A fungus is a tiny type of germ that usually doesn’t cause any problems. They are all around us. You can only see them with a microscope. But fungi can infect your lungs in some situations, particularly if you have other serious illnesses. It can be very serious and requires specialist care.
What are Fungal Infections?
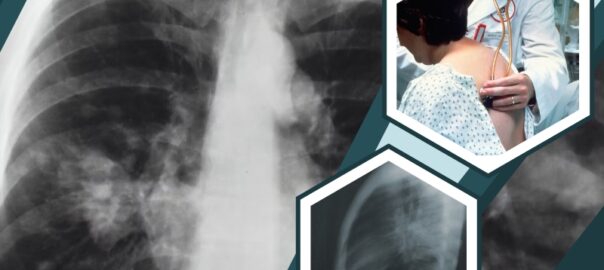
Fungi may cause lung disease through direct infection of pulmonary tissue, infection of pulmonary air spaces/lung cavities, or their ability to trigger an immunological reaction when fungal material is inhaled. The latter mechanism is involved in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, aspergillus-induced asthma, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis due to fungi.
Except for aspergillosis, these infections are usually not present to any significant degree in immunocompetent residents of the UK. They are more likely to affect those who have traveled abroad to areas where they are endemic or arise as opportunistic infections in patients who are immunocompromised due to oncological treatment due to immunomodulation following solid organ transplantation or HIV infection. Pulmonary infection occurs after inhalation of spores/conidia or by the reactivation of latent infection. Hematogenous dissemination of fungal infection leading to a systemic mycosis tends to occur chiefly in immunocompromised patients.
Types of Fungal Infections
- Fungal nail infections
- Vaginal candidiasis
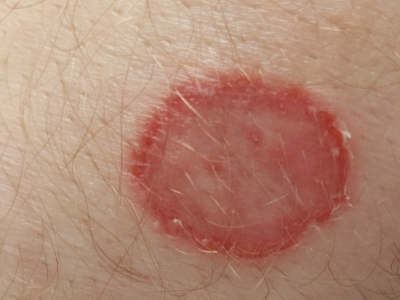
- Ringworm
- Candida infections of the mouth, throat, and esophagus
- Blastomycosis
- Cryptococcus gattii infection
- Paracoccidioidomycosis
- Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever)
- Histoplasmosis
- Aspergillosis
- Canadida auris infection
- Invasive candidiasis
- Candidiasis
- Cryptococcus neoformans infection
- Mucormycosis
- Talaromycosis
- Fungal eye infections
- Sporotrichosis
- Mycetoma
Signs and Symptoms of Fungal Infections
Symptoms of fungal infections can range from mild to very serious. The exact symptoms depend on the type of fungus that has caused the infection. Some common symptoms include:

- Asthma-like symptoms
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Muscle aches or joint pain
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Chest pain
- Itchy or scaly skin
Fungal infections can affect many parts of the body, including:
- Hair
- Skin
- Lungs
- Bloodstream
- Brain
- Gastrointestinal system
- Vagina
Symptoms of fungal infections can mimic other conditions, so it’s important to consult your physician for a complete exam and diagnosis.
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Fungal Infections
Antifungal medicines can kill a fungus. Or they may stop it from multiplying or growing. There are several classes of antifungal medications and different types of medicines. Your healthcare provider will select the best prescription medicine. Or they may guide you to an effective over-the-counter (OTC) treatment.
There are OTC and prescription antifungal medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider about what treatment to use.
Antifungals come in different forms, including:
- Injections (shots) or IV
- Oral pills or liquids
- Topical (skin) creams, ointments, gels and sprays
- Vaginal suppositories
Treatment length varies depending on the fungal infection. Some fungal skin infections like ringworm clear up in a few weeks. But clearing up some fungal nail, blood, and lung infections can take months or years.
Recommended medication used for fungal infection:
- Indinavir – the drug is in a class of medications called protease inhibitors. Indinavir inhibits the HIV viral protease enzyme, which prevents cleavage of the gag-pol polyprotein, resulting in noninfectious, immature viral particles.
Antifungal medications treat fungal infections affecting skin, nails, lungs, and other organs. Some fungal infections clear up in a few weeks. Others may need months of treatment. Taking antifungal medicines for an extended period or failing to complete the prescribed treatment may lead to antifungal resistance.
Medication safety depends on the antifungal drug. Breastfeeding infants who develop thrush can get antifungal mouth drops. Their moms also need treatment, typically with an antifungal skin cream. Your healthcare provider can determine whether it’s okay for you or your child to take an antifungal medicine.
Side effects from antifungals vary. Results depend on the type of drug, dosage (strength), and fungus. You may experience the following:
- Abdominal pain, upset stomach, and diarrhea
- Itchy skin, burning sensation, or skin rash
Rarely, an antifungal drug may cause serious problems like:
- Liver damage (jaundice)
- Severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis
- Severe allergic skin reactions, such as blisters and peeling skin