What Is Viral Infection?
A virus is a small piece of material that looks for a host to live inside and multiply. Unlike bacteria, they can survive on their own while viruses need a living host to survive. When a virus enters the host cell, it takes over the command center of the cell and starts to imitate the copies of itself.
The viral infection occurs when a virus infects a host cell and begins replicating. The infection may be localized, known as a localized infection, or may spread throughout the body, known as a systemic infection.
What Are The Types Of Viral Infection?
Viral infections can affect different areas and systems of the body, the most common of which is the respiratory system. The following are some examples of common viral infections may include:
1. Viral Respiratory Infections
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Adenovirus
- Rhinovirus (common cold)
- Influenza (the flu)
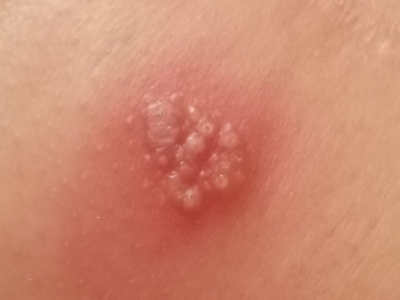
2. Viral Infections with Skin Rashes
3. Viral Sexually Transmitted Infections
4. Other Viral Infections
- Norovirus (stomach flu)
- Viral hepatitis
How To Prevent Viral Infection?
Several viral infections can be completely avoided by a simple vaccine. Vaccines are currently available for:
- HPV
- Hepatitis B
- Chickenpox and shingles
- Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR)
- Influenza
- COVID-19
Practicing good personal hygiene and lifestyle habits is another effective strategy for preventing disease. This includes:
- Learning about strategies to reduce your risk of contact with virus-bearing vectors, like ticks and mosquitoes
- Practicing food safety techniques to lessen exposure to pathogens that can cause food poisoning
- Engaging in safe sex practices to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs)

Treatment for Viral Infection
Symptom management is usually used to treat viral infections. Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used to ease pain and reduce fever while resting for fatigue until the virus is gone. Viral infections are difficult to treat. Hepatitis C, for instance, requires a strict medication regimen for several weeks up to a few months before the virus is cleared from your body. If you take medications early enough after being exposed to other viruses, you may speed up your recovery. The medications in this category include those that treat influenza and shingles (herpes zoster). While HIV medications keep the virus under control, they do not cure it. Their primary role is to prevent it from replicating and causing more damage.
Medications used for viral infections may include:
For viral infections, their lots of things that you can do over the counter to help your symptoms. Unfortunately, there is no medication that we can give that will speed your recovery, so mainly it’s making you feel better while your body’s fighting off the infection over about a week.