AIDS Transmission
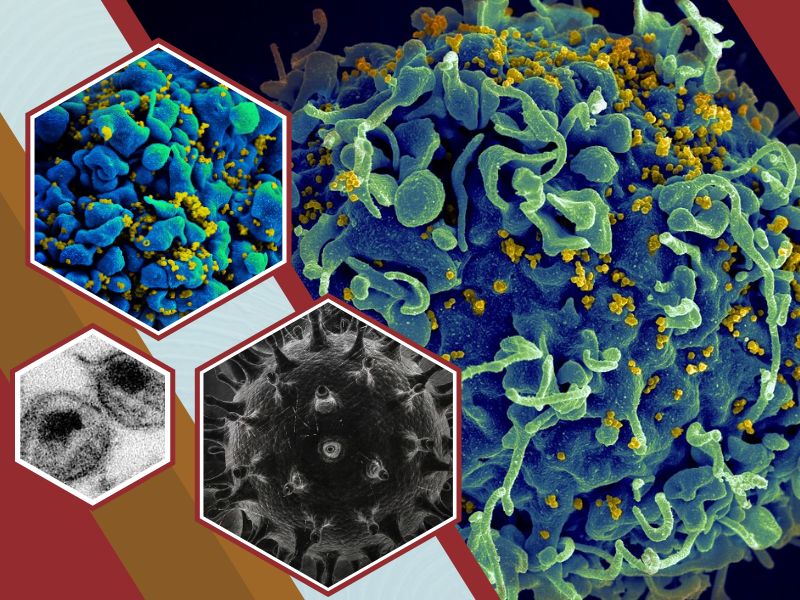
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a chronic, potentially life-threatening condition that is caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). By damaging your immune system, HIV interferes with the ability of your body to fight diseases and infections.
HIV is a sexually transmitted infection that can spread by contact with infected blood or from mother to child during childbirth, pregnancy, or breastfeeding. Without medications, it may take years before HIV weakens your immune system to the point that you’ll develop AIDS.
Symptoms of AIDS

The signs that you have AIDS include:
- Skin rashes
- Headaches
- Sore throat
- Feeling tired, dizzy, and lightheaded
- Getting bad infections a lot
- Chronic pelvic inflammatory disease
- Bad yeast infections
- Bruising more easily than normal
- Losing lots of weight quickly
- Swollen or firm glands in your throat, armpit, or groin
- Having diarrhea, fevers, or night sweats for a long time
- Deep, dry coughing spells
- Feeling short of breath
- Bleeding from the mouth, nose, anus, or vagina
- Purplish growths on your skin or inside your mouth
- Feeling very numb in your hands or feet, losing control of your muscles and reflexes, not being able to move, and losing strength in your muscles
How does HIV become AIDS?
CD4 T cells – white blood cells that play an important role in fighting disease – are destroyed by HIV. You will have a weak immune system if you have fewer CD4 T cells.
A person can be infected with HIV for years with few or no symptoms before they develop AIDS. If you have an AIDS-defining complication, such as a severe infection or cancer, or your CD4 T cell count drops below 200, you will be diagnosed with AIDS.
Risk Factors for AIDS
Anyone of any age, race, sex or sexual orientation can be infected with AIDS. However, you are at greatest risk of AIDS if you:
- Use IV drugs – people who use IV drugs often share syringes and needles. This exposes them to droplets of other people’s blood.
- Have a sexually transmitted infection – many of these infections produce open sores on your genitals. These sores act as doorways for HIV to enter your body.
- Have unprotected sex – use a new condom every time you have sex. Anal sex is riskier than is vaginal sex. Your risk of HIV increases if you have multiple sexual partners.
How does AIDS transmit?
AIDS is not passed on easily from one person to another. The virus does not spread through the air like cold and flu viruses. The infection lives in the blood and some body fluids. To get it, one of these fluids from someone with the infection has to get into your blood. The body fluids that contain enough HIV to infect someone are:
- Breast milk
- Blood
- Semen
- Vaginal fluids, including menstrual blood
- Lining inside the anus
Other body fluids like sweat, saliva, or urine, do not contain enough of the virus to infect another person.
AIDS Treatment
This disease cannot be cured, but there are very effective treatments that allow most people with the virus to live a long and healthy life.
The treatment for AIDS is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART involves taking a combination of medicines every day. ART is recommended for everyone who has the infection. It cannot cure HIV, but medications help people live longer and healthier lives. ART also reduces the risk of transmission.



