instructions for Children and Adults
- Age 7 to 14 years. The usual dose is 4 mg two or three times a day, adjusted as necessary to the size and response of the patient. The dose is not to exceed 16 mg a day.
- Age 2 to 6 years. The usual dose is 2 mg two or three times a day, adjusted as necessary to the size and response of the patient. The dose is not to exceed 12 mg a day.
- Adults. The total daily dose for adults should not exceed 0.5 mg. The therapeutic range is 4 to 20 mg a day, with the majority of patients requiring 12 to 16 mg a day.
Side Effects of Cyproheptadine
- Drowsiness or dizziness
- Dry mouth, throat, nose, or mouth
- Blurry vision or constipation
- Restlessness in children

Rare side effects of Cyproheptadine that may need medical attention include:
- A light-headed feeling
- Seizure and convulsions
- Little or no urination
- Fast or pounding heartbeats
- A feeling of passing out
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Ringing in your ears
- Pale or yellowed skin
- Dark colored urine
- Fever and weakness
Warnings and Precautions When Taking Cyproheptadine
- You should inform your doctor if you have narrow-angle glaucoma, a stomach ulcer or obstruction, an enlarged prostate, urination problems, or if you are having an asthma attack as this medication is not advisable for these conditions.
- This medication is not permissible if you are breastfeeding a baby, if you are elderly, or if you have a debilitating disease unless given by a doctor for emergency reasons.
- This medicine can cause you to have a false positive drug screening test. If you provide a urine sample for drug screening, tell the laboratory staff that you are taking this medicine.
- You should not use antihistamine medication to make a child sleepy.
- Tell your doctor if you have changes in weight caused by the prescription.
- Ensure to complete the treatment period noted by your doctor. Avoid stopping abruptly.
Bacterial Infection Gone With Amoxicillin
What is Amoxicillin?
Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic that fights bacteria. It is used to treat many different types of infections caused by bacteria. It is also sometimes used together with another medication called clarithromycin to treat stomach ulcers caused by H.pylori infection.
Examples of Bacterial Infections
- Tonsillitis. It is an inflammation of the tonsils caused by a viral infection and or bacterial infection. Tonsillitis is a common condition in children, teenagers, and young adults.
- Urinary tract infection. UTI is an infection in any part of the urinary system such as the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most infections involve the bladder and the urethra.
- Bronchitis. It is an infection of the main airways of the lungs causing them to become irritated and inflamed. Symptoms include cough, which may bring up yellow-grey mucus.
- Pneumonia. It is an infection that inflames the air sacs in the lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus that causes cough with phlegm, fever, and chills. A variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, can cause pneumonia.
Other bacterial infections that occur in the ear, nose, throat, and skin are also treated with this medication along with other prescriptions given by doctors.
Usage, Dosage, and Storage
You can take it by mouth with a glass of water. It is permissible either before or after a meal. Avoid chewing or breaking the tablet. If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it’s nearly time for your next dose. In this case, just leave out the missed dose and take your next dose at the usual time. Avoid taking two tablets at the same time as it leads to overdoing and other risks.
The dose of this medicine varies from person to person depending on your condition. Follow your doctor’s orders or the directions on the label that includes information on the average doses of this medicine. If your dose is different, do not change it unless your doctor tells you to do so.
For the treatment of gonorrhea, the quantity is based on body weight and must be determined by your doctor. The usual dose is 50 milligrams per kilogram of body weight per day, combined with other single-dose medication.
Storage of Amoxicillin
- Ask your healthcare professional how you should dispose of any medicine you do not use.
- Store the medicine in a closed container at room temperature, away from heat, moisture, and direct light, and keep from freezing.
- Keep out of the reach of children.
- You may store the oral liquid in the refrigerator. Throw away any unused medicine after 14 days. Do not freeze.
- Do not keep outdated medicine or medicine no longer needed.
- To protect young children from poisoning, always lock safety caps and immediately place the medication in a safe location
Side Effects of Amoxicillin?
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea and changes in taste
- Headache and rashes
- Itching and skin blisters
- Peeling and hives
- Wheezing and difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Swelling of the face, throat, tongue, lips, and eyes
Seek immediate help if you or your child experience any severe symptoms such as:
- Cloudy or bloody urine
- Decreased urination
- Swelling of any part of the body
- Confusion
- Severe nausea and vomiting
- Severe diarrhea that may occur with or without fever and stomach cramps
How to Cope With the Side Effects of Amoxicillin?
Stick to simple meals if you feel nauseous and do not eat rich or spicy food. It might help to take your medicine after a meal or snack. For diarrhea, drink plenty of fluids, such as water to avoid dehydration. Signs of dehydration include peeing less than usual or having dark, strong-smelling pee.
Precautions When Taking Amoxicillin
- If your or your child’s symptoms do not improve within a few days check with your doctor.
- This medicine may cause a serious allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. Call your doctor right away if you have a skin rash, shortness of breath, and trouble breathing.
- It may cause diarrhea, and in some cases, it can be severe. Do not take any medicine or give medicine to your child to treat diarrhea without first checking with your doctor.
- In some young patients, tooth discoloration may occur while using this medicine.
- Birth control pills may not work while you are using this medicine.
- Do not take other medicines unless they have been discussed with your doctor.
Hives: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Hives are a skin reaction that causes itchy welts. It often starts as itchy patches that turn into swollen welts that vary in size. These swellings appear and fade at random as the reaction runs its course. Chronic hives can be very uncomfortable and interfere with sleep and daily activities.
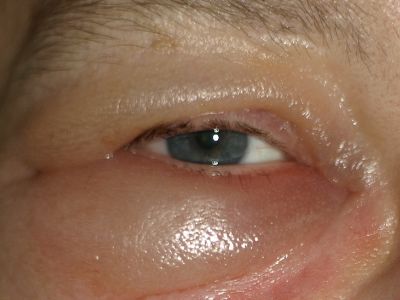
Signs and Symptoms?
- Batches of swellings can arise anywhere on the body
- Ridges that might be red, purple or skin-coloured
- Swellings that vary in size
- Welts that appear and fade repeatedly
- Itchiness which can be intense
- Painful swelling around the lips, cheeks, and eyes
- Flares triggered by heat, exercise or stress
- Symptoms that persist for more than six weeks and recur often
See your healthcare provider if you have severe conditions that last for more than a few days. Seek emergency medical care if:
- Chronic rashes do not put you at sudden risk of a serious allergic reaction
- If you get this condition as part of a severe allergic reaction
- You experience dizziness, trouble breathing
- You experience severe swelling of the tongue, lips, mouth or throat
What Causes Hives?
The swellings that come with this reaction are caused by the release of immune system chemicals, such as histamine, into your bloodstream. The specific cause of this condition depends on their type such as:
- Physical urticaria. These are caused by something that stimulates the skin such as cold, heat, vibration, pressure, sun exposure, sweating, or exercise. It usually occurs right where the skin was stimulated and rarely appears elsewhere.
- Dermatographism. This is a common form of physical urticaria where swelling or rashes form after firmly stroking or scratching the skin. It can also occur along with other forms of urticaria.
- Acute urticaria. These are rashes that last less than 6 weeks. The most common causes are foods, medications, and infections. The most common foods that cause rash are nuts, chocolate, fish, tomatoes, eggs, fresh berries, and milk.
- Chronic urticaria. These are conditions that last more than 6 weeks. The cause is usually harder to identify than those causing acute urticaria. In some cases, the cause may be thyroid disease, hepatitis, infection, or cancer.
Are Hives contagious?
Unlike some other skin conditions, these are not contagious. But if you develop rashes because your skin is exposed to secretions from a plant like poison ivy, you can spread the allergenic product to others until you wash it off.

How to Diagnose Hives?
- Skin tests. Your doctor will run tests for different allergens on your skin. If your skin turns red or swells, it means you’re allergic to that substance.
- Blood tests. It checks for specific antibodies in your blood. Your body makes antibodies to fight off allergens. If your body makes too many antibodies, you can develop rashes and swelling.
Your healthcare provider will likely talk with you about your symptoms and look at your skin. One of the effective features of this condition is that the welts come and go at random. You might be asked to keep a diary to keep track of:
- What you eat and drink
- Where hives appear and how long it takes a welt to fade
- Your activities
- Any medications including herbal remedies or supplements
- Whether your hives come with painful swelling
Treatment and Management of Hives
Treatment for chronic conditions often starts with nonprescription antihistamines. If these do not help, your doctor might suggest that you try one or more medications.
Medication Used for Hives
Loratadine. It is a medication used to treat various skin allergies. works by selectively antagonizing peripheral H1 histamine receptors. It works effectively, with the results showing immediately after taking the pill.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies for Hives
- Soothe the skin by covering the itchy area with a cold washcloth or rubbing an ice cube over it for a few minutes.
- Apply an anti-itch cream or lotion with menthol for a soothing effect.
- Avoid wearing clothing that’s rough, tight, scratchy or made from wool.
- If you think a medication caused your welts, stop using it and contact your primary care provider.
- Use a nonprescription anti-itch drug to avoid drowsiness and may help ease itching.
- Protect your skin from the sun and apply sunscreen about a half hour before going outdoors.
- Avoid triggers that include foods, medications, pollen, pet dander, latex and insect stings.
Parkinson’s Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive disorder that affects the nervous system and the parts of the body controlled by the nerves. Symptoms start slowly. In the early stages of Parkinson’s disease, your face may show little or no expression. Your arms may not swing when you walk. The disease may be improved with medications.
What is Parkinson’s disease?
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a type of movement disorder that can affect the ability to perform daily activities. It is characterized by its most common motor symptoms, tremors, stiffness or rigidity of the muscles, and slowness of movement. Also, it manifests in non-motor symptoms including sleep problems, constipation, anxiety, depression, and fatigue.

Signs and Symptoms
The known symptoms of Parkinson’s disease involve loss of muscle control. However, experts now know that muscle control-related issues aren’t the only possible symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Motor-related symptoms:
- Slowed movements (bradykinesia)
- A tremor
- Rigidity or stiffness
- Unstable posture or walking gait
Additional motor symptoms can include:
- Blinking less often than usual
- Cramped or small handwriting
- Drooling
- Mask-like facial expression
- Trouble swallowing (dysphagia)
- Unusually soft speaking voice (hypophonia)
Non-motor symptoms:
- Autonomic nervous system symptoms
- Depression
- Loss of sense of smell
- Sleep problems such as periodic limb movement disorder (PLMD), rapid eye movement (REM) behavior disorder, and restless legs syndrome.
- Trouble thinking and focusing
What causes Parkinson’s disease?
Parkinson’s disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra. This leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain. Dopamine plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. A reduction in dopamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Exactly what causes the loss of nerve cells is unclear. Most experts think that a combination of genetic and environmental factors is responsible.
Treatment and Management of Parkinson’s disease
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose non-genetic cases of Parkinson’s. Doctors usually diagnose the disease by taking a person’s medical history and performing a neurological examination. If symptoms improve after starting to take medication, it’s another indicator that the person has Parkinson’s.
Several disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinson’s disease. People with Parkinson’s-like symptoms that result from other causes, such as multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies are sometimes said to have Parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinson’s, certain medical tests, as well as responses to drug treatment, may help to better evaluate the cause. Many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, so it is important to get an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible.
While there is no cure for Parkinson’s at this time, there are several treatments that can ease symptoms. The medications are the mainstay of treatment, but modalities are often used in combination. Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can be critical to the treatment plan. Surgical options also have an important role for a subset of patients with the disease. Lastly, complementary therapies can be used to treat some Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Your physician and other healthcare professionals can help you determine the best treatment plan for your symptoms.

Recommended medication that can be used to manage Parkinson’s disease:
- Ropinirole Hydrochloride – this medication can be used alone or in combination with other medications to treat the disease. The drug helps improve symptoms of the disease such as the ability to move and decrease shakiness, stiffness, slowed movement, and unsteadiness. It may also decrease the number of episodes of not being able to move.
The doctor may prescribe other medicines to treat Parkinson’s symptoms, including:
- Dopamine agonists stimulate the production of dopamine in the brain
- Enzyme inhibitors increase the amount of dopamine by slowing down the enzymes that break down dopamine in the brain
- Amantadine to help reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
Obesity: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Obesity is a complex disease involving an excessive amount of body fat. It isn’t just a cosmetic concern. It’s a medical problem that increases the risk of other diseases and health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. There are many reasons why some people have difficulty losing weight. Usually, obesity results from inherited, physiological and environmental factors, combined with diet, physical activity, and exercise choices.
What is Obesity?
Overweight and obesity are defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a health risk. A body mass index (BMI) over 25 is considered overweight, and over 30 is obese. The issue has grown to epidemic proportions, with over 4 million people dying each year as a result of being obese in 2017 according to the global burden of disease.
Obesity is one side of the double burden of malnutrition and today more people are obese than underweight. Once considered a problem only in high-income countries, overweight and obesity are now dramatically on the rise in low- and middle-income countries, particularly in urban settings. The vast majority of overweight or obese children live in developing countries, where the rate of increase has been more than 30% higher than that of developed countries.

Signs and Symptoms
The most obvious symptom is the increase in weight therefore the symptoms that may be presented arise from this increase in weight that, among others, other symptoms may include:
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Back and joint pains
- Excessive sweating
- Intolerance to heat
- Infections in skin folds
- Fatigue
- Depression
- The feeling of shortness of breath
The main signs also derive from the magnitude of the excess weight, the most common:
- Acanthosis nigricans is a skin disorder characterized by the presence of hyperkeratosis and hyperpigmentation in the skin folds and armpits.
- Stretch marks due to distension and rupture of the elastic fibers of the skin or vinous in the case of obesity due to endocrinological alteration.
- Swelling and varicose veins in the lower limbs.
- Waist circumference greater than 94 cm in men and 88 cm in women.
- High blood pressure level > 140/90 mmHg.
- Body Mass Index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2.
What Causes Obesity?
Several factors can play a role in gaining and retaining excess weight. These include diet, lack of exercise, environmental factors, and genetics.
- Food and Activity. People gain weight when they eat more calories than they burn through activity. This imbalance is the greatest contributor to weight gain.
- Genetics. Research shows that genetics plays a role in obesity. Genes can directly cause obesity in such disorders as Prader-Willi syndrome.
- Health Conditions and Medications. Some hormone problems may cause overweight and obesity, such as underactive thyroid, Cushing syndrome, and polycystic ovary syndrome. Certain medicines also may cause weight gain, including some corticosteroids, antidepressants, and seizure medicines.
- Stress, Emotional Factors, and Poor Sleep. Some people eat more than usual when they are bored, angry, upset, or stressed.

Treatment and Management of Obesity
The best way to treat obesity is to eat a healthy, reduced-calorie diet, and exercise regularly. To do this you should:
- Eat slowly and avoid situations where you know you could be tempted to overeat
- Eat a balanced, calorie-controlled diet as recommended by your GP or weight loss management health professional
- Take up activities such as fast walking, jogging, swimming, or tennis for 150 to 300 minutes a week
- Join a local weight loss group
You may also benefit from receiving psychological support from a trained healthcare professional to help change the way you think about food and eating. If lifestyle changes alone don’t help you lose weight, a medication called orlistat may be recommended. If taken correctly, this medication works by reducing the amount of fat you absorb during digestion. Your GP will know whether Orlistat is suitable for you.
The drug is used with an individualized low-calorie, low-fat diet, and exercise program to help people lose weight. Orlistat is in a class of medications called lipase inhibitors. It works by preventing some of the fat in foods eaten from being absorbed in the intestines.
In rare cases, weight loss surgery may be recommended.
Strongyloidiasis: Symptoms and Treatment
What is Strongyloidiasis?
Strongyloidiasis is a disease caused by a nematode, or a roundworm, in the genus Strongyloides. Strongyloides stercoralis is one of over 40 species within this genus that may cause disease in birds, reptiles, amphibians, livestock, and other primates. The virus sometimes infects primates, dogs, and cats, and some strains infecting dogs and primates can infect humans as well.

Signs and Symptoms?
- Upper abdominal burning or pain
- Alternating diarrhea and constipation
- Rash
- Diarrhea and vomiting
- Weight loss
- Cough
- Intermittent episodes of constipation
- Red hives near the anus
Severe symptoms may include:
- Hoarseness
- Inflammation of the lungs
- Respiratory failure
- Coughing up blood
It can be severe and life-threatening in persons who:
- Are taking corticosteroids for asthma
- Have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Exacerbations, lupus, and gout
- Have conditions requiring steroids for immunosuppression or symptomatic relief
- Are infected with the virus HTLV-1
- Have leukemia or lymphoma or are transplant recipients.
In case of severe side effects, ensure to seek immediate medical help from the nearest medical facility.
Causes of Strongyloidiasis
It is caused by a nematode, or a roundworm, in the genus Strongyloides. Once they are in your small intestine, they lay their eggs. Adult females can lay up to 40 eggs per day. Either these eggs are passed out in the stool and continue to contaminate the soil, or they remain inside of you and cause autoinfection. When the worms burrow back into your intestines or the skin around your anus, they re-infect you.
The Risk Factors of Strongyloidiasis

This is often found in wet, moist areas, including South America, Africa, and the Southeastern United States. Your risks increase if you travel in those areas for a longer period. This condition is found more often in the following people:
- Living in institutions
- Who are socioeconomically disadvantaged
- Those living in rural areas
- Those working in agriculture
- Contact with contaminated soil
- Walking barefoot
- Contact with sewage or human waste
Diagnosis and Treatment of Strongyloidiasis
Strongyloidiasis can be challenging to diagnose because examining the stool under a microscope does not always show the infection. Doctors may recommend stool tests for five sessions to ensure the diagnosis. It can also sometimes be diagnosed with a blood test and some cases may diagnose by testing fluid from your lungs or small intestine.
Treatment is recommended for all persons found to be infected, whether symptomatic or not, due to the risk of developing hyperinfection syndrome. Additionally, it is suggested that patients be considered for testing before being initiated on any immunosuppressive therapy, particularly corticosteroids.
A sputum or stool culture should be negative for 2 weeks for people with a weakened immune system or hyperinfection syndrome. In some cases, antibiotics are required to treat bacterial infections as well.
How Fast Do Symptoms After Exposure?
Most people do not know when their exposure happened. For those who do, a local rash can occur immediately. Coughing usually occurs several days later and the abdominal symptoms typically occur approximately 2 weeks later, and larvae can be found in the stool about 3 to 4 weeks later.
How to Prevent Strongyloidiasis?
In countries where sanitation and human waste disposal have improved, strongyloidiasis has been mostly eliminated. Additional strategies to prevent strongyloidiasis include the following:
- Wearing shoes when you walk on the soil
- Cleaning up after dogs
- Managing sewage and feces properly
- Avoiding contact with sewage and feces
Medication Used for Strongyloidiasis
Ivermectin is a recommended treatment for this condition. It is a disease caused by a roundworm. This drug is effective in treating this kind of condition. It works by paralyzing and inactivating the gut of parasites in humans. It stops the adult one from producing larvae. It kills the newly developed parasite and works to treat the infection.
What are the Side Effects of Ivermectin?
- Abdominal Pain
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Rashes
- A headache
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Coughing
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Weakness
Inform your doctor right away if you experience this symptom. If you develop other side effects it’s better to visit your doctor. Seek medical attention.
Epilepsy: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a chronic disease of the brain that affects around 50 million people worldwide. It is characterized by recurrent seizures, which are brief episodes of involuntary movement that may involve a part of the part or the entire body. It is sometimes accompanied by loss of consciousness and control of bowel or bladder function.
Types of Epilepsy
1. Generalized
It usually starts during childhood. However, it can also affect adults. This affects both the left and right sides of the brain. Additionally, these may be either motor, which involves physical movement, or non-motor, which does not. Symptoms involve:

- Jerking movements
- Weakness or limp limbs
- Muscle twitching
- A rigid and tense muscle
- Full-body epileptic spasms
These may include these symptoms:
- A sudden stop in movement
- Staring into space
- Fluttering eyelids
- Brief twitches
2. Focal epilepsy
This can feel like an uneasy feeling in the stomach, similar to the feeling of riding a rollercoaster. They can start in one area and move to others. As the seizure progresses, a person can experience motor and non-motor symptoms such as:
- Spasms
- Jerking
- Muscle twitching
- Repeated movements, like clapping or chewing
Some non-motor symptoms of focal seizures include:
- Waves of hot or cold
- Lack of movement
- Changes in emotions and thoughts
- Goosebumps
3. Combined generalized and focal
Someone with combination epilepsy has both generalized and focal seizures. The symptoms described above can therefore be mixed together.
4. Unknown epilepsy
Symptoms of non-motor and motor epilepsy can be present in people with this type. Motor seizures often present as tonic-clonic. These can have the following symptoms:
- Rapid, convulsing, and rhythmic jerking
- Loss of consciousness and stiffening
- Bluish face from lack of oxygen
- Loss of bowel and bladder control
Non-motor symptoms include:
- Vacant starring
- Stillness
- Sudden and stopped movement
Signs and Symptoms?
Patients tend to have the same type of seizure each time, so the symptoms will be similar.
- Temporary confusion
- Stiff muscles
- Uncontrollable jerking movements of the legs and arms
- Loss of consciousness or awareness
- Psychological symptoms such as fear, anxiety, or déjà vu
Causes of Epilepsy
The causes may vary for each person, and some people have no identifiable cause. Some cases are linked directly to genetics, trauma, autoimmune disorders, metabolic abnormalities, or infectious diseases. Causes include:
- Genetic causes. Some types run in families passed down from one generation to the next. Occasionally, it can occur due to genetic changes that were inherited and are occurring for the first time.
- Metabolic causes. Your body processes the food you eat with enzymes. A problem with one of these enzymes can make your body unable to break down food or produce energy.
- Infections. Infection is probably the most common cause worldwide. Attacks that occur as a result of an infection in the brain are considered infectious epilepsy.
- Autoimmune epilepsy. Your body’s immune system protects you from foreign substances and other things that could harm it. It is caused by a change in your body’s immune function.
- Structural causes. Certain abnormal structures in the brain can increase the risk of seizures. This might be something you are born with or develop later in life. Most structural causes can be seen in imaging of the brain with an MRI.

Diagnosis and Treatment of Epilepsy
To diagnose your condition, your doctor will review your symptoms and medical history. Your evaluation may include:
- A neurological exam. To diagnose your condition and determine its type, your doctor may assess your behavior, motor abilities, mental function, and other attributes.
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan. An MRI can reveal abnormalities in the structure of your brain, such as tumors, bleeding, or cysts, that may be causing your seizures.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Your doctor may detect lesions or abnormalities in your brain that could be causing your seizures.
- Blood tests. An infection, genetic condition, or other condition that triggers the condition may be detected through a blood sample taken by your doctor.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG). This is the most common test used to diagnose epilepsy. The electrodes record the electrical activity of your brain.
Treatment or Medication for Epilepsy
Doctors may recommend you take one anti-seizure medication to decrease the frequency and intensity of their attacks by taking a combination of medications. Gabapentin is very effective in treating and managing the condition. It reduces abnormal excitement in the brain and relieves pain by changing the way the body senses discomfort.
What Age Does Prostate Enlargement Start?
The prostate is a small gland in men that produces semen. It is located below the bladder in front of the rectum, and it wraps around the tube that carries urine and semen out of the body. The prostate tends to grow larger as you get older. But, if your prostate gets too large, it can cause several health issues including prostate enlargement.

Symptoms of Prostate Problems
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Blood in urine or semen
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Painful ejaculation request urge to urinate at night
- Frequent pain or stiffness in the lower back
- Pain or stiffness in the hips, rectal, or pelvic area
- Dribbling of urine
Less common signs and symptoms include:
- Urinary tract infection
- Inability to urinate
- Blood in the urine
Age When Prostate Enlargement Start
Prostate growth is a normal part of aging. At the age of 25, the adult prostate begins to enlarge slowly. The condition is called benign prostatic hyperplasia, but it has nothing to do with cancer. Around the age of 50, many men begin to have uncomfortable symptoms as a result of prostate enlargement.
The signs and symptoms of prostate enlargelemt are accompanied by frequent urination at night or often difficulty getting a strong stream started or emptying the bladder. This happened because the prostate gland surrounds the tube that carries urine from the bladder and out through the penis. As the prostate grows, it compresses that tube, and that makes urination tough.
Can Men in Their 20’s Develop an Enlarged Prostate?
Studies show that men can develop microscopic signs of benign prostatic hyperplasia as early as in their 20s and 30s. In contrast, BPH or enlarged prostate is very rare in men in their 20s. Typically, urinary symptoms in men during their 20s are caused by other problems. Prostate enlargement may cause symptoms but it’s usually from infection rather than from growth.
The prevalence of symptomatic BPH is low in men aged 30-39, but there are a significant number of men starting to exhibit symptoms of an enlarged prostate at this age. In most cases, symptoms are mild, but they can also be moderate or severe enough to require treatment.

Risk Factors
Most men have continued prostate growth throughout life. Prostate enlargement can cause urinary symptoms or substantially block urine flow in many men as a result of this continued growth. Risk factors for prostate gland enlargement include:
- Aging. In men younger than 40, prostate gland enlargement rarely causes symptoms. About one-third of men experience moderate to severe symptoms by age 60, and about half do so by age 80.
- Family history. Prostate problems are more likely to affect you if you have a blood relative with prostate issues, such as your father or brother.
- Diabetes and heart disease. BPH is associated with diabetes, heart disease, and beta blockers.
Medications for Enlarged Prostate
Dutasteride is a recommended medication for prostate enlargement. This is used to treat a disorder known as benign prostatic hyperplasia found in men. It inhibits and lowers the amount of the hormone that causes prostate growth. Discuss with your doctor the benefits and risks of taking this medication to ensure a successful treatment.
Other Recommended Prescriptions for Enlarged Prostate
- Alpha-blockers. These medications relax the bladder neck muscles and muscle fibers in the prostate, making urination easier.
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. These medications shrink your prostate by preventing hormonal changes that cause prostate growth
- Combination drug therapy. Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors may be prescribed together if either medication alone is ineffective.
- Tadalafil. Prostate enlargement may also be treated with this medication, which is commonly used to treat erectile dysfunction.

Lifestyle and Home Remedies to Manage Enlarged Prostate
- Limit beverages to avoid middle-of-the-night trips to the toilet.
- Pee when you first feel the urge. Waiting too long might overstretch the bladder muscle and cause damage.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol as they can increase urine production, irritate the bladder and worsen symptoms.
- Stay active. Inactivity contributes to urine retention. Even a small amount of exercise can help reduce urinary problems caused by an enlarged prostate.
- Keep warm because colder temperatures can cause urine retention.
Medication for ADHD
Medications play a vital role in managing and treating ADHD. Doctors will work together to figure out which medication works for you along with the proper schedule and dosage. ADHD treatment requires a combination of medication, therapy, behavior changes, and skills training.
The Most Popular ADHD Medications
Choosing the best ADHD medication for you or your child, or deciding whether to medicate at all, is an incredibly personal decision. The ADHD medications prescribed to both children and adults are broadly categorized as follows:
- Stimulants. These are the first-line treatment for ADHD which includes amphetamine and methylphenidate, the most widely used treatment for ADHD, and their derivatives.
- Non stimulants. These are given to patients who don’t respond to stimulants. Non-stimulant medications include atomoxetine, guanfacine, and clonidine. Non-stimulants may also be prescribed for use alongside stimulants to treat symptoms that the latter does not alleviate.
Antidepressants are also used but the FDA has not specifically approved antidepressants for the treatment of hyperactivity disorder. However, healthcare providers sometimes prescribe them alone or in combination with a stimulant. The antidepressants providers typically prescribe for ADHD work on the dopamine and norepinephrine levels in your brain.

Other popular prescriptions are:
- Adderall XR (amphetamine)
- Concerta (methylphenidate)
- Dexedrine (amphetamine)
- Evekeo (amphetamine)
- Focalin XR (dexmethylphenidate)
- Quillivant XR (methylphenidate)
- Ritalin (methylphenidate)
- Strattera (atomoxetine hydrochloride)
- Vyvanse (lisdexamfetamine dimesylate)
How Do Medications Work for ADHD?
Prescriptions work in various ways depending on the type and severity of your condition. However, all medications regardless of the category increase the levels of important chemicals in your brain and improve the symptoms of ADHD, including increasing attention span and reducing hyperactivity. Both stimulants and non-stimulant drug also controls impulsive behavior and manage other executive dysfunction.

What are the Typical Side Effects of ADHD Prescriptions?
- Reduced appetite
- Stomach pain
- Headaches
- Sleep disturbances
Some side effects associated with non-stimulants include:
- Excessive tiredness
- Stomach pain
- Nausea and dizziness
- Reduced appetite
How Do Stimulant Medications Treat ADHD?
ADHD is a neurological disorder, resulting from the deficiency of neurotransmitters in specific areas of the brain. Stimulant medications used to treat ADHD stimulate specific cells within the brain to produce more of this deficient neurotransmitter.

Who Should Not Take a Stimulant Drug?
Younger patients under the age of 12 and pregnant patients should avoid using stimulants. Patients who are susceptible to stimulants should either avoid using or minimize their dose depending on doctors’ recommendations. Stimulants are also not permissible to patients who have:
- Underlying heart problems
- Glaucoma
- Severe anxiety, nervousness, and agitation
- Tourette’s syndrome
- A history of psychosis or are psychotic
How Do Nonstimulants Work to Treat ADHD?
Non stimulant is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor that works by increasing concentrations of norepinephrine and dopamine in the prefrontal cortex. It regulates behavior and thus helps with ADHD symptoms.
An example drug for this condition is Atomoxetine. It is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). It works by causing a selective inhibition of the pre-synaptic norepinephrine transporter. The dose of this prescription should be reduced in patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction.
The recommended starting dosage of Atomoxetine should be initiated at a total daily dose of 0.5 mg/kg and increased after a minimum of 3 days. It should be administered either as a single daily dose in the morning or as evenly divided doses in the morning and late afternoon or early evening. Seek immediate help in cases of unexpected side effects.
How is ADHD Medication Dosed?
- Dosage form or route of administration. Each unit of liquid medication is stated on the patient information sheet inside the medication’s box or packaging.
- Dose quantity and Strength. Over a given period, a specific amount of medication is released into the blood. This includes the number value for each product represents the total amount of the medication in the tablet, liquid, or patch.
- The release mechanism or duration of Administration. An indication of how long a medication will remain active and available. The release of medication from stimulants can occur over a time frame as short as an hour, as long as four hours, or as long as eight or twelve hours.
Vegetarian Diet Can Lower Your Risk of Heart Disease
According to a meta-analysis published in the American Journal of Preventive Cardiology, vegetarians reduce the risk of death from ischemic heart disease. Vegetarian diets, including vegan eating patterns, were associated with a 30% reduced risk of death from ischemic heart disease compared to non-vegetarian diets.

How Does Vegetarianism Protect the Heart?
A plant-based diet is more healthful for the heart than a meat-heavy one. Vegetables are rich in fiber and phytonutrients, which reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. Fiber fights high cholesterol. The vegetarian diet is high in fiber from fruits, vegetables, beans, and grains, which is suitable for managing cholesterol.
Vegetables have fewer calories for a healthy weight and are extra antioxidants. A vegetarian diet eliminates fats from animal products and replaces them with high-fiber foods, which fill you up more so you eat less, lowering your risk of obesity. Eating more fruits and vegetables means you are getting more of the nutrients, like antioxidants, that protect against heart disease.
Vegetables that Reduce Your Risk of Heart Disease
- Kale. The trendy superfood contains essential heart-healthy nutrients which improve blood flow.
- Spinach. A serving of spinach contains more potassium that, helps ease stress on the blood-vessel walls and it helps the body remove excess sodium
- Swiss chard. Just one serving of the vegetable contains more than three times your daily value of vitamin K, an essential nutrient for brain, bone, and heart health.
- Broccoli. This vegetable has antioxidant effects that reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Brussels sprouts. Folate is an essential nutrient for healthy cell growth and plays an active role in heart health.
- Collard greens. Collard greens have magnesium that helps lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension. It helps blood vessels relax, increasing blood flow through the body and easing pressure on the heart.
- Green Beans. The little pod within the green beans is a starchy legume full of fiber and folate, which have many benefits for heart health. It fights inflammation and may help prevent hypertension through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.

Medications for the Types of Heart Disease
Aside from healthy eating, taking your medications for hypertension, cholesterol, and heart health is also essential in managing heart disease. Take your maintenance pills to ensure healthy and improved heart health. The typical prescription drugs for heart and blood pressure-related conditions are:
Foods To Eat And Avoid With Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is an impairment in how the body regulates and uses sugar as a fuel. It is a chronic condition that results in too much sugar circulating in the bloodstream. Eventually, high blood sugar levels can lead to circulatory, nervous, and immune disorders.
Facts You Should Know About Type 2 Diabetes
- The vast majority of people with diabetes have Type 2 diabetes.
- Diabetes is a leading cause of death in the world. Type 2 diabetes is preventable through proper diet and exercise.
- Diabetes is the leading cause of blindness, kidney failure, amputation, and other conditions.
- Type 2 diabetes is more common in older adults, but the increase in children with obesity has led to more cases of type 2 diabetes in younger people.
Foods to Eat With Type 2 Diabetes
Here are some examples of nutritious foods that your diet should include:

- Fruits such as oranges, berries, apples, peaches, and pears.
- Whole grains include quinoa, faro, brown rice, and sugar-free oats.
- Vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, zucchini, cucumber, and cauliflower.
- Lentils, chickpeas, and beans
- Nuts and seeds such as almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and pumpkin seeds
- Protein-rich foods such as seafood, lean cuts of red meat, and tofu
- Heart-healthy fats such as olive oil, avocados, canola oil, sesame oil
- Beverages such as water, black coffee, unsweetened tea, and vegetable juice
Foods to Avoid With Type 2 Diabetes
- High-fat meat
- Full-fat dairy
- Sweeteners such as brown sugar and honey
- Sugar-sweetened beverages
- Desserts, ice cream, candies, cookies, and baked goods
- Processed foods such as chips, convenience meals, and processed meat
- Trans fats such as vegetable shortening, fried foods, and hydrogenated oils
The Worst Drinks for Type 2 Diabetes
- Regular soda. Soda takes the top spot on the list of drinks to avoid, as one can of soda already contains 40 grams of sugar and 150 calories.
- Energy drinks. Energy drinks can be high in caffeine and carbohydrates, which can cause a spike in blood sugar.
- Sweetened or unsweetened fruit juices. Bottled or canned fruit juices can add a high amount of carbohydrates to your diet and are pure sugar. This combination can wreak havoc on your blood sugar and increase your risk for weight gain.
Best Exercises If You Have Diabetes
- Walking
- Dancing
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Aerobic dance
- Weightlifting
- Pilates
- Calisthenics
- Strength training
- Yoga
Medication for Type 2 Diabetes
Aside from a healthy diet and exercise, you can also manage type 2 diabetes through recommended medications. The goal of the treatment is to maintain healthy blood sugar and reduce the effects of its symptoms. Monitoring your blood sugar and taking Metformin to utilize glucose and enhance insulin-mediated glucose disposal in muscle and fat.
Spasticity
What is Spasticity?
Spasticity refers to an abnormal increase in muscle tone or stiffness that interferes with movement, and speech, or may be painful or uncomfortable. It is usually caused by nerve damage within the brain or spinal cord that controls muscle movement that causes spasms.
What Are the Symptoms of Spasticity?
- Overactive reflexes
- Increased muscle tone
- Involuntary movements such as contractions and spasms
- Pain
- Abnormal posture
- Decreased functional abilities
- Permanent contraction of the muscle and
- Bone and joint deformities
Causes of Spasticity
Generally, spasticity is caused by damage or disruption to areas of the brain and spinal cord responsible for controlling muscle and stretch reflexes. An imbalance in inhibitory and excitatory signals, which causes the muscles to lock in place, can cause these disruptions. Spasticity can be harmful to growing children as it can affect muscles and joints. Different degrees of spasticity can be experienced by people with brain injury, spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, or multiple sclerosis.
Nonsurgical Treatments for Spasticity
- Speech therapy. Speech therapy can help you with speech, communication, and swallowing if you have spasticity in your mouth, face, or throat muscles.
- Casting or bracing. To improve range of motion and facilitate function, you can use casts or braces to stretch spastic muscles.
- Physical therapy. A physical therapist generally focuses on lower extremity stretching and strengthening exercises and mobility training.
- Occupational therapy. Most occupational therapists focus on stretching, strengthening, and training the upper extremities for daily activities such as bathing, grooming, and cooking.
- Assistive devices. A person with spasticity can benefit from a variety of assistive devices that can make everyday tasks easier and more efficient.
Spasticity Treatment
It is important to treat spasticity to improve comfort, mobility, and independence. Our treatment goals include relaxing the muscles as much as possible, relieving pain and stiffness, promoting optimal long muscle growth, and improving ambulation and independence for them.
Medications may be used individually or in combination. Tizanidine is a medication that reduces rigidity, upper motor neuron spasticity, and hyperreflexia. It inhibits polysynaptic reflexes and reduces muscle tone and frequency of muscle spasms. Buy Tizanidine here for spasticity treatment.
Soft Tissue Injuries
What are Soft-tissue Injuries?
Soft tissue injuries involve the muscles, tendons, or ligaments of various areas of the body. Several activities can cause soft-tissue damage and as a result, there may be pain, swelling, bruising, or damage.
Common Symptoms of Soft Tissue Injuries
- Bursitis or inflammation due to repeated stress
- Contusion
- Muscle Sprains or an injury to a ligament or joint capsule from overstretching
- Muscle Strains due to traumatic stretching or tear to a muscle or tendon
- Inflammation or irritation of a tendon
How Soft Tissue Injuries Occur
All soft tissue injuries vary in terms of severity that falls into the following category:
- Grade 1 or Mild. Resulting in tenderness and swelling, these soft tissue injuries are caused by overstretching of the body’s fibers.
- Grade 2 or Moderate. There is often tearing of the soft tissues of the joints, resulting in a feeling of looseness and tenderness as well as pain, swelling,, and swelling in the joint. As a result, pressure or body weight cannot be applied to the injured joint, and the individual needs to stay off it for at least a few weeks.
- Grade 3 or Severe. There is a significant recovery time required for these injuries due to the complete tears of the soft tissues. Following an injury, people are often unable to use the joint or muscle area at all. Symptoms of severe soft tissue injuries include swelling, pain, and instability.
Treatment for Soft Tissue Injuries
Nabumetone is a medication that is used to treat symptoms of soft tissue injury. It is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Take the recommended dose of this medication per day as per directed by your doctor.

Prevention
Conditioning and training can prevent many soft-tissue injuries. Other prevention tips include:
- Warm-up. Warm up to prepare for exercise, even before stretching. A warm-up increases your heart rate and blood flow and loosens up your muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints.
- Drink water. Drink 1 pint of water 15 minutes before you start exercising and another pint after you cool down. Have a drink of water every 20 minutes or so while you exercise.
- Use proper equipment. Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothes that let you move freely and are light enough to release body heat.
- Aim for balanced fitness. Develop a balanced fitness program that incorporates cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and flexibility. Add activities and new exercises cautiously.
- Cool down. Before you completely stop, slow down your motions and lessen the intensity of your movements for at least 10 minutes. This phase of a safe exercise program should conclude when your skin is dry and you have cooled down.
- Stretch. Begin stretches slowly and carefully until reaching a point of muscle tension. Stretching should never result in pain, and you should never bounce on a fully stretched muscle.
- Rest. Schedule regular days off from vigorous exercise and rest when tired. Fatigue and pain are good reasons not to exercise.
Menopause
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of your menstrual cycles. It is diagnosed after you have gone 12 months without a menstrual period.
What are the First Signs of Menopause?
- Hot flashes and night sweats. Hot flashes can make you feel warm or hot suddenly for no apparent reason. Your skin may turn red and may also cause a rapid heartbeat. These can be so intense they wake you up.
- Trouble in sleeping. Waking up during the night or having trouble going to sleep can happen for lots of reasons and it may be a sign you are approaching menopause.
- You feel moody. Moodiness around the menopausal period is due to the change in hormones. If you have had anxiety or depression in the past, your symptoms may worsen during menopause.
- Forgetfulness. Forgetfulness can stem from not only menopause but also from stress. If you’re worried that you are forgetting too much, let your doctor know.
- Less interested in sex. Some women say they are less interested in sex or have trouble getting aroused when they are in menopause. It is due to the skin around your vagina may become drier. This can make sex hurt.
- Some physical changes. You may also notice your hair and skin become drier and thinner. Some women gain weight during menopause. There is also the possibility that your body will become more fat around the waist and less muscle overall as well.
What are the 3 Stages of Menopause?
- Perimenopause. It is the time leading up to menopause. During this time, hormone levels begin to decline and menstrual cycles become erratic and irregular. Hot flashes and dry vaginal skin are common menopause side effects.
- Menopause. A woman who hasn’t had a period for 12 months in a row has stopped producing the hormones that cause her menstrual cycle. Once this has occurred, you enter postmenopause.
- Postmenopause. It is the time after menopause has occurred. Postmenopause is your lifelong state once it occurs. Heart disease and osteoporosis are among the health conditions associated with postmenopause.
What is the Average Age of Menopause?
Menopause can happen in your 40s or 50s, but the average age is 51 in the United States. Signs and symptoms, including changes in menstruation, can vary among women. Keep up with regular visits with your doctor for preventive health care and any medical concerns.
Treatment for Menopause
Menopause has NO TREATMENT. However, some medications help in relieving your signs and symptoms and preventing or managing chronic conditions that may occur with aging. Estradiol Valerate is a treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. It is largely responsible for the development and maintenance of the female reproductive system.
Interesting Facts About Mosquitoes
Mosquito season usually starts in the spring when temperatures outside reach 50 degrees Fahrenheit. Mosquito season can last throughout summer and fall. Mosquitoes emerge from hibernation where there is a warm spring following a cold winter. After mating, almost all females begin looking for blood to produce more eggs, even though their life cycles, habitats, and tolerance to cold vary.
Facts About Mosquitoes

- Only female mosquitoes bite. Male mosquitoes make do just fine with plants, but females need a blood meal before they can lay eggs.
- Flood-prone soil or shallow water are ideal places for females to lay their eggs.
- Around 250 million people are infected with malaria each year, mostly children in Africa, and approximately one million die from it.
- There are over 3,000 different species of mosquitoes throughout the world.
- It is estimated that mosquitoes live less than 2 months.
- A mosquito doesn’t have teeth. It uses its serrated proboscis to pierce the skin and locate capillaries.
- The bumps from bites are caused by saliva. The proboscis has two tubes. One draws blood and the other pumps saliva. The saliva usually causes minor allergic reactions, causing swelling and itching around the bite site.
- Mosquitoes are drawn to humans by their breath. Their receptors can detect carbon dioxide released when we exhale.
- Female mosquitoes can lay up to 300 eggs at a time and will lay eggs up to three times before they die.
- Mosquitos can hibernate and may live up to six months.
Medications for Mosquito Bites
- Apply a lotion, cream, or paste. Nonprescription hydrocortisone cream can ease the itching caused by bites. You can also dab the bite with a paste made from baking soda and water.
- Use a cool, moist cloth or cold pack to soothe the bite for a few minutes.
- Take an oral antihistamine. For stronger reactions, try taking a nonprescription antihistamine.
Natural Home Remedies for Mosquito Bites

- Oatmeal can help relieve itching and swelling due to its compound that contains an anti-irritant.
- Crushed ice is also ne of the home remedies for mosquito bites. The cold also numbs the skin, which can give you immediate but short-term relief.
- Aloe vera gel has been shown to reduce pain from burns and help them heal faster.
- Onions may reduce the bite’s sting and irritation. Onions also have natural antifungal and antibacterial properties.
- Peppermint oil can also relieve itching.
- Applying honey to a bite may help reduce inflammation and prevent infection.
Importance of Immunization
Immunization is a process by which a person becomes protected against a disease through vaccination. Protection by immunization is similar to the immunity a person would get from disease, however, instead of getting the disease you get a vaccine to build your immunity.
Why is Immunization Important?
Vaccinations not only protect your child from deadly diseases, such as polio, tetanus, and diphtheria, but they also keep other children safe by eliminating or greatly decreasing dangerous diseases that used to spread from child to child. Infectious diseases can be prevented by immunization for yourself, your children, and future generations. Immunization helps wipe out diseases that could spread now and into the future.
How Many Shots Do Children Need?
- Children at the age of 2 must have the following immunization shots:
- One vaccination for measles, mumps, and rubella
- Three vaccinations for hepatitis B
- One vaccination for varicella or chicken pox (must be verified by doctors)
- Three vaccinations for rotavirus
- Four vaccinations for pneumococcal disease
- Four vaccinations for Haemophilus influenza
- Three to four polio vaccinations
- Four vaccinations for diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis
Five Important Reasons to Vaccinate Your Child
- Immunizations can save your child’s life. More diseases can now be prevented thanks to advances in medical science. Diseases that once caused thousands of children to suffer injuries or deaths have been completely eradicated, while others are on the verge of extinction.
- Immunization protects others you care about. Children are safer when they are fully immunized, so make sure you and your children are fully immunized. You and your family will be protected, and your friends and family will be protected as well.
- Immunizations can save time and money. Some vaccine-preventable diseases can save you from prolonged disabilities and prevent from taking a toll on your finances because of lost time at work, medical bills, or long-term disability care. In contrast, getting vaccinated against these diseases is a good investment and usually covered by insurance.
- Vaccination is very safe and effective. Science, doctors, and healthcare professionals carefully review vaccines before giving them to children. Injections may cause some discomfort and may cause some pain, redness, or tenderness at the injection site, but this is minimal compared to the pain, discomfort, and trauma caused by diseases these vaccines prevent.
- Immunization protects future generations. Vaccines have significantly reduced and, in some cases, eliminated many diseases that killed or severely disabled people just a few generations ago. As a result of vaccination, this virus has dramatically decreased, and there are no longer birth defects associated with it in the United States.
Final Tips on Immunizations
- Discuss the benefits and side effects with your doctor. You can also ask your doctor about the possible side effects that may occur after immunization.
- Ask your doctor’s office if it participates in an immunization registry for references in case of lost records.
- Be informed on the dates of immunization to avoid missed shots.
- Always bring your immunization record to keep updated.
The Benefits of Breastfeeding for Both Mother and Baby
Breastfeeding has health benefits for both the mother and baby. The nutrition and growth that breast milk provides to a baby are ideal for the development of the baby. The benefits of breastfeeding include protecting the baby and mother against certain illnesses.
Foods to Eat While Breastfeeding
Make healthy choices to fuel your milk production. Choose protein-rich foods, such as lean meat, eggs, dairy, beans, lentils, and seafood with low mercury levels. Fruits and vegetables, along with whole grains, should be included in your diet.
Breast milk will taste different if you eat a variety of foods while breastfeeding. As a result, your baby will be exposed to different tastes, which will make it easier for them to accept solid foods in the future.
You might need to continue taking a daily multivitamin and mineral supplement until your baby is weaned to ensure you and your baby are getting all the vitamins you need.

Benefits of Breastfeeding for the Mother
- Reducing her breast cancer risk.
- Reducing her ovarian cancer risk.
- Reducing her risk of developing osteoporosis.
- Burning calories and using mom’s fat stores for her breast milk.
- Producing oxytocin, which helps contract the uterus back to its pre-pregnancy size.
- Saving money, since breastfeeding is free.
- Lowering her chance of developing postpartum depression, since breastfeeding allows pregnancy hormones to reduce slowly, instead of abruptly.
Benefits of Breastfeeding for the Baby
Breast milk contains live immunity. When a baby consumes breast milk, they receive both immediate and lifelong immunities. Breast milk provides the specific nutrients that meet your baby’s needs.
Here are other benefits of breastfeeding:
- Can reduce your baby’s risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
- Can reduce your baby’s risk of developing middle ear infections, allergies, and diabetes, since breast milk contains no artificial sugar.
- Allows babies to feel close to the home base that they’ve known while in the womb. Hearing your heartbeat and feeling your warm skin will help her transition from the inner world to the outer world.
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a polyunsaturated fatty acid found in breast milk, helps support proper brain development.
How Breastfeeding Can Be Challenging
The process of breastfeeding isn’t always easy. The process of learning this skill may take some time for new moms and babies. Breastfeeding is a new concept for many women of childbearing age, either because their mothers didn’t do it, or because other women in their lives didn’t do it either. There will be times when difficulties arise. After delivery, you’ll be exhausted and sore, and your baby will likely want to eat several times a night in the middle of the night for the first few weeks. The belly of your baby is about the size of a nickel.
The first couple of weeks is a time when the baby requires small, frequent feedings. Breastfed babies typically eat eight to twelve times in 24 hours. Lactation consultants can help you determine whether or not your baby is getting enough milk. Your milk production may seem inadequate at first, but it will increase.
Another time breastfeeding can be challenging is when your baby is not latching properly. A good latch means better milk transfer and less pain and discomfort for you. If you’re still experiencing nipple pain for more than two minutes into a feeding after two weeks of feeding, contact a board-certified lactation consultant for help.
What Is The Main Cause Of High Triglycerides?
The most common causes of high triglycerides relate to diet and metabolism. Also, excess body weight and a high-fat, high-carb diet, several health conditions may contribute.
If you’ve been diagnosed with high triglycerides, you may be looking for ways to make your diet and exercise routines healthier, but some other culprits should also be on your radar.
What Are High Triglycerides?
Triglycerides are a kind of fat that is found in the blood. Cholesterol is another kind. Stored in fat cells for later use, triglycerides are a major energy source. Normal amounts are important for good health. Eating more fat than the body burns can lead to high triglyceride levels.
High triglyceride levels may result in the hardening of the arteries, which increases the risks of heart attack, stroke, and heart disease. They can be part of metabolic syndrome, which also includes too much fat around the waist, high blood sugar, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
Sometimes high triglyceride levels mean poorly controlled type 2 diabetes, liver or kidney disease, low thyroid hormone levels, or rare genetic conditions.

What Are the Causes and Symptoms of High Triglycerides?
Causes of High Triglycerides may include:
- Obesity
- Eating too much unhealthy food
- Genetics
Certain illnesses include:
- Poorly controlled diabetes
- Kidney disease
- Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
Some drugs such as:
- Steroids
- Birth control pills
Drinking a lot of alcohol can also increase the levels of triglycerides.
Most people with High Triglycerides have no symptoms. Very high levels of Triglycerides can cause small fat deposits under the skin and painful inflammation of the pancreas called pancreatitis.

Managing High Triglycerides
Dos
- Exercise regularly.
- Eat fish.
- Stop smoking.
- Eat more fruits and vegetables and high-fiber foods.
- Lose weight by changing your diet and doing aerobic exercise, such as jogging, walking, bicycling, or swimming. Exercise at least 30 minutes daily.
Don’ts
- Don’t drink more than two alcoholic drinks each day.
- Don’t forget to treat other medical conditions such as diabetes and an underactive thyroid.
- Don’t change your diet or medicines without your doctor’s approval.
How Are High Triglycerides Treated?
High triglycerides, like high cholesterol, are a potentially serious health problem. But, with lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medications, most people will be able to successfully manage their condition and reduce their cardiovascular disease risk.
If diet, exercise, and other lifestyle changes are not enough to lower your triglycerides or your doctor feels your numbers are too high to address the problem with lifestyle interventions alone, they may recommend medication.
- Gemfibrozil – this medication is in a class of lipid-regulating medications called fibrates. The drug works by reducing the production of triglycerides in the liver. As a result, it lowers your levels of triglycerides.
How Can I Increase My Eyelash Hair?
If you want to increase your eyelash hair, there are several treatments you can use. Eyelash hair is known to protect the eyes from light debris. They are also like sensors that warn your eyes of potential danger when objects come close. Just like the hair on your head, eyelash hair naturally falls out and replaces itself in a natural cycle. It is normal to lose between one and five eyelashes each day. Most of the time, some shedding and thinning is completely natural and nothing to worry about.

Causes of Eyelash Hair Loss
These are the most common culprits:
- Excessive rubbing and friction
- Bacterial infection especially from expired makeup
- Allergic reactions
- False lashes
When to See a Specialist?
If you have ruled out the lists above and the problem persists, it may be time to see a specialist to look into underlying conditions. It is more concerning if lashes fall out on both lids, which could indicate a more systemic problem. Seek immediate help if you notice accompanying hair loss on the eyebrows and the scalp, or you also have skin changes such as itching, redness, or scaling, this may be a sign of a health problem or condition such as:
- Thyroid Disorders
- Blepharitis
- Trichotillomania
- Alopecia Areata
- Certain Cancers
Proven Way to Increase Your Eyelash Hair
Grooming Your Eyelash Hair
Proper eyelash hair maintenance can improve the health of your eyelashes which makes it less likely for them to break. This can make them appear longer and thicker. Some eyelash hair grooming tips include:
- Removing eye makeup at the end of each day
- Regularly brushing your eyelashes with an eyelash brush
- Washing your face and eyes with gentle soap daily
Medication
- Bimatoprost is the only medication approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that makes eyelashes grow longer and thicker. Your doctor can prescribe this medication, which you apply regularly to the lash line of the upper eyelid. It delivers full results when used daily for at least two months. Once you begin using Bimatoprost, you must continue using it regularly to maintain the results.
How To Prevent Eyelash Hair Loss?
- Remove makeup gently as rubbing or tugging your eyelash hair can make them fall out.
- Use new mascara because you might be allergic to your brand and not know it.
- Ditch your eyelash hair curler. It can cause eyelash hair to come out, especially if you tug or use them while wearing mascara.
- It is recommended to take off makeup before bed. Eyelashes coated with mascara are more brittle and prone to breakage.
- Remove carefully any false eyelashes and extensions. These products adhere to your natural lashes with medical-grade glue. Removing the glue can take your lashes out along with it. Make sure to use a gentle, oil-based cleanser.
What Are Signs Of Acute Pain?
There are several signs associated with acute pain since the term itself is quite vague and broad. Conversely, if you’re experiencing acute pain, it’s important to take some time off to rest and receive sufficient treatment. After all, the only way to get back on track as soon as possible is to fully heal. Failing to receive proper care can only lead to complications and even more time off the field to do the things you want to get done.
What Is Acute Pain?
Acute pain is a sensation you feel as soon as you experience an injury. For instance, if you slice open a finger while chopping vegetables, break a bone, or fall down the stairs, you are going to feel acute pain. It’s a signal from your body that it has just undergone physical trauma. Commonly, the pain stops once the injury heals.

Signs of Acute Pain
Acute pain tends to be of relatively short duration. The most common signs of acute pain may include:
- Weakness
- Numbness
- Sharp pain
- Tingling
- Throbbing
- Stabbing pain
- Burning
Common Causes of Acute Pain
Besides blunt trauma examples, a person could also suffer from acute pain because of any of the following reasons:
- Sprains and strains of a body part
- Going to the dentist
- Giving birth
- Infections on a cut
- Getting burned
- Slipping and falling
- Menstrual cramps
- Passing a kidney stone
- Bumping a body part against a hard surface
The range of pain can vary significantly depending on what’s causing it or the severity of the injury.
Effects of Acute Pain
The effects of acute pain extend far beyond an injured body part. Debilitating pain will affect other areas of a person’s life as well. People suffering from severe pain often find it difficult to sleep or lose their appetite because of it. In a worst-case scenario, it may lead to depression or addiction to pain medication, depending on where the pain is located.

Acute Pain Treatment
Every person’s pain is unique, just as every person’s life is unique. It is also important to provide them with the right pain management treatments and medications. People differ in their pain treatment to ensure that they receive effective treatment based on their unique characteristics.
Initial treatment may include some of the following:
- Opioid medications
- Muscle relaxant medications
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Stress reduction
- Resting the affected part of the body
- Application of heat or ice
- Physical therapy
- Exercise
- Bioelectric therapy
A secondary tier of treatments may include
- Antidepressant medications
- Anticonvulsants
- Steroid injections to reduce tissue inflammation
- Acupuncture
- Nerve blocks
- Trigger point injections to treat muscle spasms
Recommended medication:
- Tramadol – this drug is a narcotic-like pain reliever that is effective in managing acute and chronic pain.
Can Streptococcus Pneumoniae Be Cured?
Doctors usually recommend antibiotics to cure Streptococcus Pneumoniae. Antibiotic treatment for serious infections typically includes broad-spectrum antibiotics until results of antibiotic sensitivity testing are available.
What is Streptococcus Pneumoniae?
Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) is the bacteria responsible for pneumococcal disease. When someone with this disease coughs or sneezes, the bacteria spreads. Pneumococcus bacteria can cause infections in many parts of the body including:
- Blood (bacteremia)
- Lungs (pneumonia)
- Brain and spinal cord tissue (meningitis)
- Ears (otitis)
- Sinuses (sinusitis)
Symptoms of Streptococcus Pneumoniae

Symptoms of Streptococcus Pneumoniae depend on the part of the body affected. Symptoms can include:
- Fever
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Stiff neck
- Confusion
- Increased sensitivity to light
- Joint pain
- Chills
- Ear pain
- Sleeplessness
- Irritability
In severe cases, pneumococcal disease can cause hearing loss, brain damage, and death.
Who Is At Risk?
Children at Risk for Streptococcus Pneumoniae
Children at increased risk for this disease include those younger than 2 years old and those with:
- Chronic heart, lung, or kidney disease
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak
- Cochlear implant
- Diabetes
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Sickle cell disease, a damaged spleen, or no spleen
- HIV infection, cancer, solid organ transplant, or another condition or taking medicine that weakens the immune system
Adults at Risk for Streptococcus Pneumoniae
Adults 65 years or older are at increased risk for the disease. Adults of all ages are also at increased risk if they have:
- Cochlear implant
- CSF leak
- Diabetes
- Alcoholism
- Chronic heart, lung, kidney, or liver disease
- Nephrotic syndrome
- HIV infection, cancer, solid organ transplant, or another condition or taking medicine that weakens the immune system
- Sickle cell disease, a damaged spleen, or no spleen
Adults who smoke cigarettes are also at increased risk for the disease. Chronic lung illnesses that increase the risk of an adult for the Streptococcus Pneumoniae include asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, and emphysema.

How to Diagnose Streptococcus Pneumoniae?
If doctors suspect Streptococcus Pneumoniae is serious, they will collect blood or cerebrospinal fluid samples. In the brain and spinal cord, cerebrospinal fluid surrounds them. You can see how lumbar puncture fluid is collected in the illustration below. A laboratory tests the samples after they have been collected by doctors. By growing the bacteria in the laboratory, it is possible to identify the specific type of bacteria that is causing the infection. A doctor can select the right antibiotic based on the cause, including the type of infection.
Adults can be diagnosed using a urine test. The diagnosis of ear and sinus infections is usually based on the history and physical examination findings that support the diagnosis.
Treatment for Streptococcus Pneumoniae
It is common for broad-spectrum antibiotics to be used as the first line of treatment for serious infections until results of antibiotic sensitivity testing are available. Antibiotic sensitivity testing shows which antibiotics will be most successful. Broad-spectrum antibiotics work against a wide range of bacteria. Once the sensitivity of the bacteria is known, doctors may choose a more targeted antibiotic. The most recommended medicine is:
- Cephalexin – this is a first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that is active against streptococci.
The Most Common Rheumatic Disorders
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of Rheumatic Disorder. This affects about 27 million adults in the United States alone. Osteoarthritis is a chronic condition characterized by the breakdown of the joint’s cartilage.
The breakdown of cartilage causes the bones to rub against each other, causing stiffness, pain, and loss of movement in the joint. Patients who have been diagnosed with Osteoarthritis are generally cared for by an Orthopedic Specialist.
What are the Risk Factors of Rheumatic Disorder?
The rheumatic disorder can develop in people of any age, sex, or race. There are several different forms of rheumatic disorder and some people are more susceptible to some than others. Some contributing factors to the disease include age, gender, genetics, and environmental factors. Some people are at higher risk for developing a rheumatic disorder, including those people who carry the PTPN22 gene, women, Hispanics, and African Americans.
Common Types of Rheumatic Disorder

- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Bursitis
- Crohn’s Disease
- Gout
- Infectious Arthritis
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR)
- Polymyositis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Scleroderma
- Sjogren’s Syndrome
- Spondyloarthropathies
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Tendonitis
What Causes Rheumatic Disorder?
In many cases, the cause depends on the type of rheumatic disorder. But researchers believe that some or all of the following may play a role:
- Genes and family history
- Lifestyle choices such as being overweight
- Trauma
- Infection
- Nervous system problems
- Metabolic problems
- Too much wear and tear and stress on a joint or joints
- Environmental triggers
- Certain hormones
Rheumatic Disorder Diagnosis
Diagnosis of rheumatic disorder begins with a discussion of your medical history. Your doctor will talk with you about your symptoms, including:
- How much pain you’re in
- Factors that worsen the pain
- Where you feel pain or other symptoms
- When your symptoms began and whether they’re constant or change throughout the day
- Drugs, body positions, and other things that may relieve your symptoms

Rheumatic Disorder Treatment
Various types of medication are prescribed to treat rheumatic disorder. Some drugs only treat symptoms like pain and inflammation, while others can alter the course of the disease.
Depending on the condition, medication may include:
- Oral analgesics (painkillers)
- Topical analgesics
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Corticosteroids
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
- Prednisolone – this medicine is a man-made form of a natural substance (corticosteroid hormone) made by the adrenal gland. Prednisolone lessens the immune system’s response to various diseases to reduce symptoms such as pain and swelling.
Medicine that is usually recommended for rheumatic disorder:
Besides medication, various other types of treatments may be prescribed for a rheumatic disorder such as:
- Physical therapy
- Hot and cold therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Relaxation therapy
- Specific exercise regimes to increase muscle strength and joint flexibility
- Splints, braces, and assistive devices to support weak joints
- Surgery
Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension
Prevention and treatment of hypertension start with a basic understanding of blood pressure. The American Heart Association defines blood pressure as the force exerted by the heart on the artery walls as it beats. From the heart, blood flows to all parts of the body through arteries. When the blood pressure in the arteries is too high during heartbeats, the artery walls are damaged, which can contribute to heart disease.

Symptoms of Hypertension
Even if blood pressure readings reach dangerously high levels, many people with high blood pressure have no symptoms.
Symptoms of high blood pressure may include headaches, shortness of breath, or nosebleeds, but these aren’t specific and usually appear only after high blood pressure has reached a severe or life-threatening level.
Risk Factors of Hypertension
Hypertension has many risk factors including:
- Age – your risk increases as you age, until about 64 years hypertension is more common in men, and women are more likely to develop it after the age of 65.
- Family history – hypertension tends to run in families.
- Being obese or overweight – the more you weigh, the more blood you need to supply oxygen and nutrients to your tissues.
- Lack of physical activity – inactive people tend to have higher heart rates. Lack of physical activity also increases the risk of being overweight.
- Using tobacco – raise your blood pressure temporarily, but the chemicals in tobacco can damage the lining of your artery walls.
- Too much salt and too little potassium in the diet – too much salt in your diet can cause your body to retain fluid which raises blood pressure. Also, a proper balance of potassium is critical for good heart health.
- Drinking too much alcohol – over time, heavy drinking can damage your heart. Having more than one drink a day for women and more than two drinks a day for men may affect your blood pressure.
- Stress – high levels of stress can lead to a temporary increase in blood pressure.

How to Prevent and Treat Hypertension
The following lifestyle changes to help prevent and treat hypertension:
- Eat healthily: Limiting sodium intake per day can reduce high blood pressure since sodium holds excess fluid in the body creating a burden on the heart.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Having less than two drinks per day for men and less than one drink per day for women is recommended.
- Exercise: Exercise strengthens the heart allowing it to pump blood with less effort.
- Lose weight: Losing weight will decrease the amount of pressure it takes to move blood around the body. Quit smoking: Quitting smoking should be a top priority for people with and without high blood pressure.
Medication used for Hypertension:
- Olmesartan – this is in a class of drugs called angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Olmesartan works by blocking the action of certain natural substances that tighten the blood vessels which allows the blood to flow more smoothly and the heart to pump more efficiently.
What Are The Types Of Sexual Dysfunction?
Sexual Dysfunction occurs during any phase of the sexual response cycle. This prevents you from experiencing satisfaction from sexual activity. People of all ages experience sexual dysfunction, although the chances increase as you age.
Types of Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction is generally classified into four categories:
- Desire Disorders: Lack of sexual desire or interest in sex.
- Orgasm Disorders: Delay or absence of orgasm (climax).
- Arousal Disorders: Inability to become physically aroused or excited during sexual activity.
- Pain Disorders: Pain during intercourse.

What Causes Sexual Dysfunction?
Sexual dysfunction usually does not occur overnight. For example, pain during intercourse or ejaculatory/orgasmic challenges be susceptible to have their roots in other conditions that affect the body. Listed below are likely causes of sexual dysfunction.
- Health Changes: When the body endures major illnesses or challenges affecting the blood vessels, this can affect sexual functioning.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Hormones are known to have a key role to play in sexual health and wellness. Any changes in the production of hormones can affect performance and satisfaction during sexual activities.
- Alcohol and Drug Use: Alcohol and drug usage have many downsides including a negative impact on sexual performance.
- Psychological Factors: In some cases, anxiety about upcoming obligations, or even performance during sex can contribute to challenges during intimate moments.
How Is Sexual Dysfunction Diagnosed?
Most of the time, you realize something is interfering with your enjoyment (or your partner’s enjoyment) of a sexual relationship. A complete history of symptoms and physical examination are usually the first steps your provider takes. Diagnostic tests may be ordered to rule out medical problems that may be contributing to the dysfunction. In most cases, lab testing plays a very limited role in the diagnosis of sexual dysfunction.
It helps a clinician understand the underlying cause of the problem and recommend the most appropriate treatment if attitudes about sex and other contributing factors are evaluated and help diagnose the problem.
How Is Sexual Dysfunction Treated?
Most types of sexual dysfunction can be addressed by treating the underlying physical or psychological problems. Other treatment strategies include:
- Mechanical Aids: Aids such as vacuum devices and penile implants may help men with erectile dysfunction.
- Behavioral Treatments: These involve various techniques including insights into harmful behaviors in the relationship or self-stimulation for treatment of problems with arousal or orgasm.
- Sex Therapy: Therapists are often good marital counselors. For the couple who wants to begin enjoying their sexual relationship, you can work with a trained professional.
- Psychotherapy: Therapy with a professional counselor can help you address sexual trauma from the past, feelings of anxiety, and poor body image. All of these factors may affect sexual function.
- Medication: Tadalafil is the most recommended medication for sexual dysfunction. This drug is a class of medications called phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors. Tadalafil works to treat sexual dysfunction by increasing blood flow to the penis during sexual stimulation.
What Causes Excessive Sleepiness?
The most common causes of excessive sleepiness are sleep deprivation and disorders such as insomnia and sleep apnea. Uncontrollable yawning, heavy eyelids and the prevailing impulse to doze off during the day are signs of excessive sleepiness. Struggling to stay awake can drag down performance in daily activities, put a strain on social and personal relationships, and create serious risks especially when driving.

Signs and Symptoms of Excessive Sleepiness
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Hallucinations
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Decreased energy
- Restlessness
- Constant, recurrent episodes of extreme sleepiness during the day
- Difficulty waking up in the morning or after daytime naps, sometimes appearing confused or combative
- Slow thinking, slow speech, inability to focus or concentrate, and memory problems
- Sleeping longer than 10 or more hours yet still being very sleepy during the day and having difficulty remaining awake during the day
Causes of Excessive Sleepiness
Excessive sleepiness is not a condition in itself instead, it is a symptom caused by an underlying problem.
Sleepiness Caused by Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation may be short-term or chronic and can itself be caused by numerous sleep disorders and other medical conditions:
- Failure to Prioritize Sleep: Choosing to stay up late to watch a series or wake up early to go to the gym are examples of how sleep can get bumped down the list of priorities. This can cause drowsiness the next day, and the problem can accumulate over time.
- Insomnia: This condition can make it hard to fall asleep or stay asleep for as long as you want.
- Sleep Apnea: It creates fragmented sleep that typically causes daytime drowsiness and may affect up to 20% of adults.
- Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS): This condition causes a strong sensation of needing to move one’s extremities and is a known risk for disrupting total sleep time and sleep quality.
- Poor Sleep Quality: Sleep insufficiency isn’t just about a low quantity of sleep it’s also about sleep quality.
- Pain: Virtually any ailment that induces pain can complicate sleep and make a person prone to drowsiness during the day.
- Frequent Nighttime Urination: This condition involves needing to get up from bed during the night to pee and is estimated to affect up to one out of three older adults and one out of five younger people.
Sleepiness Caused by Other Medical and Brain Conditions
- Medications
- Mental health problems
- Several brain conditions
- Neurodegenerative diseases
- Neurodevelopmental disorders
- Metabolic problems

Treatment for Excessive Sleepiness
Treatment depends on what is causing your sleepiness. There are both lifestyle changes and medication approaches:
- Maintain good sleep habits such as establishing a regular sleeping schedule, having an environment that allows for sleep, and limiting caffeine and exercise before bedtime.
- Taking Armodafinil promotes wakefulness. This drug is in a class of medications called wakefulness-promoting agents. It works by changing the amounts of certain natural substances in the area of the brain that controls sleep and wakefulness.
What Causes Nausea and Vomiting?
Nausea and Vomiting can occur separately depending on the cause. Usually, nausea and vomiting are harmless, but they can be a sign of a more serious illness.
Nausea is an uneasiness of the stomach that often comes before vomiting. Vomiting is the forcible voluntary or involuntary emptying of stomach contents through the mouth.

Possible Causes of Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are not diseases, but they are symptoms of many conditions such as:
- Motion sickness or seasickness
- Early stages of pregnancy
- Medication-induced vomiting
- Infections
- Heart attack
- Concussion or brain injury
- Brain tumor
- Ulcers
- Some forms of cancer
- Overeating
- A reaction to certain smells or odors
- Bulimia or other psychological illnesses
- Bowel obstruction
- Appendicitis
- Gastroparesis or slow stomach emptying
- Ingestion of toxins or excessive amounts of alcohol
- Intense pain
- Emotional stress
- Gallbladder disease
- Food poisoning
When to Call the Doctor about Nausea and Vomiting?
Call your doctor or for medical help about nausea and vomiting if:
- Nausea lasts for more than a few days or if there is a possibility of being pregnant.
- The home therapy is not working, dehydration is present, or there is a known injury that occurred which may be the cause of vomiting.
- The vomiting occurs for more than a day or if nausea and vomiting last more than 24 hours.
- An infant or child under six years vomits for more than a few hours or if diarrhea is also present, as well as if there is a fever, signs of dehydration, or hasn’t urinated for 4-6 hours.
- A child over the age of six years vomit lasts one day, diarrhea combined with vomiting lasts for more than 24 hours, there are signs of dehydration, a fever higher than 101 degrees, or the child hasn’t urinated for six hours.
Seek medical care if any of the following occur with vomiting:
- Diarrhea
- Rapid breathing or pulse
- There is blood in the vomit
- Severe headache or stiff neck
- Severe abdominal pain
- Lethargy, confusion, or a decreased alertness
How to Treat Vomiting?
Treatment for vomiting includes:
- Drinking gradually larger amounts of clear liquids.
- Avoid solid food until the vomiting episode has passed.
- Pregnant women experiencing morning sickness can eat some crackers before getting out of bed or eat a high-protein snack before going to bed.
- Vomiting linked with cancer treatments can often be treated with another type of drug therapy.
How to Prevent Nausea?
There are several ways to prevent nausea from developing:
- Eat slowly.
- Drink liquids between meals.
- Try to eat when you feel less nauseated.
- Avoid hard-to-digest foods.
- Consume cold foods or room temperature if you are nauseated by the smell of hot or warm foods.
- Rest after eating with your head elevated about 12 inches above your feet.
Medication Used For Nausea and Vomiting
- Dimenhydrinate – this is in a class of medications called antihistamines that is usually recommended to treat nausea and vomiting. Dimenhydrinate reduces the effects of the natural chemical histamine in the body that might be the cause of nausea and vomiting.
Maintenance of the Female Reproductive System
The maintenance of the female reproductive system helps prevent infertility and certain diseases or infections. The female reproductive system is susceptible to trauma, imbalances, and infections that may hinder pregnancy, usher in infectious disease, or cause infertility. While there is no definite way to stop disease, there are precautions to take to keep your reproductive system healthy.
How Does The Female Reproductive System Work?
The female reproductive system performs several functions. Oocytes, also known as ova, are produced by the ovaries. The oocytes are then transferred to the fallopian tube, where they are fertilized by sperm. During the reproductive cycle, the uterine lining thickens in response to normal hormones, and then the fertilized egg moves to the uterus. After implanting into the uterus, the fertilized egg can continue to develop inside the thickened uterine lining. A lack of implantation results in menstrual flow, which sheds the uterine lining. In addition, female reproductive hormones are produced by the female reproductive system, which maintains the reproductive cycle.
A woman’s reproductive system gradually stops producing the female hormones necessary for reproduction during menopause. The result is irregular menstrual cycles or no periods at all. The woman is considered menopausal after her menstrual cycle has stopped for one year.

How to Maintain a Healthy Reproductive System?
- Maintain A Healthy Lifestyle. Enough sleep, exercise, healthy body weight, and proper diet are habits that help your reproductive system.
- Quit Smoking. Studies have shown that smoking can compromise certain areas of the female reproductive system. Also, smoking during pregnancy can affect your unborn child to congenital abnormalities.
- Go For Regular Screenings. It is recommended to go for routine screening. These will make sure early detection of any condition and make sure a better chance of survival.
- Practice Safe Sex. Safe sex is important for preventing diseases.
- Increase Consumption of Calcium and Magnesium. Calcium is effective for premenstrual fatigue, cravings, and depression. Magnesium relieves sugar cravings, headaches, dizziness, and low blood sugar linked with PMS.
Using Estradiol Valerate to Help Maintain a Healthy Reproductive System
Estradiol Valerate is a female hormone largely responsible for the development and maintenance of the female reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics. This medication has several functions including:
- Female reproductive growth
- Development of secondary sexual characteristics – the changes that begin around puberty are driven by estradiol.
- Involvement in disease – research shows that estrogen activates certain cancer-causing genes called oncogenes that raise the risk of breast cancer and endometrial cancer.
- Estradiol Valerate during the menstrual cycle – during the menstrual cycle, follicles on the ovaries secrete estradiol, which triggers a series of events that may cause a surge in luteinizing hormone and induces ovulation.
- Estradiol Valerate during pregnancy – the estradiol level rises during pregnancy. This medicine is thought to play a role in maintaining the pregnancy and in the role of estrogens in initiating labor.
- Estradiol Valerate in bone health – this helps support enough bone growth and maintain the health of bones and joints.
Causes and Treatment of Laryngitis
Laryngitis is caused by an inflammation of the voice box (larynx). Swelling of the voice box can be triggered by an infection, such as bronchitis, cold, or flu. The problem could also be something as simple as overuse.
With proper treatment, Laryngitis should go away in no more than 3 weeks. Sometimes, this condition lasts longer and becomes chronic, but there are ways to help yourself feel better.

What Are The Symptoms Of Laryngitis?
In most cases, the symptoms of laryngitis last less than a couple of weeks and are caused by something minor. Less often, laryngitis symptoms are caused by something more serious or long-lasting. Laryngitis symptoms can include:
- Weak voice or voice loss
- Hoarseness
- Sore throat
- Dry throat
- Dry cough
- Tickling sensation and rawness in your throat
What Causes Laryngitis?
There are two types of Laryngitis with different causes:
Acute Laryngitis
Most cases of laryngitis are temporary and improve after the underlying cause gets better. Causes of acute laryngitis include:
- A vocal strain that is caused by yelling or overusing your voice
- Viral infections similar to those that cause a cold
- Bacterial infections, even though these are less common

Chronic Laryngitis
Chronic laryngitis lasts longer than three weeks. This type of laryngitis is generally caused by exposure to irritants over time. Chronic laryngitis can cause vocal cord strain and injuries or growths on the vocal cords. Chronic laryngitis can be caused by:
- Chronic sinusitis
- Excessive alcohol use
- Inhaled irritants, such as chemical fumes, allergens, or smoke
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Habitual overuse of your voice (such as in singers or cheerleaders)
- Smoking
Less common causes of chronic laryngitis include:
- Infections with certain parasites
- Bacterial or fungal infections
Other causes of chronic hoarseness include:
- Cancer
- Bowing of the vocal cords
- Vocal cord paralysis can cause nerve injury due to surgery, cancer, injury to the chest or neck, nerve disorders, or other health conditions
Diagnosis for Laryngitis
Laryngitis is characterized primarily by hoarseness. Voice changes can range from mild hoarseness to almost complete voice loss, depending on the severity of infection or irritation. Symptoms and medical history may be reviewed by your doctor if you have chronic hoarseness. Your doctor may listen to your voice and examine your vocal cords, and you may be referred to an ear, nose, and throat specialist.
These techniques sometimes are used to help diagnose laryngitis:
- Biopsy – if there are any suspicious areas, your doctor may use this technique
- Laryngoscopy – your doctor can visually examine your vocal cords by using a light and a tiny mirror to look into the back of your throat
Treatment for Laryngitis
Laryngitis often gets better on its own within a week. Self-care measures, such as voice rest, drinking fluids, and humidifying your air, also can help improve symptoms.
Medication used for this condition:
- Azithromycin – this is proven to be effective to treat Laryngitis. Azithromycin is in a class of medications called macrolide antibiotics. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria.
What Are The First Signs Of Metastatic Breast Cancer?
Metastatic Breast Cancer is known as stage IV which has spread to another part of the body, most commonly to the bones, lungs, brain, or liver. Breast cancer can have different signs for different people. Most don’t notice any signs at all. The most common sign is a lump in your breast or armpit. Others include skin changes, pain, a nipple that pulls inward, and unusual discharge from your nipple.
What Are the Early Signs of Metastatic Breast Cancer?

Without treatment, breast cancer can spread to other parts of your body. You may have:
- Bone pain
- Double vision
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Headache
- Changes in brain function
- Trouble breathing
- Belly swelling
- Muscle weakness
- Yellow skin or eyes (jaundice)
What Causes Metastatic Breast Cancer?
A cancerous cell can invade nearby lymph nodes or blood vessels. The cancer cells then travel through lymph vessels or blood vessels throughout the body. Fluids and blood flow through these vessels. Small tumors can form when cancer cells migrate to new locations.
Who Is At Risk For Metastatic Breast Cancer?
Some people are at higher risk for metastatic breast cancer after finishing certain cancer treatments. The risk depends on various features of cancer including:
- The stage at your first diagnosis
- Tumor characteristics (type of cancer cells)
- Treatment received

Diagnosis for Metastatic Breast Cancer
If you have a history of breast cancer and develop any signs of metastatic breast cancer, your doctor may recommend one or more of the following tests to see if cancer has returned:
- Blood tests
- Whole-body bone scan, with or without x-rays of specific bones
- MRI of the spine or brain
- CT scan of the chest, abdomen, pelvis, or brain
- PET scan
- X-ray or ultrasound of the abdomen or chest
- Biopsy of any suspicious area
- Bronchoscopy, if you have a constant cough or trouble breathing
- A tap, removal of fluid from the area with symptoms to check for cancer cells
Treatment for Metastatic Breast Cancer
The main treatment for metastatic breast cancer is a systemic therapy. This treatment cures the entire body. Systemic therapy may be linked with a combination of:
- Chemotherapy
- Hormonal therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Your health care team will plan your treatment based on:
- Past breast cancer treatments
- Symptoms
- Body parts cancer has reached
- Tumor biology, or how the cancer cells look and behave
Medication can be used for Metastatic Breast Cancer:
This medicine is a hormone-based drug that works by binding to estrogen receptors and blocking the effects of estrogen, a natural female hormone in the breast tissue. This slows down the growth and multiplication of breast cancer cells. As a result, it slows the progression of metastatic breast cancer.
Treatment For Rheumatism
Rheumatism treatment helps slow the progression of many rheumatic diseases. It is recommended to seek an early diagnosis as rheumatism is painful and progressive which means they worsen over time.
What is Rheumatism?
Rheumatism is classified as several diseases under rheumatic disorders. Several diseases are classified under rheumatic disorders. The term rheumatism is a loosely used layperson term to describe rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid disorders include those that affect joints, muscles, and bones. They are common and have a huge impact on the health of a vast population worldwide. The more severe conditions lead to inflammatory rheumatic diseases that cause joint and organ destruction. These are a leading cause of severe pain, disability, and even death that affects the quality of life and may lead to several comorbidities or associated ailments.
Common Symptoms of Rheumatism
Symptoms of Rheumatism may include:
- Fatigue
- Tender, warm, and swollen joints
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Joint stiffness is usually worse in the mornings and after inactivity
Early rheumatism tends to affect your smaller joints first, mainly the joints that attach your fingers to your hands and your toes to your feet. As the condition progresses, the symptoms often spread to the wrists, elbows, shoulders, knees, ankles, and hips. In most cases, symptoms occur in the same joints on both sides of your body.
Causes of Rheumatism
Rheumatism is caused by the immune system that attacks the healthy body tissue. The immune system normally makes antibodies that attack bacteria and viruses that help fight infection. If rheumatism attacks, your immune system mistakenly sends antibodies to the lining of your joints, where they damage the tissue surrounding the joint.
This causes the thin layer of cells that covers the joints to become inflamed and sore and releases chemicals that damage nearby:
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Cartilage
- Bones
If rheumatism is not treated, these chemicals slowly cause the joint to lose its shape and alignment. Eventually, it can destroy the joint completely.
Treatment for Rheumatism
Treatment for Rheumatism can help reduce inflammation in the joints, relieve pain, prevent or slow down joint damage, lessen disability and allow you to be as active as possible. There are medications available to help stop Rheumatism from getting worse and lessen your risk of further problems.
Even though there’s no cure for rheumatism, early treatment, and support including medicine, lifestyle changes, supportive treatments, and surgery can reduce the risk of joint damage and limit the impact of the condition.
Medications usually used:
- Methotrexate
- Leflunomide
- Hydroxychloroquine
- Sulfasalazine
- Ibuprofen
- Naproxen
- Diclofenac
Medicine mostly recommended to manage Rheumatism:
This medicine is in a class of medications called opiate (narcotic) analgesics. Tramadol works by changing the way the brain and nervous system respond to pain.
What Is The Treatment Of Acute Malaria?
Malaria is a tropical disease transmitted by mosquitoes. Without early diagnosis and treatment, it can be fatal. People who have acute malaria usually feel sick with chills.
The world health program distributes preventive drugs and insecticide-treated bed nets to protect people from mosquito bites to reduce malaria infections. WHO recommends malaria vaccines for children who live in malaria-prone countries.
Causes of Acute Malaria
The mosquito becomes infected when it bites someone with malaria. When a mosquito bites someone else, it transmits a parasite to the other person’s bloodstream. From there, the parasite multiplies. Various parasites may infect humans with malaria.
Malaria can be transmitted to an unborn child in rare cases when the mother is pregnant and has the illness. It’s possible, but unlikely, for malaria to be passed through blood transfusions, organ donations, and hypodermic needles.

Signs and Symptoms of Acute Malaria
Signs and symptoms of acute malaria are similar to the symptoms of flu including:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Breathing problems
- Cough
- Chest pain
- Muscle aches
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Chills that shake your whole body
- Fever and sweating
As malaria worsens, it causes jaundice and anemia. The most severe form of malaria is known as cerebral malaria which may progress to a coma.
Malaria symptoms usually appear 10 days to one month after the person was infected. Depending on the type of parasite, symptoms can be mild. Some people don’t feel sick for up to a year after the mosquito bite. Parasites can sometimes live in the body for several years without causing symptoms.

Diagnosis for Acute Malaria
You will be asked about your symptoms and travel history by your health care provider. It is important to share the information about the countries you have visited recently so that your health care provider can identify your risk.
Your health care provider will take a sample of your blood and send it to a lab to see if you have malaria parasites. The blood test will tell your health care provider if you have malaria and will also identify the type of parasite that causes your symptoms. Your health care provider will use this information to decide the right treatment.
Treatment for Acute Malaria
It is recommended to seek treatment right away if you have malaria. Your doctor will prescribe you medications to kill the malaria parasite. Some medications are given along with other drugs.
- Hydroxychloroquine is usually recommended for the treatment and management of acute malaria. This drug is relatively well-tolerated. It has been proven to be safe and has been used for several decades already. Hydroxychloroquine can be prescribed to adults and children of all ages. It can also be safely taken by pregnant women and nursing mothers.
What Are The Types Of Psychosis?
Psychosis is a condition that affects the way your brain processes information. This might involve seeing or hearing things that other people cannot see or hear and believing things that are not true. Psychosis should be treated as soon as possible, as early treatment can be more effective. The doctor may ask you some questions to help determine what’s causing your psychosis.
Types Of Psychosis

Hallucinations could include:
- Hearing voices that other people don’t
- Experiencing smells, tastes, and sensations that have no apparent cause
- Seeing objects that seem to be distorted or move in ways that they usually wouldn’t
- Seeing things that other people don’t
2. Delusions
Many people have beliefs that lots of other people don’t share, but a delusion is usually a belief that nobody else shares and which other experiences show can’t be true. It is natural for delusions to feel completely real to you when you are experiencing them.
You might think that you are a very important person. For instance, you may believe that you are powerful and rich or that you can control the weather or the stock markets. These kinds of beliefs are sometimes called delusions of grandeur. Some delusions can also be very frightening and can make you feel endangered or unsafe. For example, you might feel that something or someone is trying to control, harm, or kill you. These ideas are sometimes called paranoid delusions.
3. Disorganized Thinking and Speech
Hallucinations and delusions can make your thoughts and emotions feel confused and disorganized, but disorganized thinking can also be a specific type of psychosis.
Mental health experts may use the following terms to describe what you are experiencing:
- A flight of ideas is when your thoughts move very quickly between ideas, making connections and seeing meaning between things that other people might not see.
- A racing thought is when your thoughts fly through your head very quickly. You may feel as if they are out of control when you experience them.
Several people find that they experience racing thoughts and a flight of ideas at the same time. If you have disorganized thinking you might:
- Find it difficult to keep your attention on one thing.
- Speak very fast and trip over your words so that other people may find it hard to understand what you are saying.
- Change the topic of conversation very quickly as your thoughts move from one thing to another.
- Link words together because of the way they sound rather than what they mean, which can make your speech sound jumbled to other people.
When To Get Medical Advice?
If you are experiencing symptoms of psychosis you should see a medical doctor right away. Psychosis must be treated as soon as possible, as early treatment can be more in effect.
The medical doctor may ask you some questions to help define what’s causing your psychosis. They should also refer you to a mental health specialist for further assessment and treatment.
Treatment for Psychosis
Treatment for psychosis may involve using a combination of:
- Psychological therapy
- Antipsychotic medicine
- Social support
Some people are recommended to take antipsychotics on a long-term basis. The medicine usually recommended is:
- Cholopormazine – this medication belongs to the class of drugs called phenothiazine antipsychotics. It works by helping to restore the balance of certain natural substances in the brain which lessens aggressive behavior and the desire to hurt yourself or others.
Symptoms and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis is a central nervous system disease wherein the symptoms vary widely and depend on the amount of nerve damage it causes. Some people with a severe condition of Multiple Sclerosis may lose the ability to walk independently or not at all, others as well may experience long periods of remission without any new symptoms. Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis helps speed recovery from attacks and manage the symptoms it causes.
What Causes Multiple Sclerosis?
It is unknown what causes multiple sclerosis. It is regarded as an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks its tissues. The immune system malfunction that causes multiple sclerosis destroys the fatty substance that coats and protects nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord (myelin).
Myelin is like the insulation coating on a wire. When the protective myelin is damaged and the nerve fiber is exposed, the signals traveling along that nerve fiber may be slowed or blocked. There is no clear reason why multiple sclerosis develops in some people but not others. Environmental and genetic factors seem to play a role.
Signs and Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis
Signs and symptoms of multiple sclerosis may vary greatly from person to person and throughout the disease depending on the location of affected nerve fibers. Common symptoms include:
- Tremor, lack of coordination, or unsteady gait
- Weakness or numbness in one or more limbs that typically occurs on one side of your body at a time, or on your legs and trunk
- Electric-shock sensations that happen with certain neck movements, especially bending the neck forward
Vision problems are also common including:
- Blurry vision
- Prolonged double vision
- Partial or complete loss of vision, usually in one eye at a time, often with pain during eye movement
Other symptoms that may also occur are:
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Slurred speech
- Tingling or pain in parts of your body
- Problems with sexual, bowel, and bladder function
Risk Factors of Multiple Sclerosis
These factors may increase your risk of developing multiple sclerosis:
- Women are more than two to three times as likely as men are to have multiple sclerosis.
- Family history.
- Having low levels of vitamin D and low exposure to sunlight.
- Smokers who experience an initial event of symptoms that may signal multiple sclerosis are more likely than nonsmokers to develop a second event that confirms relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.
- Certain autoimmune diseases may have a slight chance of developing multiple sclerosis.
Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis
Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis typically focuses on speeding recovery from attacks, slowing the progression of the disease, and managing the symptoms of the condition.
Treatment may include:
- Plasma exchange (Plasmapheresis)
- Corticosteroids such as oral prednisone and intravenous methylprednisolone
- Ocrelizumab
- Glatiramer Acetate
- Fingolimod
- Dimethyl Fumarate
- Teriflunomide
- Siponimod
Managing Anxiety-Related Insomnia
Anxiety and insomnia are not the same conditions, but people with insomnia could have anxiety. Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, trouble staying asleep, and/or early waking. Anxiety and stress are closely linked, and they are among the chief causes of insomnia. Anxiety-related Insomnia may have several factors and treatment may vary depending on the condition.
What Are The Possible Of Causes Anxiety And Insomnia?
Anxiety is a normal part of life. The causes of anxiety disorders aren’t fully understood. Life experiences such as traumatic events seem to trigger anxiety in people who are already prone to anxiety. Inherited traits also can be a factor.
Insomnia is a sleep disorder that is marked by problems getting to sleep, staying asleep through the night, and sleeping as long as you would like into the morning. Common causes of insomnia include stress, an irregular sleep schedule, mental health disorders like anxiety, poor sleeping habits, depression, physical illnesses and pain, neurological problems, medications, and specific sleep disorders. For many people, a combination of these factors can initiate and aggravate insomnia.
The Link between Anxiety and Insomnia
Constant worry during the day often carries over into night which can cause mental hyperarousal. It can keep you from falling asleep.
Once you do get to sleep, anxiety also can prevent you from staying asleep long enough to feel fully rested. Anxiety has been compared to your body’s alarm system, it can help keep you safe and out of potentially dangerous situations. However, if that alarm goes off all the time and for no real reason, it can keep you from getting enough deep sleep. All of this can create stress over not being able to get to sleep or get enough sleep which can lead to even more anxiety.

How to Manage Anxiety-Related Insomnia?
- Try To Relax: If you’re lying awake at night with your heart pounding, it’s likely your fight or flight response has been triggered. Try to get your body back into a relaxed, resting state and take a deep breath.
- Get Up And Do Something: Sometimes, a useful way to lessen your anxiety is to physically focus on something completely different.
- Give Yourself Enough Time For Sleep: You must give yourself the chance to get this amount of sleep.
- Be Organized And Prepare For The Next Day: You can try making a to-do list so you know you’ve got everything covered before you go to bed. This can help to lessen your worries as you know everything is in hand for the next morning.
- Practice Good Sleep Hygiene: Try and keep a consistent sleep routine. You should also try to limit your intake of caffeine, sugar, and alcohol late at night.
Medications Can Be Used for Anxiety-Related Insomnia
It may take some trial and error to discover which treatments work best for you. For an appropriate prescription, it is best to consult your doctor.
Health Risks of Chronic Alcohol Abuse
Chronic Alcohol Abuse refers to drinking in a way that is not controlled, being preoccupied with alcohol, or continuing to drink despite its negative effects. It is also associated with having to consume more alcohol to achieve the same effect and experiencing withdrawal symptoms when you reduce or stop drinking rapidly. Alcohol abuse can lead to alcoholism.
Alcohol use that risks your health or safety or causes other alcohol-related problems is considered unhealthy. The term also refers to binge drinking, when a male or female has five or more drinks within two hours. Binge drinking causes significant health risks.

Health Risks of Chronic Alcohol Abuse
Too much alcohol can harm you physically and mentally in lots of ways. Health risks may include:
- Liver damage
- Heart disease
- Brain and nervous system problems
- Anemia
- Cancer
- Gout
- Seizures
- Infections
- Digestive problems
- Sleep disturbances
Factors That May Affect Chronic Alcohol Abuse
Many factors influence how drinking alcohol affects your body and behavior, including genetics, psychology, social factors, and the environment. Certain people may be more susceptible to alcohol use disorders due to a different and stronger impact of drinking.
Too much alcohol may alter the normal function of the areas of your brain responsible for pleasure, judgment, and the ability to control your behavior over time. The result may be a craving for alcohol to try to restore good feelings or reduce negative ones.

Diagnosis for Chronic Alcohol Abuse
You are likely to start by seeing your primary health care provider. If your provider suspects that you have a problem with alcohol, you may be referred to a mental health provider. To evaluate your problem with alcohol, your provider will likely:
- Ask you some questions related to your drinking habits
- Perform a physical exam
- Suggest lab tests and imaging tests
- Complete a psychological evaluation
Treatment for Chronic Alcohol Abuse
Treatment for chronic alcohol abuse can vary, depending on your needs. Treatment may involve a short-term intervention, individual or group counseling, an outpatient program, or a residential inpatient stay. Working to stop alcohol use to improve quality of life is the main treatment goal. Treatment for chronic alcohol abuse may include:
- Detox and withdrawal – this generally takes 2 to 7 days. You may need to take sedating medications to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
- Learning new skills and making a treatment plan – this may include goal setting, use of self-help manuals, behavior change techniques, counseling, and follow-up care at a treatment center.
- Psychological counseling – will help you better understand your problem with alcohol and support recovery from the psychological aspects of alcohol use.
- Treatment for psychological problems – chronic alcohol abuse commonly occurs along with other mental health disorders. If you have a certain mental health condition, you may need talk therapy, medications, or other treatment.
- Oral medications – certain medications may help you prevent drinking.
Medications used for chronic alcohol abuse:
What Are The Warning Signs Of A Heart Attack?
On the onset of the warning signs of a heart attack, call 911 or the local emergency team immediately. A heart attack is caused by reduced or blocked blood flow to the heart. Blockages in coronary arteries are typically caused by fat, cholesterol, and other substances accumulating. Plaques consist of fatty deposits, which contain cholesterol. There is a possibility that a plaque may rupture and produce a clot. This may cause the heart muscle to be damaged or destroyed. Heart attacks are also known as myocardial infarction.

Eight Warning Signs of A Heart Attack
1. Uncomfortable Pressure
This is the first symptom of a heart attack which is an uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center of your chest. This discomfort may come in waves lasting more than a few minutes at a time.
2. Pain in Other Areas of the Body
Heart attack pain can occur in places other than the chest, like the shoulders, arms, back, neck, or jaw. Considering the vagus nerve is connected to not only the heart, but also the brain, chest, neck, and abdomen, you may feel those pain signals in other areas of the body aside from the heart area.
3. Dizziness
Lightheadedness or dizziness coupled with shortness of breath and chest pain may signify a reduction in blood volume and a drop in blood pressure, which means a heart attack could be on its way.
4. Fatigue
Feeling exhausted after a sleepless night or a stressful day is normal. This sign is especially prominent in women.
5. Nausea or Indigestion
Gastric symptoms develop when the heart and other areas of the body aren’t receiving enough blood supply. It can be misjudged as acid reflux or heartburn, so it’s important to reach out to your doctor.
6. Sweating
Unless you have just exercised, breaking out into a cold sweat or perspiring extremely could signal a heart attack. During a heart attack, your nervous system activates a fight or flight response that puts you in survival mode and might cause sweating.
7. Heart Palpitations
The heart can begin to get irritable when it lacks nutrient-filled blood, which leads to the sensation of heart palpitations. If you feel like you’re having heart palpitations, make sure you contact your doctor right away.
8. Shortness of Breath
Walking up the stairs used to be a breeze, but if you recently have been finding it harder and harder to make the climb, seek medical attention immediately. Although this doesn’t certainly mean you’re about to have a heart attack at this moment, it could be a sign that your heart is in danger.
Treatment for Heart Attack
Each minute after a heart attack, more heart tissue is damaged or dies. Urgent treatment is necessary to fix blood flow and restore oxygen levels. Oxygen is given straightaway.
Medications to treat a heart attack or its symptoms might include:
Symptoms and Types of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic disorder of the digestive system that affects the large intestine. People with this condition experience abnormal inflammation which may result in open sores called ulcers inside the colon and rectum.
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis?
- Genetic Causes: In some families, ulcerative colitis is inherited. Researchers have identified genetic variations that may contribute to Ulcerative Colitis, but they are not sure exactly how these differences are linked directly to the disease.
- Overactive Intestinal Immune System: By attacking viruses, bacteria, and other threats, the immune system protects the body. These invaders are suspected of confusing the immune system and tricking it into launching an immune response against the lining of the large intestine, resulting in Ulcerative Colitis.
- Emotional Stress: Ulcerative colitis does not appear to be caused by this. Some studies suggest that it can cause Ulcerative Colitis flare-ups in some people who have already developed it.
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
- Abdominal cramps, discomfort or pain
- Persistent diarrhea with blood, pus, or mucus in the stool
- Urgent and loose bowel movements
- Bloody stool
- Nausea
- Weight loss
- Slowed or delayed growth in children
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Anemia due to excessive intestinal bleeding
Types of Ulcerative Colitis
Five types of Ulcerative Colitis are identified largely by where they are located in the body or their severity.
1. Ulcerative Proctitis
This is usually the mildest form of Ulcerative Colitis. It is limited to the rectum and rectal bleeding may be the only sign or symptom.
2. Proctosigmoiditis
This type affects the lower end of the colon along with the rectum and is sometimes called the sigmoid colon. Symptoms include abdominal cramps/pain and bloody diarrhea.
3. Left-Sided Colitis
This type causes cramps on the left side of the abdomen that affects the rectum and the portion of the colon on the left side of the body. Signs and symptoms include weight loss and bloody diarrhea.
4. Pancolitis
Pancolitis can affect the entire colon which causes multiple symptoms including major weight loss, bloody diarrhea, pain, abdominal cramps, and fatigue.
5. Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis
This condition is rare but affects the entire colon. Symptoms include pain, fever, and bloody diarrhea.
How To Diagnose Ulcerative Colitis?
To diagnose ulcerative colitis, doctors review your symptoms and medical and family history and perform a physical exam and tests. Medical tests may include stool tests, blood tests, and endoscopy of the large intestine.

Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis treatment usually involves either drug treatment or surgery.
1. Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Sulfasalazine
- Mesalamine
- Balsalazide
- Olsalazine
2. Corticosteroids
3. Immune System Suppressors
- Azathioprine
- Mercaptopurine
- Cyclosporine
- Tofacitinib
4. Biologics
- Infliximab
- Adalimumab
- Golimumab
- Vedolizumab
- Ustekinumab
5. Other Medications
- Loperamide
- Acetaminophen
Even when you are not experiencing symptoms, take your medication as prescribed. You may experience flare-ups if you skip the medications you’re supposed to take. The best way to manage ulcerative colitis is to follow your treatment plan and talk to your healthcare provider on a regular basis.
What is Hypersensitivity Syndrome?
Hypersensitivity Syndrome is your body’s reactions to medications that result from an enhanced immunologic or inflammatory response. Infection-fighting T-cells in your immune system are unleashed in response to the medication which causes eruptions on your skin and damage to your internal organs.
Several factors make Hypersensitivity Syndrome different from an ordinary drug reaction. These include when it:
- Symptoms appear to go into remission, but relapses can occur later
- Causes autoimmune disorders to develop down the line
- Re-activates common herpes viruses that may be dormant in your body
- Involves more than one organ in your body
What Are The Symptoms Of Hypersensitivity Syndrome?
While several drug allergies cause an instant reaction, the symptoms of Hypersensitivity Syndrome generally appear 3 weeks to 3 months after the medication was started. Symptoms can come and go for months or even years.

Common symptoms may include:
- Scaly, flaky skin
- Fever
- Facial swelling
- A pink or red rash with or without pus-filled bumps or blisters
- Swollen or tender lymph nodes
- Swollen saliva glands
- Difficulty moving normally
- Headache
- Dry mouth
- Abnormalities in your white blood cell counts
- Seizures
- Coma
Who’s At Risk for Hypersensitivity Syndrome?
Scientists have discovered that genes play an essential role in whether you’re likely to have a severe drug reaction. However, genetics is not the only factor. Studies show you may be more likely to experience Hypersensitivity Syndrome if:
- You’re over 20 years old
- You’ve had a rheumatic or collagen rheumatic disease before
- You’ve had a viral infection in the past few weeks
- You have a condition that requires you to take antibiotics often
Possible Causes of Hypersensitivity Syndrome
Scientists are still learning about these interactions, but what they have discovered so far shows that certain drugs are more likely to be involved in these reactions:
- Medications used to treat tuberculosis include Ethambutol, Rifampin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide, and Streptomycin
- Seizure medications including Mexiletine, Phenytoin, Phenobarbital, Carbamazepine, Lamotrigine, Valproic Acid, and Zonisamide
- Antibiotics such as Ampicillin, Azithromycin, Dapsone, Amoxicillin, Levofloxacin, Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Clindamycin, Minocycline, and Vancomycin
- Antiretrovirals such as Nevirapine and Efavirenz
- Anti-inflammatory medications, including ibuprofen, celecoxib, and diclofenac
- Cancer therapies including Sorafenib, Vismodegib, Imatinib, and Vemurafenib
- Drugs used to treat hepatitis C, including Boceprevir and Telaprevir
- Allopurinol and Febuxostat, lower uric acid in people with gout, kidney stones, and cancer
- Rivaroxaban, a blood thinner
- Acetaminophen, an over-the-counter pain reliever
- Omeprazole, an over-the-counter heartburn medication
- Sulfasalazine, an arthritis medication
How Is Hypersensitivity Syndrome Treated?
The first step in treating Hypersensitivity Syndrome is to stop the medication that’s causing the reaction. You must be prepared for your symptoms to get worse right after you stop taking the medication.
It’s also important to understand that your symptoms may come and go for some time after you’re treated. That pattern is also common with this condition. After stopping the medication, your doctor may treat you with corticosteroids to control some of your symptoms. If you’ve developed a secondary infection as a result of the reaction, you may also need a course of antibiotics.
Heartburn Prevention Tips
What Is Heartburn?
Heartburn is an uncomfortable burning feeling in your chest that can move up your neck and throat. The pain is often worse after eating, in the evening, or when lying down or bending over. The uncomfortable burning feeling that is more frequent or interferes with your daily routine may be a symptom of a more serious condition that needs medical care.
It’s not uncommon to experience occasional heartburn. However, you may have chronic acid reflux called GERD if you suffer from frequent and severe heartburn. You should seek medical attention if you frequently suffer from heartburn.
What Does Heartburn Feel Like?

Heartburn typically feels like a burning sensation behind your breastbone, in the center of your chest. Other symptoms of heartburn may include:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Pain in your chest when you bend over or lay down
- A burning feeling in your chest that can last anywhere from a few minutes to a couple of hours
- A hot, sour, acidic, or salty taste in the back of your throat
- A burning feeling in your throat
What Can Trigger Heartburn?
The things you do daily can cause heartburn. Some people suffer from heartburn due to their eating habits and lifestyle. Eating large portions of food, eating too close to bedtime, or even being stressed can be considered these habits.
Certain foods and drinks can also trigger heartburn for some people including:
- Citrus juices
- Caffeinated beverages
- Carbonated beverages
- Tomatoes
- Tomato-based products
- Alcohol
- Onions
- Citrus fruits
- High-fat foods
Heartburn can also be caused by lifestyle habits. Lifestyle habits play a significant role in heartburn-related illnesses. Among the lifestyle habits that may trigger heartburn are:
- Having a high-stress level
- Wearing tight clothes and belts
- Being overweight
- Being a smoker
How Is Heartburn Treated?
Prevention Tips
You can often prevent and manage heartburn by making changes to your lifestyle. These changes include:
- Avoiding overeating
- Not going to bed with a full stomach
- Wearing loose-fitting clothes
- Eating slowly
- Avoiding certain foods that might trigger heartburn
- Not smoking. Nicotine can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter.
- Sleeping on your left side helps with digestion and the removal of acid from your stomach and esophagus more quickly.
- Raising the head of your bed so that your head and chest are higher than your feet.
- Planning your exercise to avoid heartburn. Wait at least two hours after a meal before exercising. If you work out any sooner, you may trigger heartburn. You should also drink plenty of water before and during exercise.
Medications
Over-the-counter medications for heartburn usually include acid blockers and antacids. If nonprescription treatments don’t work or you rely on them often, see your health care provider. You may need prescription medication and further testing.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects more than just the joints. Some people can suffer damage to many different body systems, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
The immune system mistakenly attacks your body’s tissues when rheumatoid arthritis occurs. Rheumatoid arthritis, in contrast to osteoarthritis, causes swelling of your joints that can eventually result in bone erosion and joint deformity, instead of the wear-and-tear damage associated with osteoarthritis.
The inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis can also damage other parts of the body. While new treatments for severe rheumatoid arthritis have improved dramatically, they still can lead to severe disabilities.

What Are The Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis may include:
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Joint stiffness is usually worse in the mornings and after inactivity
- Tender, warm, and swollen joints
Early rheumatoid arthritis tends to affect your smaller joints first, particularly the joints that attach your fingers to your hands and your toes to your feet. As it progresses, the symptoms often spread to the shoulders, hips, elbows, ankles, knees, and wrists. In most cases, symptoms occur in the same joints on both sides of your body.
Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Factors that may increase your risk of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Family history – if a member of your family has rheumatoid arthritis, you may have an increased risk of the disease.
- Your sex – women are more likely than men to develop rheumatoid arthritis.
- Age – rheumatoid arthritis can occur at any age, but it most commonly begins in middle age.
- Excess weight – people who are overweight appear to be at a somewhat higher risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
- Smoking – cigarette smoking increases your risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis, particularly if you have a genetic predisposition for developing the disease. Smoking also appears to be associated with greater disease severity.
Diagnosis for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis can be difficult to diagnose in its early stages because the early symptoms imitate those of many other diseases. There is no one blood test or physical finding to confirm the diagnosis. During the physical exam, your doctor will check your joints for swelling, redness, and warmth. Your doctor may also check your reflexes and muscle strength.

Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis
There is no specific cure for rheumatoid arthritis. However, clinical studies indicate that remission of symptoms is more likely when treatment begins early with medications known as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Medications can be used for rheumatoid arthritis:
The types of medications recommended by your doctor will depend on the severity of your symptoms and how long you’ve had rheumatoid arthritis. Always ask for instructions when taking certain medications.
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
Type 2 Diabetes is a common type of diabetes. It is a disease that occurs when your blood glucose is too high. Blood glucose or blood sugar is the main source of energy and comes mainly from the food you eat.
A hormone made by the pancreas called insulin helps glucose get into your cells to be used for energy. Your body doesn’t produce enough insulin or doesn’t use it efficiently if you have type 2 diabetes. In this case, too much glucose remains in your blood and not enough reaches your cells.

Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes often develop slowly. You can be living with this disease for years and not know it. When symptoms are present, they may include:
- Unintended weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Increased hunger
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
- Areas of darkened skin, usually in the armpits and neck
- Slow-healing sores
- Frequent infections
Who Is At Risk Of Developing Type 2 Diabetes?
You are more likely to develop Type 2 Diabetes if you:
- Are obese or overweight
- Are older than 45
- Had gestational diabetes while pregnant
- Have high blood pressure
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Have pre-diabetes
Complications of High Blood Sugar Levels
Potential complications of high blood sugar levels from Type 2 diabetes can include:
- Heart disease
- Kidney disease
- Skin conditions
- Stroke
- Urinary tract infections and bladder infections
- Digestive problems
- Eye problems
- Hearing loss
- Liver problems, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Foot problems, including leg and foot ulcers
- Gum disease and other mouth problems
- Peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage)
- Sexual dysfunction
Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
These steps will help keep your blood sugar level closer to normal, which can delay or prevent complications.
1. Healthy Eating
- Modest servings of low-fat dairy, low-fat meats, and fish
- Healthy cooking oils, such as olive oil or canola oil
- Fewer calories
- A regular schedule for meals and healthy snacks
- Fewer refined grains, starchy vegetables, and sweets
- Smaller portion sizes
- More high-fiber foods, such as fruits, nonstarchy vegetables, and whole grains
2. Physical Activity
Exercise is important for losing weight or maintaining a healthy weight. It also helps with regulating blood sugar levels.
- Aerobic exercise
- Resistance exercise
- Limit inactivity
3. Weight Loss
Blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, triglycerides, and blood pressure are better controlled with weight loss. Overweight people may notice improvements in these factors after losing as little as 5% of their body weight. As you lose weight, you will see a greater impact on your health and disease management.
4. Monitoring Your Blood Sugar
Your doctor will direct you on how often to check your blood sugar level to make sure you remain within your target range. You should keep a record of your measurements to share with your doctor.
5. Diabetes Medications
Diabetes medications that help lower insulin levels or insulin therapy may be prescribed by your doctor if diet and exercise are not sufficient to maintain your target blood sugar level. Diabetes medications that help lower insulin levels include the following.
Treatment for Alopecia
Treatment for Alopecia is crucial. Before pursuing it, you may need to talk with your doctor about the cause and the treatment options.
Alopecia is a condition that causes hair loss which may affect just your scalp or your entire body. This condition can be the result of hormonal changes, heredity, medical condition, or a normal part of aging. Alopecia is more common in men.

Symptoms of Alopecia
Alopecia can appear in many different ways. It can come on suddenly or slowly and might affect just the scalp or the whole body.
Symptoms may include:
- Patches of scaling that spread over the scalp
- Full-body hair loss
- Sudden loosening of hair
- Circular or patchy bald spots
- Gradual thinning on top of the head
See your doctor if you are troubled by persistent hair loss in you and want to pursue treatment. For women who are experiencing a receding hairline, talk with your doctor about early treatment to avoid significant permanent baldness. Also, talk to your doctor if you notice sudden or patchy hair loss or more than usual hair loss when combing or washing your hair. Sudden hair loss can signal an underlying medical condition that requires treatment.
Causes of Alopecia
Hair loss is typically related to one or more of the following factors:
- Family history (heredity)
- Hormonal changes and medical conditions
- Medications and supplements
- Radiation therapy to the head
- A very stressful event
- Hairstyles and treatments

Diagnosis for Alopecia
Before making a diagnosis, your doctor will likely give you a physical exam and ask about your hair care routine, your diet, and your medical and family history. You might also have tests such as:
- Pull test – your doctor gently pulls several dozen hairs to see how many come out. This helps determine the stage of the shedding process.
- Blood test – this might help uncover medical conditions that can cause hair loss.
- Scalp biopsy – your doctor scrapes samples from the skin or a few hairs plucked from the scalp to examine the hair roots under a microscope. This can help determine whether an infection is causing hair loss.
- Light microscopy – your doctor uses a special instrument to examine hairs trimmed at their bases. Microscopy helps uncover possible disorders of the hair shaft.
Treatment for Alopecia
Effective treatments for some types of hair loss are available. You might be able to reverse hair loss, or at least slow it. Treatments for hair loss include medications and surgery.
- Hair transplant surgery – hair transplant can make the most of the hair you have left. During a hair transplant procedure, a dermatologist or cosmetic surgeon removes hair from a part of the head that has hair and transplants it to a bald spot.
- Laser therapy – The FDA has approved a low-level laser device as a treatment for hereditary hair loss in men and women. A few small studies have shown that it improves hair density.
- Medications – medications are available to treat pattern baldness. The most common options include Minoxidil (Rogaine), Finasteride (Propecia), Dutasteride (Avodart), and Spironolactone.
Eye Cataract Treatment
Treatment for Eye cataracts may include cataract surgery if you have impaired vision that interferes with your usual activities. The surgery is generally safe and effective.
A cataract is a clouding of the lens of your eye. For people with cataracts, seeing through cloudy lenses is a bit like looking through a frosty or fogged-up window. Clouded vision caused by cataracts can make it more difficult to drive a car, read, or see the expression on a friend’s face. Most cataracts develop slowly and don’t disturb your eyesight early on. But with time, cataracts will eventually interfere with your vision.
Signs and Symptoms of Eye Cataract
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Double vision in a single eye
- Seeing halos around lights
- Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription
- Sensitivity to light and glare
- Need for brighter light for reading and other activities
- Clouded, blurred, or dim vision
- Increasing difficulty with vision at night
If you have any changes in your vision, make an appointment for an eye exam. Also, see your doctor right away if you develop sudden vision changes, eye pain, or headache.

At-Risk for Eye Cataract
Factors that may increase your risk of eye cataracts may include:
- Prolonged use of corticosteroid medications
- Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol
- Increasing age
- Diabetes
- Previous eye injury or inflammation
- Previous eye surgery
- Excessive exposure to sunlight
- Smoking
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
Diagnosis for Eye Cataract
To diagnose a cataract, your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms, and perform an eye examination. Your doctor may conduct several tests including:
- Visual acuity test – this test uses an eye chart to measure how well you can read a series of letters. Using a chart or a viewing device with progressively smaller letters, your eye doctor determines if you have 20/20 vision.
- Slit-lamp examination – this allows your eye doctor to see the structures at the front of your eye under magnification.
- Retinal exam – To prepare for a retinal exam, your eye doctor puts drops in your eyes to open your pupils wide. This makes it easier to examine the back of your eyes.
- Applanation tonometry – This test measures the fluid pressure in your eye. There are multiple different devices available to do this.

Treatment for Eye Cataract
Surgery is the only way to get rid of a cataract, but you may not need to get surgery right away.
1. Home treatment
- Use brighter lights at home or work
- Wear anti-glare sunglasses
- Use magnifying lenses for reading and other activities
2. New glasses or contacts
- A new prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses can help you see better with cataracts early on.
3. Surgery
- Your doctor might suggest surgery if your cataracts start getting in the way of everyday activities.
Most people don’t need to rush into surgery. Talk about your options with your doctor. Waiting to have surgery usually won’t harm your eyes or make surgery more difficult later.
- See your doctor for regular check-ups
- Tell your doctor if cataracts are getting in the way of your everyday activities
- Encourage family members to get checked for cataracts, since they can run into families
- Ask your doctor about the benefits and risks of cataract surgery
Symptoms of Presbyopia
Symptoms of Presbyopia may develop gradually. You may first notice the symptoms after the age of 40.
Presbyopia is a condition that causes gradual loss of the ability of your eye to focus on nearby objects. This condition is usually noticeable in your early to mid-40s and continues to get worse until around the age of 65.
What Causes Presbyopia?
Light reflected from objects is focused by the cornea and the lens to form an image in your eye. The closer the object is, the more the lens bends.
- The lens is a clear structure about the size and shape of an M&M’s candy.
- The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped front surface of your eye.
- Both of these structures bend light entering your eye to focus the image on the retina which is located on the inside back wall of your eye.
The lens is somewhat flexible, unlike the cornea, and can change shape as a result of a circular muscle surrounding it. The circular muscle relaxes when you view something from a distance. The muscle constricts as you look at something nearby, allowing the relatively elastic lens to curve and change its focus.
With age, your lens hardens, causing presbyopia. Your lens can no longer change shape to focus on close-ups as it becomes less flexible. As a result, these images appear out of focus.

What Are The Symptoms Of Presbyopia?
You may notice these symptoms are worse if you are tired or are in an area with dim lighting.
- Blurred vision at normal reading distance
- A tendency to hold reading material farther away to make the letters clearer
- Eyestrain or headaches after reading or doing close-up work
Seek medical care right away if these occur:
- See flashes of light, black spots, or halos around lights
- Have double vision
- Have a sudden loss of vision in one eye with or without eye pain
- Experience sudden hazy or blurred vision
How To Diagnose Presbyopia?
To diagnose Presbyopia, you need to have a basic eye exam. Your doctor may use various instruments and ask you to look through several lenses to test your distance and close-up vision. During your eye health exam, your eye doctor may put drops in your eyes to dilate your pupils. Several hours after the exam, you may experience increased sensitivity to light. Dilation enables your doctor to more easily view the inside of your eyes.

Treatment for Presbyopia
Treatment for Presbyopia includes wearing corrective eyeglasses or contact lenses, undergoing refractive surgery, or getting lens implants for presbyopia. However, if you are a good candidate for presbyopia surgery the first step to see is to have a comprehensive eye exam and a consultation with a refractive surgeon who specializes in the surgical correction of presbyopia.
Vuity (Pilocarpine Hydrochloride) is an approved eye drop used to treat presbyopia. It is a cholinergic muscarinic receptor agonist that works to improve near and intermediate visual acuity by contracting the iris sphincter muscle to constrict the pupil.
Symptoms of Glaucoma
Symptoms of glaucoma may vary depending on the type of glaucoma a person has. Most people have open-angle glaucoma and angle-closure glaucoma, the most common types of glaucoma.
Glaucoma is an eye condition that damages the optic nerve. The damage is often caused by abnormally high pressure in your eye. Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of blindness for people over the age of 60. It can occur at any age but is more common in older adults.

Symptoms of Glaucoma
The signs and symptoms of glaucoma vary depending on the type and stage of your condition. For example:
- Tunnel vision in the advanced stages
- Patchy blind spots in your side or central vision, frequently in both eyes
Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma
- Halos around lights
- Eye redness
- Severe headache
- Eye pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Blurred vision
If glaucoma is left untreated, it will eventually cause blindness. Even with treatment, about 15% of people with glaucoma become blind in at least one eye within 20 years.
Who Are At Risk Of Having Glaucoma?
Chronic forms of glaucoma can destroy vision before any symptoms are apparent. Be aware of these risk factors:

- Taking corticosteroid medications, especially eyedrops, for a long time
- Being over age 60
- Being extremely nearsighted or farsighted
- Having a family history of glaucoma
- Having certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, and sickle cell anemia
- Having corneas that are thin in the center
- Having high internal eye pressure
- Having had an eye injury or certain types of eye surgery
How To Diagnose Glaucoma?
To diagnose glaucoma, your doctor will review your medical history and conduct a comprehensive eye examination. However, there are several tests including:
- Measuring corneal thickness (pachymetry)
- Inspecting the drainage angle (gonioscopy)
- Testing for optic nerve damage with a dilated eye examination and imaging tests
- Checking for areas of vision loss (visual field test)
- Measuring intraocular pressure (tonometry)
Treatment for Glaucoma
Treatment and regular checkups can help slow or prevent vision loss, especially if you catch the disease in its early stages.
Glaucoma is treated by lowering your eye pressure. Depending on your situation, your options may include prescription eye drops, oral medications, laser treatment, surgery, or a combination of any of these.
Some of the eye drop medication is absorbed into your bloodstream, you may experience some side effects unrelated to your eyes. To lessen this absorption, close your eyes for one to two minutes after putting the drops in.
If you have been prescribed multiple eye drops or you need to use artificial tears, space them out so that you are waiting at least five minutes in between types of drops. Ask your health care provider for proper instructions.
Causes of Cryptorchidism
The causes of Cryptorchidism are not yet clear and vary in several factors. Cryptorchidism is also known as an undescended testicle. It is a testicle that hasn’t moved into its proper position in the bag of skin hanging below the penis before birth. This type of condition is uncommon in general, but common among baby boys born prematurely.
Symptoms of Cryptorchidism
Not seeing or feeling a testicle where you would expect it to be in the scrotum is the main symptom of an undescended testicle.
- An arrested testicle in one or both testes stays in the inguinal
- An ectopic testicle in which one or both testes descend
- An absent testicle in which the testes do not develop.
- Ascending testicle in which the testes are originally in a normal scrotal position. This can require surgery to correct.
About 80% of undescended testicles are tangible. The testicle is usually located at the end of the inguinal canal, a channel that carries the spermatic cord towards the penis and scrotum.
Causes and Risk Factors of Cryptorchidism

The exact cause of cryptorchidism is not known. However, a combination of genetics, maternal health, and other environmental factors might disrupt the hormones, physical changes, and nerve activity that influence the development of the testicles.
In their early stages, all fetuses contain structures that can develop into male or female reproductive organs. Children inherit their sex chromosomes from their parents. According to researchers, the testicles may start to develop incorrectly at this point. Other causes and risk factors may include:
- Low birth weight or premature birth
- Family history of undescended testicles or other problems of genital development
- Conditions that restrict growth such as Down syndrome or an abdominal wall defect
- Alcohol use or cigarette smoking by the mother during pregnancy
Treatment for Cryptorchidism
Treatment aims to move the undescended testicle to its right position in the scrotum. Treatment before 1 year of age might lower the risk of complications of an undescended testicle. Earlier is better, but it’s recommended that surgery takes place before the child is 18 months old.
- Surgery: An undescended testicle is usually corrected with surgery. This procedure can be done either with a laparoscope or with open surgery. Your surgeon will likely recommend doing the surgery when your son is about 6 months old and before he is 12 months old. Early surgical treatment appears to lower the risk of later complications.
- Hormone treatment: This involves the injection of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). This hormone could cause the testicle to move to your son’s scrotum.
- Other treatments: If your son doesn’t have one or both testicles, you might consider saline testicular prostheses for the scrotum that can be implanted during late childhood or adolescence. These prostheses give the scrotum a normal appearance.
HIV Infection
HIV infection is a chronic, potentially life-threatening condition. HIV is a virus that damages the cells in your immune system and weakens your ability to fight everyday infections and diseases.
This infection can spread in different ways:
- Through unprotected sex with a person with HIV. This is the most common way that it spreads.
- Through contact with the blood of a person with HIV
- From mother to baby during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding
- By sharing drug needles
What Are The Symptoms of HIV Infection?

The symptoms of HIV infection vary depending on the phase of infection:
1. Primary Infection (Acute HIV)
Some people infected by HIV develop a flu-like illness within 2 to 4 weeks after the virus enters the body. This illness may last for a few weeks. Possible symptoms may include:
- Rash
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches and joint pain
- Cough
- Sore throat and painful mouth sores
- Swollen lymph glands, mainly on the neck
- Night sweats
2. Clinical Latent Infection (Chronic HIV)
HIV is still present in the body and white blood cells at this stage of infection. However, during this time, many people may not have any symptoms.
3. Symptomatic HIV infection
As the virus continues to grow and destroy immune cells, you may develop mild infections or chronic symptoms such as:
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Pneumonia
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Oral yeast infection (thrush)
- Shingles (herpes zoster)
4. Progression to AIDS

If HIV is left untreated, it typically turns into AIDS in about 8-10 years. You have a severely damaged immune system when you have AIDS. You’re more likely to contract diseases that would not normally cause illness in a person with a healthy immune system. Symptoms of these may include:
- Chronic diarrhea
- Sweats
- Swollen lymph glands
- Chills
- Recurring fever
- Weight loss
- Skin rashes or bumps
- Persistent white spots or unusual lesions on your tongue or in your mouth
- Persistent, unexplained fatigue
- Weakness
How Is HIV Infection Diagnosed?
HIV infection can be diagnosed via blood or saliva testing. Available tests include:
- Nucleic acid tests (NATs)
- Antigen/antibody tests
Discuss which HIV test is best for you with your health care provider. You may still need a follow-up test to confirm the results if any of these tests are negative.
Treatment for HIV Infection
Various medications can control HIV and prevent complications. These medications are called antiretroviral therapy (ART). Everyone diagnosed with HIV should be started on ART, regardless of their stage of infection or complications. Each class of drugs blocks the virus in different ways. Treatment involves combinations of drugs from different classes to:
- Avoid creating new drug-resistant strains of HIV
- Account for individual drug resistance
- Maximize suppression of the virus in the blood
The classes of anti-HIV drugs include:
- Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs)
- Nucleoside or nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)
- Protease inhibitors (PIs)
- Integrase inhibitors
- Entry or fusion inhibitors
Types of Viral Infection
What Is Viral Infection?
A virus is a small piece of material that looks for a host to live inside and multiply. Unlike bacteria, they can survive on their own while viruses need a living host to survive. When a virus enters the host cell, it takes over the command center of the cell and starts to imitate the copies of itself.
The viral infection occurs when a virus infects a host cell and begins replicating. The infection may be localized, known as a localized infection, or may spread throughout the body, known as a systemic infection.
What Are The Types Of Viral Infection?
Viral infections can affect different areas and systems of the body, the most common of which is the respiratory system. The following are some examples of common viral infections may include:
1. Viral Respiratory Infections
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Adenovirus
- Rhinovirus (common cold)
- Influenza (the flu)
2. Viral Infections with Skin Rashes
3. Viral Sexually Transmitted Infections
4. Other Viral Infections
- Norovirus (stomach flu)
- Viral hepatitis
How To Prevent Viral Infection?
Several viral infections can be completely avoided by a simple vaccine. Vaccines are currently available for:
- HPV
- Hepatitis B
- Chickenpox and shingles
- Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR)
- Influenza
- COVID-19
Practicing good personal hygiene and lifestyle habits is another effective strategy for preventing disease. This includes:
- Learning about strategies to reduce your risk of contact with virus-bearing vectors, like ticks and mosquitoes
- Practicing food safety techniques to lessen exposure to pathogens that can cause food poisoning
- Engaging in safe sex practices to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs)

Treatment for Viral Infection
Symptom management is usually used to treat viral infections. Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used to ease pain and reduce fever while resting for fatigue until the virus is gone. Viral infections are difficult to treat. Hepatitis C, for instance, requires a strict medication regimen for several weeks up to a few months before the virus is cleared from your body. If you take medications early enough after being exposed to other viruses, you may speed up your recovery. The medications in this category include those that treat influenza and shingles (herpes zoster). While HIV medications keep the virus under control, they do not cure it. Their primary role is to prevent it from replicating and causing more damage.
Medications used for viral infections may include:
For viral infections, their lots of things that you can do over the counter to help your symptoms. Unfortunately, there is no medication that we can give that will speed your recovery, so mainly it’s making you feel better while your body’s fighting off the infection over about a week.
Triggers of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Triggers of Irritable bowel syndrome affect the large intestine. Cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and diarrhea or constipation are the signs and symptoms of IBS. Only a small number of people with IBS have severe signs and symptoms. Some people can control their symptoms by managing their diet, lifestyle, and stress. More severe symptoms can be treated with medication and counseling.
What Triggers Irritable Bowel Syndrome?

Irritable Bowel Syndrome symptoms can be triggered by:
- Stress – most people with IBS have worse or more frequent signs and symptoms during periods of increased stress. While stress may aggravate symptoms, it doesn’t cause them.
- Food – food allergy rarely causes IBS, but many people have worse symptoms when they eat or drink certain foods or beverages, including wheat, citrus fruits, dairy products, cabbage, beans, milk, and carbonated drinks.
What Causes Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
- Muscle contractions in the intestine – Contractions that are stronger and last longer than normal can cause gas, bloating, and diarrhea. Weak intestinal contractions can slow food passage and lead to hard, dry stools.
- Nervous system – Abnormalities in the nerves in your digestive system may cause you to experience greater than normal discomfort when your abdomen stretches from gas or stool.
- Severe infection – IBS can develop after a severe bout of diarrhea caused by bacteria or a virus.
- Changes in gut microbes – changes in bacteria, fungi, and viruses, which normally reside in the intestines and play a key role in health.
How To Diagnose Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
During the first visit, your doctor will likely conduct a complete medical history, a physical examination, and tests to rule out other conditions. Your doctor will most likely use one of the following sets of diagnostic criteria for IBS once other possible causes have been ruled out:
- Rome criteria: These criteria include abdominal pain and discomfort lasting on average at least one day a week in the last three months.
- Type of IBS: For treatment, IBS can be divided into three types, based on your symptoms: constipation-predominant, diarrhea-predominant or mixed.

Warning Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Rectal bleeding
- Fever
- The onset of signs and symptoms after age 50
- Weight loss
- Nausea or recurrent vomiting
- Anemia related to low iron
- Abdominal pain, especially if it’s not related to a bowel movement, or occurs at night
- Diarrhea that is persistent or awakens you from sleep
Treatment for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
The following types of drugs are used to treat IBS:
- Antibiotics such as Amoxicillin
- Bulking agents
Causes of Rabies
The rabies virus spreads to humans through the saliva of infected animals. Most often, the virus is transmitted through bites.
Rabies is most often transmitted by bats, coyotes, foxes, raccoons, and skunks in the United States. Most rabies cases in developing countries are caused by stray dogs.
A person with rabies will almost always die once they show signs and symptoms of the disease. For this reason, anyone who may have a risk of contracting rabies should receive rabies vaccinations for protection.
Causes of Rabies
The rabies virus causes a rabies infection. The virus can spread via the saliva of infected animals which can spread the virus by biting another animal or a person.
In rare cases, rabies can be spread when infected saliva gets into an open wound or the mucous membranes, such as the eyes or mouth. This could happen if an infected animal licked an open cut on your skin.
Signs and Symptoms of Rabies

The first signs and symptoms of rabies may be very similar to those of the flu and may last for days. Later signs and symptoms may include:
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Headache
- Nausea
- Agitation
- Hyperactivity
- Anxiety
- Confusion
- Difficulty swallowing
- Excessive salivation
- Insomnia
- Partial paralysis
- Fear brought on by attempts to drink fluids because of difficulty swallowing water
Diagnosis of Rabies
There is no way to know whether the animal has the rabies infection at the time a potentially rabid animal bites you. Also, it is common not to find bite marks. Your doctor may recommend several tests to detect the rabies virus. However, they may need to be repeated later to confirm whether you are carrying the virus.
Your doctor will likely recommend treatment as soon as possible to prevent the rabies virus from infecting your body if there’s a chance you may have been exposed to the rabies virus.

Treatment for Rabies
If you have been bitten by an animal that is known to have rabies, you will receive shots to prevent the rabies virus from infecting you. If the animal that bit you can’t be found, it may be safest to assume that the animal has rabies. However, this will depend on several factors, such as the type of animal and the situation in which the bite occurred.
Rabies shots include:
- A fast-acting shot (rabies immune globulin) to prevent the virus from infecting you. This is given if you haven’t had the rabies vaccine.
- A series of rabies vaccinations to help your body learn to identify and fight the rabies virus. If you haven’t previously had the rabies vaccines, you’ll receive four injections over 14 days. If you have had the rabies vaccine, you’ll have two injections over the first three days.
If rabies is left untreated, it is almost always fatal. When someone with rabies starts experiencing symptoms, they usually do not survive. This is why it is very essential to seek medical attention right away following an animal bite, especially if the bite is from a wild animal.
Symptoms and Causes of Lazy Eye
A lazy eye is also known as amblyopia. This condition is characterized by a reduced vision in one eye caused by abnormal visual development early in life. The lazy eye often wanders inward or outward. This condition usually develops from birth up to age 7 years. It is the leading cause of decreased vision among children. Rarely, lazy eye affects both eyes.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent long-term problems with your child’s vision. The eye with poorer vision can usually be corrected with glasses or contact lenses, or patching therapy.
What are the symptoms of a Lazy Eye?
The symptom of the lazy eye may include:
- Squinting or shutting an eye
- Head tilting
- Poor depth perception
- Abnormal results of vision screening tests
- An eye that wanders inward or outward
- Eyes that appear to not work together
See a doctor if you notice an eye wandering after the first few weeks of life. A vision check is especially important if there’s a family history of crossed eyes, childhood cataracts, or other eye conditions.
What causes Lazy Eye?
A lazy eye develops as a result of abnormal visual experiences early in life which alter the nerve pathways between the thin layer of tissue behind the eye and the brain. Weakened eyes are less sensitive to visual stimuli. As the ability of the eyes to work together diminishes, the brain suppresses or ignores input from the weaker eye. Lazy eyes can be caused by anything that blurs a child’s vision or causes the eyes to cross or turn out. Among the most common causes are:
- Muscle imbalance (strabismus amblyopia)
- The difference in sharpness of vision between the eyes (refractive amblyopia)
- Deprivation is a problem with one eye.
Diagnosis of Lazy Eye

A doctor will perform an eye exam to check for eye health, wandering eyes, differences in vision between both eyes, or poor vision in both eyes. The eyes are usually dilated with eyedrops. It is common for eye drops to cause blurred vision for several hours to a day. The method used to test vision depends on your child’s age and stage of development:
- Preverbal children – a lighted magnifying device can be used to detect cataracts.
- For children aged 3 and older – tests using pictures or letters can assess the child’s vision. Each eye is covered in turn to test the other.
Treatment for Lazy Eye
Treatment options depend on the cause of the lazy eye and on how much the condition is affecting the vision. Your doctor might recommend:
- Corrective eyewear
- Eye patches
- Bangerter filter
- Surgery
- Eyedrops
For most children with lazy eyes, proper treatment improves vision within weeks to months. Treatment might last from six months to two years.
Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism is a condition that causes a combination of the movement abnormalities seen in Parkinson’s disease. These include slowness, stiffness, tremor, and imbalance. However, not everyone who has Parkinsonism has Parkinson’s disease.
The most common form of Parkinsonism is Idiopathic Parkinson’s. A person who has Parkinsonism will also have another disorder that causes additional neurological symptoms, ranging from dementia to the inability to look up and down.

Symptoms of Parkinsonism
People with Parkinsonism usually start to develop symptoms at anywhere from age 50 to 80. Parkinson’s disease can cause varying and progressive symptoms throughout its course. Some of the most common symptoms associated with the disease include:
- Slowed, affected movements
- Difficulty showing facial expressions
- Muscle stiffness
- Tremor, especially on one hand
- Speech changes
A person with Parkinsonism may have some of these symptoms. Other symptoms of the disease may include:
- Dementia
- Rapid onset and progression of symptoms
- Early problems with balance
- Issues with the autonomic nervous system, such as problems with controlled movements or spasms
- Each underlying cause of Parkinsonism, such as dementia with Lewy bodies, also has its own unique set of symptoms.
What Causes Parkinsonism?
Parkinsonism can be caused by Parkinson’s disease itself as well as another underlying condition. Other causes may include:
- Repeated head trauma, such as injuries sustained in boxing
- Medications such as those used to treat psychosis, major psychiatric disorders, and nausea
- Certain neurodegenerative disorders, such as multiple system atrophy, Lewy body dementia, and progressive supranuclear palsy
- Exposure to toxins, such as cyanide, carbon monoxide, and organic solvents
- Certain brain lesions, such as tumors, or fluid buildup
- Metabolic and other disorders, such as Wilson’s disease or chronic liver failure

How to diagnose Parkinsonism?
- A doctor will start by taking a person’s health history and reviewing their current symptoms. They will ask for a medication list to determine if any medicines could be causing the symptoms.
- A doctor will also recommend blood testing to check for underlying potential causes.
- In addition, a doctor will also order imaging scans to examine the brain and body for other causes, such as a brain tumor.
- Doctors can perform a test that tracks the movement of dopamine in the brain. This is known as the DaT-SPECT test.
Treatment for Parkinsonism
These medications are related to dopamine and can increase the amount of dopamine available in the brain. However, people with Parkinsonism not only have problems producing dopamine but also have damaged or destroyed cells that cannot respond to dopamine. Doctors can find Parkinsonism challenging to treat because the symptoms of the condition do not always respond as well or at all to medications that boost dopamine.
Parkinsonism treatment usually helps reduce the symptoms whenever possible to help them maintain independence. Doctors often recommend physical and occupational therapy because they can help a person keep their muscles strong and improve balance.
Measles: Signs and Symptoms
Measles is a childhood infection caused by a virus that can now almost always be prevented with a vaccine. This infection is also called rubeola. Measles can be serious and even fatal for small children. For more than a decade, the infection hasn’t been widespread in the U.S. as they have a high vaccination rate in general.
Most of the measles cases originated outside the country and occurred in people who were unvaccinated or who didn’t know whether or not they had been vaccinated.
What Causes Measles?
Measles is caused by an extremely contagious virus called morbillivirus. If 10 people weren’t vaccinated in a room with someone with measles, 9 of them would get measles. This infection is spread by:
- Sharing drinks or food with someone with measles.
- Contaminated droplets are spread through the air when you sneeze, cough, or talk.
- Kissing someone who has measles.
- Shaking hands or holding hands or hugging someone with measles.
- From pregnant people to their babies either during the pregnancy, delivery, or while nursing.

What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Measles?
The signs and symptoms of measles appear around 10 to 14 days after exposure to the virus. The signs and symptoms usually may include:
- Fever
- Runny nose
- Sore throat
- Dry cough
- Inflamed eyes
- A skin rash made up of large, flat blotches that often flow into one another
- Tiny white spots with bluish-white centers on a red background are found inside the mouth on the inner lining of the cheek
How to Diagnose Measles?
Your doctor can usually diagnose measles depending on the characteristics of the disease. However, many doctors have never seen measles, and the rash can be confused with several other illnesses. If needed, a blood test can confirm whether the rash is truly measles. The measles virus can also be established with a test that usually uses a throat swab or urine sample.
Treatment for Measles
There’s no exact treatment for established measles infection. However, some measures can be taken to protect vulnerable individuals who have been exposed to the virus.
- Immune serum globulin – infants, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems who are exposed to the virus may receive an injection of antibodies called immune serum globulin. These antibodies can prevent measles or make symptoms less severe when given within six days of exposure to the virus.
- Post-exposure vaccination – Non-immunized people, including infants, may be given the measles vaccination within 72 hours of exposure to the measles virus to protect against the disease.

Medications used for measles:
You should not give aspirin to children or teenagers who have measles symptoms. Though aspirin is approved for use in children older than age 3, children and teenagers recovering from chickenpox or flu-like symptoms must never take aspirin. Aspirin has been linked to Reye’s syndrome, a rare but potentially life-threatening condition, in such children.
Pregnancy and Postpartum Depression
Recent research shows that about 1 in 8 women experience symptoms of postpartum depression. Also, a recent analysis found the rate of depression diagnoses at delivery is increasing and it was seven times higher in the present years.
Having a baby is challenging and every woman deserves support. If you are experiencing emotional changes or think that you may be depressed, make an appointment to talk to your health care provider as soon as possible. Most people get better with treatment and getting help is the best thing you can do for you and your baby.
When Do Symptoms of Postpartum Depression Occur?
Symptoms usually develop within the first few weeks after giving birth, but may begin earlier, during pregnancy, or later up to a year after birth. Women with postpartum depression have intense feelings of sadness, anxiety, or despair that prevent them from being able to do their daily tasks. This condition may be mistaken for baby blues at first, but the symptoms are more intense and last longer, and may eventually interfere with your ability to care for your baby and handle other daily tasks.

Postpartum Depression Symptoms
- Intense irritability and anger
- Fear that you’re not a good mother
- Hopelessness
- Depressed mood or severe mood swings
- Loss of appetite or eating much more than usual
- Excessive crying
- Difficulty bonding with your baby
- Diminished ability to think clearly, concentrate or make decisions
- Withdrawing from family and friends
- Inability to sleep or sleeping too much
- Overwhelming fatigue or loss of energy
- Reduced interest and pleasure in activities you used to enjoy
- Recurrent thoughts of death or suicide
- Feelings of worthlessness, shame, guilt, or inadequacy
- Restlessness
- Severe anxiety and panic attacks
- Thoughts of harming yourself or your baby
Can Postpartum Depression Be Prevented Or Avoided?
Postpartum depression cannot be prevented or avoided. However, if you have a history of depression or postpartum depression after giving birth to other children, you can prepare for it by keeping your mind and body healthy. Eat healthy during your pregnancy, exercise, and learn stress reduction strategies. Once your baby is born, stay away from alcohol and caffeine. Continue to make healthy lifestyle decisions.
Treatment for Postpartum Depression
Effective depression treatment can include a combination of medication therapy, counseling, and referrals. When discussing medications with your provider, let her or him know if you are pregnant, thinking about becoming pregnant, or breastfeeding. You and your provider can decide if taking medicine while pregnant or breastfeeding is right for you.
See your doctor earlier in your pregnancy or sooner after giving birth if you are worried you will have postpartum depression. Postpartum depression is treated much like any other depression. Support, counseling or talk therapy, and prescription medicines such as antidepressants can help.
Treatment for HPV Infection
What is HPV Infection?
HPV Infection is a viral infection that causes skin or mucous membrane growths. There are more than 100 varieties of human papillomavirus (HPV). Some types of infection cause warts and others might cause certain types of cancer.
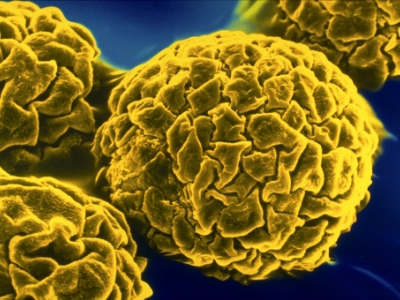
What causes HPV Infection?
HPV is transmitted to your body through a cut, abrasion, or small tear in your skin. It is mainly transmitted through direct skin contact. HPV infections in the genital region can be contracted through sexual activity, anal sex, and another skin-to-skin contact. In some cases, HPV infections resulting in oral or upper respiratory lesions can be contracted through oral sex.
Your baby may get an infection if you have an HPV infection with genital warts while you are pregnant. A noncancerous growth in the baby’s voice box (larynx) may be caused by the infection.
What are the symptoms of HPV Infection?
In most cases, your body’s immune system defeats an HPV infection before it creates warts. When warts do appear, they vary in appearance depending on which kind of HPV is involved:
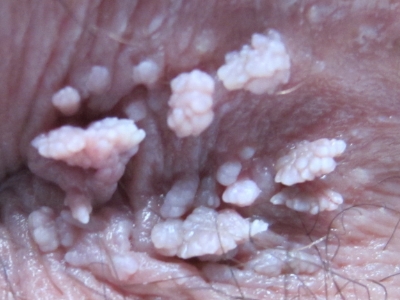
- Plantar warts: These are hard, grainy growths that usually appear on the heels or balls of your feet.
- Flat warts: These are flat-topped, slightly raised lesions. Flat wars can appear anywhere, but children usually get them on the face and men in the beard area.
- Genital warts: These might appear as flat lesions or tiny stem-like protrusions. In women, genital warts appear mostly on the vulva. In men, genital warts appear on the penis and scrotum or around the anus.
- Common warts: These might appear as rough, raised bumps and usually occur on the hands and fingers.
Who is at risk of having HPV Infection?
Risk factors for HPV infection include:
- Common warts occur mostly in children. Genital warts occur most often in adolescents and young adults.
- The more sexual partners you have, the more likely you are to contract a genital HPV infection.
- Touching someone’s warts or not wearing protection before contacting surfaces that have been exposed to HPV might increase your risk of HPV infection.
- Areas of skin that have been punctured or opened are more prone to develop common warts.
- People who have weakened immune systems are at greater risk of HPV infections.
Treatment for HPV Infection
Medications to reduce the infection are usually applied directly to the lesion and usually take many applications before they are successful. Examples include:
- Imiquimod – This prescription cream might enhance the ability of your immune system to fight HPV. Imiquimod is in a class of medications called immune response modifiers. It treats genital and anal warts by increasing the activity of the body’s immune system.
Symptoms and Causes of Contact Dermatitis
Contact Dermatitis is an itchy rash that is caused by direct contact with a substance or an allergic reaction to it. The rash is not contagious or life-threatening, but it can be very uncomfortable. Many substances can cause such reactions including plants, jewelry, fragrances, cosmetics, and soaps.
For successful treatment of Contact Dermatitis, you need to categorize and avoid what causes your reaction, if you can avoid certain substances, the rash will eventually clear up in 2-4 weeks.
What are the symptoms of Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis usually occurs on areas of your body that have been directly exposed to the reaction-causing substance. The rash usually develops within minutes to hours of exposure and can last 2-4 weeks.
Symptoms of contact dermatitis may include:
- A red rash
- Bumps and blisters, sometimes with oozing and crusting
- Dry, cracked, scaly skin
- Swelling, burning, or tenderness
- Itching, which may be severe
See your doctor if any of the following occurs:
- You are embarrassed by the way your skin looks
- The rash affects your face or genitals
- The rash doesn’t get better within three weeks
- The rash is so uncomfortable that you are losing sleep or are distracted from your daily activities
- The rash is sudden, painful, severe, or widespread
Seek medical care right away if the following situations happen:
- You think the rash has damaged the mucous lining of your mouth and digestive tract.
- Your lungs, eyes, or nasal passages are painful and inflamed, perhaps from inhaling an allergen.
- You think your skin is infected.
What Causes Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is caused by a substance that you’re exposed to which can irritate your skin or might trigger an allergic reaction. The substance could be one of the thousands of known allergens and irritants. Some people react to strong irritants after a single exposure. Others may develop symptoms after repeated exposures to even mild irritants, while some people develop a tolerance to the substance over time.

Common irritants that cause contact dermatitis include:
- Bleach and detergents
- Shampoos
- Solvents
- Rubbing alcohol
- Airborne substances
- Plants
- Fertilizers and pesticides
Treatment for Contact Dermatitis
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
To help lessen itching and soothe the infected skin, try these self-care approaches:
- Protect your hands
- Soak in a comfortably cool bath
- Avoid scratching
- Apply cool, wet compresses
- Take an oral anti-itch drug
- Apply an anti-itch cream or lotion to the affected area
- Avoid the irritant or allergen
Medication used:
- Clobetasol – is a corticosteroid used in the treatment of dermatological problems. This medicine is in a class of medications called corticosteroids that works by activating natural substances in the skin to reduce swelling, redness, and itching.
Herpes
Herpes is a common virus that causes sores on your genitals or mouth. It can be annoying and painful, but it usually doesn’t lead to serious health problems. This infection is easily spread from skin-to-skin contact with someone who has the virus.

What Are The Symptoms Of Herpes?
Primary symptoms occur when a person first develops the infection. Alongside sores or blisters, herpes may cause:
- Pain and itching
- Fatigue and a general feeling of being unwell
- Swollen lymph nodes
- A fever
- You might have these other symptoms too:
- Itching
- Pain around your genitals
- Burning when you pee if your urine touches the herpes sores
- Having trouble peeing because the sores and swelling are blocking your urethra
Herpes symptoms come and go, but that doesn’t mean the infection goes away or that you can’t spread it to other people. Once you have herpes, it might stay in your body for life.
What Causes Herpes?
Herpes infection is caused by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. These viruses are contagious and transmitted from one person to another through the skin to skin contact. Touching or kissing is the main cause of herpes simplex virus type 1 and sexual contact is the main cause of herpes simplex virus type 2 transmission.
Lifestyle Risk Factors of Herpes
Herpes is a common virus and there is an especially high risk of exposure associated with certain activities including:
- Unprotected sex – herpes simplex virus type 2 is most often transmitted from one person to another through sex. Having multiple sexual partners and having unprotected sex with partners who could be infected raise your risk.
- Sharing items – The herpes simplex virus type 1 virus can be transmitted by sharing items that have recently been exposed to the virus.
- Kissing – Kissing or other mouth contact is one of the most common ways of transmission of herpes simplex virus type 1.
- Prolonged skin-to-skin contact – Herpes gladiatorum, a type of infection caused by herpes simplex virus type 1, is characterized by sores on the face, head, and neck. This type of herpes infection is most often noted among wrestlers.
How to Diagnose Herpes?
Herpes can be diagnosed based on the appearance of lesions and laboratory tests. In general, if you don’t have any symptoms, there is no need for you to have any diagnostic testing for herpes simplex virus type 1. However, if you may have been exposed to the herpes simplex virus type 2, you may need to be tested even if you do not have lesions. The two types of herpes may cause visible skin lesions. You must see a healthcare provider, especially if you’ve never had an outbreak before.

Treatment and Medication for Herpes
Certain symptoms of herpes such as blisters typically improve on their own, without medical treatment. But if you experience severe or frequent outbreaks, a doctor can prescribe antiviral medications. Options include:
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections can affect anyone, and they can affect a wide range of body parts. This infection can be caused by a variety of fungi. Occasionally, fungi that are normally present on or inside your body can multiply out of control and lead to an infection.
Infections caused by fungi can be contagious. They can be transmitted from person to person. Disease-causing fungi can also be caught from infected animals or soil that is contaminated. If you develop signs or symptoms of a fungal infection, make an appointment with your doctor.
Types and Symptoms of Fungal Infections
1. Athlete’s foot
It’s a type of fungal infection that can affect the skin on your feet, as well as your hands and nails. The infection is caused by dermatophytes, a group of fungi that can thrive in the warm and humid areas between your toes.
Common symptoms may include:
- Itching, stinging, or burning sensation between your toes or on other parts of your foot
- Crack, peel, or blister on the skin
2. Jock itch
It’s a fungal infection that can affect the skin on your groin area, as well as your inner thighs and buttocks. This type of infection mostly affects men and boys, but women and girls can develop it too.
The symptoms of Jock itch are:
- Changes in skin color
- Flaking or cracking skin
- Itchiness
- A burning feeling
- Redness
- A rash that gets worse when you exercise

3. Ringworm
This affects the skin and scalp. Ringworm is also part of a group of fungi that grow on the skin, particularly in damp and humid parts of your body. This usually starts as a scaly, itchy rash. Over time, patches of ringworm can spread and form red rings.
4. Yeast infection
It is normal for lesser quantities of candida Albicans to be present on your skin and in your body. But when these fungi grow too much, they can cause an infection known as a yeast infection. In women, vaginal yeast infections are relatively common. They can cause:
5. Onychomycosis, or fungal infection of the nail
This usually starts as a small light-colored spot on your nail. Over time, it can cause your nail to become thicker and more brittle.
Common symptoms may include:
- Thick or brittle nail
- Lifting off the nail bed
- Flakiness or crumbling of the nail
- White or yellow streaks under the nail
- Scaling under the nail

Diagnosis for Fungal Infections
Diagnosis of fungal infection will begin with a physical exam and discussion of your symptoms. For fungal infections affecting other parts of the body, your physician may take a sample of bodily fluids, including:
- Blood
- Vaginal secretions
- Sputum
- Urine
- Cerebrospinal fluid
In some cases, your physician may take a biopsy of the affected organ. In the case of fungal masses in the respiratory system, an X-ray can help determine the amount of tissue damage.
Treatment and Medication for Fungal Infections
Some types of medications can reduce your body’s ability to ward off fungal infections. For example, antibiotics destroy helpful bacteria along with harmful bacteria. Antibiotics you can use include:
Bacterial Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a common lung infection where the air sacks of the lungs are inflamed. These sacs may also be filled with cellular debris, pus, and fluid.
Bacterial Pneumonia may involve just one small section of the lung or might include both lungs. The condition can make it tough for your body to get sufficient oxygen to your blood which may cause cells not to function well.
This type of pneumonia can be mild or serious. The severity of your condition may depend on:
- Your age
- Overall health
- The strength of the bacteria
- How quickly you are diagnosed and treated
- If you have other diseases
What causes Bacterial Pneumonia and who is at risk of developing the condition?

Bacterial pneumonia is caused by bacteria that enter the lungs and multiply. It can develop independently or as a result of another illness, such as a cold or the flu.
People who are at higher risk for pneumonia include:
- Smoking
- Living or working in a hospital setting or nursing facility
- Working in an environment with a lot of pollution
People who have these conditions may also be at an increased risk for pneumonia:
- Weakened immune system due to illness or medications
- Recent viral respiratory infections, such as the flu
- Chronic lung diseases
- Difficulty swallowing due to neurological conditions such as dementia or stroke
Doctors classify bacterial pneumonia based on whether it developed inside or outside a hospital.
What are the symptoms of Bacterial Pneumonia?
The most common symptoms of bacterial pneumonia are:
- Stabbing chest pain that worsens when coughing or breathing
- Sudden onset of chills severe enough to make you shake
- Cough with thick yellow, green, or blood-tinged mucus
- Fever of 102-105°F or above
- Other symptoms that may follow include:
- Breathlessness or rapid breathing
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Lethargy or severe fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Sweating
- Moist, pale skin
- Confusion, especially among older persons
Older adults will share all the symptoms with younger adults, but are much more likely to experience dizziness and confusion. Older adults may also be less likely to have a fever.
How to diagnose Bacterial Pneumonia?
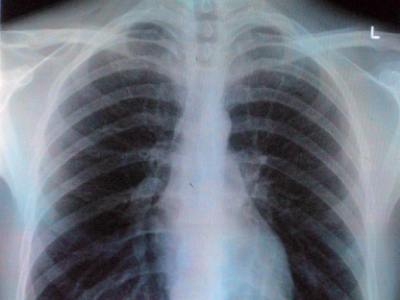
During your doctor’s first visit, he or she will ask about your medical history and perform a physical exam. A stethoscope will be used to listen to your lungs for abnormal crackling or bubbling sounds that could indicate pneumonia.
If pneumonia is suspected, your doctor may recommend the following tests:
- Sputum test
- Pulse oximetry
- Chest X-ray
- Blood tests
If you’re older than age 65 and have serious symptoms or health conditions, your doctor might order additional tests. These may include:
- Pleural fluid culture
- CT scan
Treatment and Medication for Bacterial Pneumonia
As part of pneumonia treatment, the infection must be cured and complications avoided. In most cases, community-acquired pneumonia can be treated at home with medication. Symptoms usually go away within a few days or weeks, but the tiredness can last for a month or more.
Medications recommended for the treatment of Bacterial Pneumonia include:
Types of Nutrients and Their Sources
A healthy balanced diet consists of the right amount of nutrients that the body needs to function well. The body of a person is a machine and the food is the fuel.
A person needs to consume all the types of nutrients to ensure the best possible health. These nutrients support vital functions including growth, the immune the central nervous system, and preventing disease.
The Essential Types Of Nutrients Are:
1. Minerals
Minerals are the second type of micronutrients. There are two groups of minerals known as major and trace minerals. The body needs a balance of minerals from both groups for optimal health.
Major minerals are:
- Chloride
- Potassium
- Sodium
- Sulfur
- Phosphorus
- Calcium
- Magnesium
Trace minerals are:
- Molybdenum
- Fluoride
- Iodine
- Copper
- Chromium
- Manganese
- Zinc
- Selenium
- Iron

You may get these nutrients on:
- Beans and legumes
- Whole grains
- Egg yolks
- Fortified bread and cereals
- Poultry
- Fruits
- Leafy greens
- Vegetables
- Nuts and seeds
- Milk and other dairy products
- Iodized table salt
- Seafood
- Red meats
2. Vitamins
Vitamins offer a range of health benefits including:
- Aiding brain and nervous system functioning as well as calcium absorption
- Supporting healthy blood
- Helping the body metabolize carbs and proteins
- Maintain healthy skin
- Strengthening bones and teeth
- Helping prevent or delay certain cancers
- Boosting immune system
Typically, an individual who eats a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can get all the vitamins needed in their food. On the other hand, those who eat fewer vegetables and fruits, and those with digestive conditions may need to take a vitamin supplement to lessen or avoid a deficiency.
3. Fats
People often link high-fat foods with bad health. Conversely, a person needs certain fats to help maintain optimal health. Fats give the body energy and help it carry out a range of functions. You can find healthful fats in several foods including:
- Seeds
- Vegetable oils
- Nuts
- Fish such as tuna and salmon
4. Protein
Protein is a micronutrient that each cell in the body needs to function well. It helps with the growth and development of bones, hair, muscles, and skin. It also serves as a fuel source for cells and tissues when needed.
The following foods are good sources of protein:
- Nuts
- Soy
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Beans and legumes
- Fish and other seafood
- Poultry
- Red meats
- Some grains including quinoa
5. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are needed for the body. These are sugars and starches that give energy to all the cells and tissues in the body. Carbohydrates support the following:
- Digestive function
- Energy to perform the task
- The nervous system and immune system
- Brain function
The following foods have carbohydrates:
- Barely
- Fruits
- Oatmeal
- Whole grain pasta and bread
- Vegetables
- Brown rice
- Quinoa
6. Water
Water is the most important nutrient needed. The human body is made up of mostly water. Each cell needs water to function. Water helps with several functions:
- Hydration
- Preventing constipation
- Transporting nutrients
- Shock absorption
- Flushing toxins out
The best source for water is to drink natural, unsweetened water from tap or bottled sources. Also, you can get extra water by consuming fruits that have a large amount of water.
Survival Rate of Ovarian Cancer
Living with ovarian cancer may make you wonder about the prognosis. While knowing the prognosis could be helpful, it is important to know that it is only a general guideline. The individual outlook depends on several factors such as age and overall health or wellbeing.
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of an individual with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They can’t tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
A 5-Year Relative Survival Rate
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of cancer to people in the overall population. For instance, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a certain stage of ovarian cancer is 80%, it means individuals who have that cancer are, on average, about 80% as likely as people who don’t have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Survival Rate for Ovarian Cancer
These rates are adjusted to account for women with ovarian cancer who die of other causes.
- If ovarian cancer is confined to the ovary when it’s found, the 5-year survival rate is about 92%. Note that few ovarian cancers are found at this stage.
- For all stages of ovarian cancer combined, the overall 5-year survival rate is 46%. Women who are younger when diagnosed tend to do better than older women with ovarian cancer.
- Ovarian cancer that’s grown just outside the ovary into nearby tissues has a 5-year survival rate of about 73%.
- The 5-year survival rate for women with ovarian cancer that has spread to distant parts of the body is about 28%.
What Affects Survival?
Your outcome depends on the stage of cancer when it was diagnosed. This means how big it is and whether it has spread. The type and grade of ovarian cancer affect your likely survival. Grade means how abnormal the cells look under the microscope. Your likely survival can be affected as well by whether the surgeon can remove all the tumors during the initial surgery.
Your overall health and fitness may also be affected by your survival. Doctors have a way of grading how well you are. This is called performance status. Women who have a good performance status have a better outlook. In addition, age may also affect the outcome and survival.
About the survival rates and what you might expect, you may ask your healthcare provider. Keep in mind that statistics are based on large groups of people. They cannot be used to say what will happen to you. No two people are exactly alike. Treatment and how well people respond to treatment vary.
Immune-Boosting Foods
The immune system plays an important role in keeping a person healthy. It consists of organs, cells, tissues, and proteins. They work together to ward off pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, and foreign bodies that can cause infection or disease. A pathogen triggers an immune response when it comes in contact with the immune system. Antibodies produced by the immune system attach to antigens on pathogens and kill them.
By including specific foods in one’s diet, one may be able to strengthen his or her immune system. Continue reading to discover immune system-boosting foods.
The following foods may help boost the immune system:
1. Berries
Berries have very potent antioxidants. By combating oxidative stress in the body, they boost your immunity and reduce inflammation.

2. Citrus Fruits
Citrus fruits such as grapefruits, oranges, and lemons are high in vitamin C that boosts the immune system and are thought to increase the production of white blood cells. White blood cells are key to fighting infections that ensure you are as healthy as can be.
3. Turmeric
Turmeric is a natural way to boost the immune system. Due to its immunomodulating properties, this is a great ingredient to use during times of stress or cold and flu season.
4. Broccoli
Broccoli is full of minerals, calcium, iron, and vitamins A, C, and E. It is one of the healthiest foods you can eat, partly because of its high antioxidant content.
5. Spinach
Spinach is vitamin C, antioxidants, and beta-carotene which can increase the infection-fighting ability of your immune system. It does not only boosts immune function but also provides the body with needed nutrients for cell division and DNA repair which makes you healthier and more likely to fight illnesses.
6. Red Pepper
Red pepper has twice the amount of vitamin C as citrus fruits. They are also high in vitamin A and antioxidants which keep you healthy and feeling good.
7. Kimchi
Kimchi is a fermented food that has lots of probiotics. Probiotics fight inflammation, create a healthy gut, and regulate your immune system. The majority of your immune function takes place in your gut, so if you have a healthy gut, your immune system can function optimally.
8. Ginger
Ginger is a popular food to use to fight sickness. It can help lessen inflammation which helps reduce a sore throat and curb other inflammatory illnesses. Ginger is also one of the best ways to help with nausea.
9. Garlic
Garlic helps boost immune function that helps your immune system fight germs. It has alliin which has been shown to boost the response of white blood cells when they encounter viruses.
10. Oats
Whole oats have beta-glucans that increase the activity of immune cells. To glean the most benefit from oats, consume them in their whole-grain forms, such as whole-grain and steel-cut oats. The whole grain provides immune-supportive nutrients including selenium, zinc, and vitamin E.
Treatment for Eating Disorder
Eating disorders are serious, complex mental health issues that affect both one’s emotional and physical health. People who suffer from eating disorders develop a negative relationship with food, their weight, or their appearance. These are all types of eating disorders: anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating. Treatment for eating disorders is available. Untreated people can develop potentially life-threatening conditions.
Symptoms of Eating Disorder
Symptoms of eating disorders vary by type. It may be difficult to spot an eating disorder as it often mimics dieting. If you or a loved one has an eating disorder, you may notice these changes:

- Unusual sweating or hot flashes
- Unexplained weight changes or drastic weight loss
- Frequent bathroom breaks after eating
- Thinning hair or hair loss
- Fainting, fatigue, or dizziness
- Mood swings
Other changes may also include:
- Hiding food or throwing it away
- Withdrawing from friends or social activities
- Solo dining or not wanting to eat with other people
- Food rituals
- Fixation on foods, exercise, calories, or weight loss
Eating Disorder Causes
A mix of environment, genetics, and social factors play a role in the development of the eating disorder. Some people with this disorder may use extreme measures to control food when they feel like other aspects of their lives are out of control. An obsession with food becomes an unhealthy way of coping with painful feelings or emotions. Thus, eating disorders are more about finding a healthy way to manage your emotions than about food.
Risk Factors for Eating Disorder
An eating disorder can develop at any age. Certain factors may make you more prone to developing an eating disorder such as:
- History of dieting
- A history of trauma (physical, emotional, or sexual)
- Personal history of anxiety, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Family history of eating disorders, addiction, or other mental health issues, such as depression
Other factors may include:
- Major life changes such as starting a new school or job, a divorce, or a move
- Involvement in activities that focus on a slender appearance such as gymnastics, modeling, wrestling, swimming, and running
- Perfectionistic tendencies
- Diabetes (up to one-fourth of women with Type 1 diabetes develop an eating disorder)
Eating Disorder Diagnosis
An eating disorder is diagnosed based on symptoms and eating habits. Your doctor will likely perform an exam and request tests to help pinpoint a diagnosis. You may see both your primary care provider and a mental health professional for a diagnosis.
Tests generally may include:
- Psychological evaluation – A doctor or mental health professional will likely ask about your thoughts, feelings, and eating habits.
- Physical exam – Your doctor will likely examine you to rule out other medical causes for your eating issues.
Eating Disorder Treatment

Treatment for eating disorders varies depending on your needs. Even if you don’t have a diagnosed eating disorder, an expert can help you address and manage food-related issues. Treatment may include:
- Psychotherapy – a mental health expert can detect the best psychotherapy for you. This therapy helps you understand and change distorted thinking patterns that drive behaviors and emotions.
- Medications – some people with an eating disorder have depression or anxiety. Taking antidepressants can improve the condition.
- Maudsley approach – this is a family therapy that helps those with anorexia.
- Nutrition counseling – this helps improve eating habits and develop nutritious meal plans.
How To Buy Medicines Online?
In this time of the pandemic, it would be best to carry out online transactions rather than walk in. Almost everything is now available online, so medications and health products are now accessible to everyone. It is now easier than ever to find and buy medications.
The following tips can help you stay safe at all times, especially when purchasing medicine online:
• You should discuss your medication needs with your doctor. Make sure you receive the right diagnosis and treatment. Don’t try to self-medicate.
• Make sure you buy your medicines from trusted sources.
• Buy from reputable stores.
• Be wary of false claims.
How to buy medicines in Rx2Go?
Establishing a reliable source of health products is essential. Remember, you are risking your health. With Rx2Go, you can order high-quality medications shipped worldwide.
• To find your medicine, you can use our brand and generic search options on our home page, or browse through our categories or product search section.
• Fill out the quantity box for the medicine you are looking for.
• Once the selection is complete, click on checkout and provide personal information and shipping information.
Digoxin
Digoxin is a type of medicine called a cardiac glycoside. It affects certain minerals inside heart cells that lessen the strain on the heart. As a result, it helps maintain a strong, steady, and normal heartbeat.
What condition does Digoxin treat?
Digoxin is an FDA-approved medication used for the treatment of heart failure. This medicine is usually used in combination with other medications for heart failure. Treating heart failure may help maintain your ability to walk and exercise. It may also improve the strength of your heart.
This prescription can also be used for the treatment of certain types of irregular heartbeat such as chronic atrial fibrillation. Treating an irregular heartbeat can lessen the risk of blood clots. It is an effect that may reduce your risk for a heart attack or stroke.
How does Digoxin work?
Digoxin is a form of digitalis which is a drug extracted from the foxglove plant. It works directly on the heart muscle. It raises the force with which the heart muscle contracts with each heartbeat and decelerates the rate at which the heart beats. This medication makes each heartbeat more capable of pumping blood around the body.
What is the dosage of Digoxin?
Digoxin is available in the dosage form of 0.25 mg for oral use. The recommended dosage to take for this medication depends on your medical condition and response to the drug. Usually, this medication is taken once a day. Each dose is taken with or without food.
Even though you may feel well take this medication exactly as directed to keep your heart working properly. Do not take more of it than your doctor has prescribed and do not miss any doses. Take the medicine at the same time each day. This medicine works best when there is a constant amount in the blood. If you miss a dose of this prescription and you recall it within 12 hours, take it as soon as you remember. Conversely, if you do not recall until later, never mind the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule of dosing. If you miss doses for 2 or more days in a row or if you have any questions about this, contact your doctor.
When you are taking this medication, you must get the particular amount of medicine that you need. The dose of Digoxin will be different for different individuals. Your doctor will determine the correct dose of this medication for you. Follow carefully the directions on the label given by your doctor.
What are the precautions in using Digoxin?
- Before taking this medication, tell your doctor if you are allergic to it or if you have any allergies.
- Let your doctor know if you are a pregnant or breastfeeding woman.
- Infants and children may be more sensitive to the effects of this medication, especially the effects on the heartbeat.
- This medicine may make you drowsy or dizzy. You should not drive or do any activity that needs your alertness.
- While taking this medication, limit alcoholic beverages.
- If you have preserved left ventricular systolic function, you should not use this drug. It may increase your risk of side effects such as shortness of breath or chest pain.
- If you will be receiving electrical cardioversion, your dose may be decreased or 1 to 2 days before your procedure your treatment with this prescription may be stopped. This is done to prevent heart rhythm problems.
- Digoxin is not recommended for use in people having a heart attack. Using this medicine can restrict blood flow to the heart.
- This should not be used if you have myocarditis. It may narrow your blood vessels and may also cause inflammation.
- Digoxin is cleared from your body by your kidneys. If your kidneys don’t function properly, the medicine may build up to risky levels. Your dosage must be lessened if you have kidney problems.
- Digoxin is not recommended for use if you have ventricular fibrillation. It may make your ventricular fibrillation worse.
Cost of Digoxin vs. Lanoxin
The generic Digoxin is an inexpensive heart medication that only costs $0.28 per unit of 0.25 mg and $13.99 for 50 tabs. The brand name Lanoxin costs $15.13 per unit of 0.25 mg and $756.5 for 50 tabs.
Famotidine
Famotidine is in the class of medications called histamine-2 (H2) blockers. Histamine is a chemical that naturally occurs and stimulates certain cells in the stomach to create acid. H2 blockers stop the action of histamine on the cells. As a result, it lessens the production of acid.
What condition does Famotidine treat?
This is supplied as a tablet for oral use. Famotidine is available in the dosage forms of 20 mg and 40 mg. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has already approved this medication.
How does Famotidine work?
Famotidine works by stopping histamine H2 receptors that are found in the stomach lining. Histamine which is a natural body chemical usually binds to this receptor that causes the cells to create stomach acid. By stopping histamine H2 receptors, this medicine stops histamine from binding to them. This blocks the cells from making stomach acid which is made in the stomach as the usual part of the digestive course. Generally, the linings of the duodenum and stomach are protected by a layer that fights acid occurrence. On the other hand, if this layer is impaired or large quantities of stomach acid are formed, an ulcer may progress on the lining of the duodenum stomach. This is called a peptic ulcer.
In GERD, this medication lessens the production of stomach acid. It stops extra acid flowing back into the food pipe. It also permits the esophagus to heal in reflux esophagitis. By decreasing the amount of acid in the stomach and duodenum, this drug relieves the symptoms of indigestion.
What is the dosage of Famotidine?
Famotidine is to be taken by mouth. This is usually taken once or twice a day or as directed by your doctor. If you are taking this once a day, it is usually taken at bedtime. You may take each dose with or without a meal. Swallow the tablet as a whole with a full glass of water. Do not break, chew, or crush it. Remember to take it at the same time and in the same way each day. The recommended dosage is based on your medical condition, age, and response to the treatment. You should take the right dose, not more or less.
Do not stop taking this medication without the consent of your doctor. It may cause another complication or may worsen your current condition. For the best benefit from this product, take it regularly. If you missed a dose, take it as soon as you remember it or call your doctor for instructions. Do double the dose to make up for the missed dose. Let your doctor know if your condition does not improve.
What are the precautions in using Famotidine?
- Before taking Famotidine, tell your doctor if you are allergic to it. This may not be recommended for use if you have a history of an allergic reaction. Tell also if you have any allergies. This drug may contain an inactive ingredient that causes an allergic reaction.
- This medicine may make you drowsy or dizzy. Alcohol can also make you dizzier. Do not use any machinery or do activities that need your alertness until you can do it safely. Avoid alcoholic beverages.
- Be sure to tell your doctor if you are taking any other medications such as vitamins or herbal supplements.
- Before starting this treatment, discuss with your doctor about fertility. Your ability to become pregnant or father a child may be affected.
- Consult your doctor first if you are breastfeeding women.
- Let your doctor know if you have a medical history of kidney problems, immune system problems, or other stomach problems.
- Older adults might be more sensitive to the side effects of this medication.
- Do not use this for the treatment of children younger than 12 years of age unless it is directed by your doctor.
- You should not share this with others even if they have the same symptoms as yours.
- Keep this at room temperature far from heat and moisture.
Cost of Famotidine vs. Pepcid
The generic Famotidine is an inexpensive antihistamine medication that only costs:
- $0.67 per unit of 20 mg and $20 for 30 tabs
- $1 per unit of 40 mg and $30 for 30 tabs
The brand name Pepcid costs:
- $0.77 per unit of 20 mg and $23.10 for 30 tabs
- $1.28 per unit of 40 mg and $38.49 for 30 tabs
Tadacip
Tadacip (Tadalafil) is an FDA-approved medication that is in the group of medicines called phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitors.
It comes as tablets for oral use and is available in the dosage strengths of 20 mg, 40 mg, and 60 mg.
What condition does Tadacip treat?
Tadacip is a prescription medicine used for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men.
It is also known as impotence which cannot maintain or achieve a hard erect penis for sexual activity.
It occurs due to lacking blood flow into the penis.
This medication relaxes the blood vessels in the penis by increasing the blood flow. It causes an erection which is a natural response to sexual stimulation.
How does Tadacip work?
Tadalafil acts on the erectile tissue of the penis to increase the blood flow to cause an erection.
Nitric oxide is unrestricted in the erectile tissue of the penis during sexual stimulation.
Wherein, it starts the enzyme guanylate cyclase, and the enzyme increases levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP).
It relaxes the blood vessels in the penis and permits blood to fill the spongy erectile tissues to cause an erection.
Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) is another enzyme that breaks down cGMP evading blood flow into the penis that reasons to loss of an erection.
This medication prevents the work of PDE5 that settles erectile dysfunction by letting the natural route of sexual stimulation stimulate the cGMP mechanism for attaining and keeping an erection.
What is the dosage of Tadacip?
The recommended dose of Tadacip is 20 mg once each day. The dose is to be taken before anticipated sexual activity.
The medicine may be taken between 30 minutes and 36 hours before anticipated sexual activity.
Men taking the medicine may initiate sexual activity at changing time points relative to dosing to control their optimal window of reaction. Swallow the tablet with a full glass of water.
Avoid drinking alcohol while having this medicine. Alcohol may affect your ability to get an erection.
The dosage can be lowered to 10 mg dependent on individual reaction and tolerability.
This medication may be taken with or without food. You should only take the medication when you plan to have sex.
It is not intended as a regular medication.
Let your doctor and pharmacist know about all the products you use including non-prescription, prescription drugs, food supplements, and herbal products.
If your condition does not improve, call your doctor.
What are the precautions in using Tadacip?
- Tadacip can cause a mild and short-lasting cut in blood pressure levels. Caution must be exercised if you are taking any medicine for lowering high blood pressure levels. It is recommended that you report all your current medicines to the doctor before beginning treatment with this medicine.
- This medicine should not be used in people who are receiving medicines such as riociguat and nitroglycerine. It may cause an increased risk of having serious adverse effects.
- This drug must be used carefully in patients receiving medicines to treat heart diseases and high blood pressure levels.
- In patients having a physical deformity of the penis because of cavernosal fibrosis, angulation, or Peyronie’s disease, Tadacip should be taken with caution. There is a high risk of permanent loss of sexual potency if this drug is used in patients suffering from these conditions.
- Tadacip must be taken with extreme caution if you have a disease of the blood vessels and heart. It is not recommended for use in patients who have suffered from a stroke, heart attack, or life-threatening arrhythmia within the last 6 months.
- This medicine is not recommended for use in patients less than 18 years of age since the safety and efficacy of use are not clinically established.
- This is not recommended for use in females. This is also not recommended for use if you are breastfeeding or pregnant.
- Do not use this prescription in any other condition if not given by your doctor.
Cost of Tadacip vs. Cialis
The Tadacip (Tadalafil) only costs:
- $36 for 30 pills of 20 mg
- $42 for 30 pills of 40 mg
- $83 for 30 pills of 60 mg
The brand name Cialis costs:
- $105 for 30 pills of 20 mg
- $135 for 30 pills of 40 mg
- $150 for 30 pills of 60 mg
Tamsulosin
Tamsulosin is in the class of medicines called alpha-adrenergic blockers. This relaxes the muscles in the prostate and bladder so that urine can flow easily. This medicine comes as a capsule for oral use.
What condition does Tamsulosin treat?
Tamsulosin is an FDA-approved medication used by men to treat the symptoms of an enlarged prostate. This type of condition is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). This medication helps to relieve symptoms of BPH such as:
- Weak stream
- Difficulty in beginning the flow of urine
- The need to urinate often or urgently during at middle of the night
How does Tamsulosin work?
Tamsulosin works by blocking alpha receptors that can be found in the muscle in the prostate gland. The prostate gland is only found in a man that lies at the top of the tube that connects the bladder to the outside. It often enlarges with advancing age, obstructing the flow of urine from the bladder and pressing on the urethra. This can reason to various symptoms of being unable to empty the bladder, difficulty passing urine, and needing to pass urine more urgently or often.
This medication causes the muscle in the prostate to relax. This relieves the pressure on the urethra and allows urine to flow freely past the prostate gland. Wherein, it makes it easier to pass urine and empty the bladder.
What is the dosage of Tamsulosin?
Before taking Tamsulosin, your doctor and pharmacist must know that you:
- Have ever fainted after passing urine
- Have any problems with the way your liver and kidneys works
- Have ever had an allergic reaction to a medicine or this medicine
- Ever faint or feel dizzy when you stand up
- Are using or taking any other medications. This includes any medicines you are taking which are available to buy without a prescription, as well as herbal and complementary medicines.
Take Tamsulosin exactly as your doctor tells you to do so. Swallow each medicine with a glass of water. Do not chew or break the capsules. Your first dose of this medicine may make you feel dizzy. You must take it just before you go to bed. If you feel dizzy or you start sweating, remain lying down until these symptoms have gone.
Take one capsule each day. Once the first dose is done, you can take your dose at a time of day that is appropriate for you. Even though you may take the medicine either before or after a meal, the usual advice is to take your doses after the same meal of the day each day.
What are the precautions in using Tamsulosin?
- Tamsulosin may cause dizziness mostly when you first start taking it. This might affect your capability to drive. Make sure your responses are normal before you drive or do things that would be risky if you were not fully alert.
- Try to keep your regular appointments with your doctor. This is so your doctor can check on your progress. Your doctor may want to take your blood pressure from time to time, particularly when you first start the treatment.
- You are advised not to drink alcohol while you are on Tamsulosin. Alcohol increases the risk of side effects from this drug.
- Consider reducing or stopping the amount of caffeine you drink. Caffeine may make your symptoms worse, so you need to drink less of these things.
- If you are a smoker, stopping smoking may significantly improve your symptoms. This is because nicotine irritates the bladder. You can ask your doctor for advice on quitting.
- If you are having an operation or dental treatment, tell the person carrying out the treatment that you are taking Tamsulosin. Your blood pressure might drop rapidly if you will be having an anesthetic.
- If you are having also cataract surgery, it is mainly essential that you tell your surgeon that you are taking Tamsulosin. Since floppy iris syndrome is an eye problem that has developed in some people and your doctor might recommend you to stop taking this medication for a short while.
Cost of Tamsulosin vs. Flomax
The generic Tamsulosin comes in a strength of 0.4 mg that only cost:
- $0.57 per unit of 0.4 mg and $17 for 30 pills
The brand name Flomax costs:
- $2.17 per unit of 0.4 mg and $64. 95 for 30 pills




