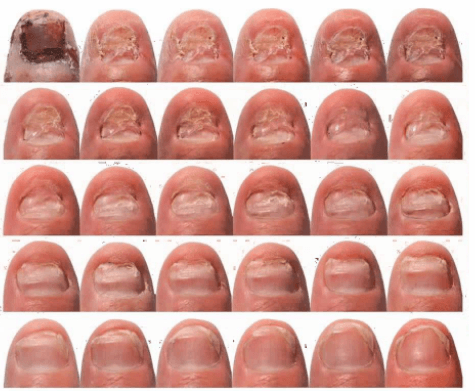
Fungal Nail Infections

Nail infections caused by fungi can cause nails to become discolored, thick, and more likely to break and crack. The same fungi that cause jock itch, athlete’s foot, and ringworm can cause nail infections.
Who is at Risk for Fungal Infections?
Fungal infections are more likely to develop if you:
- Have diabetes
- Age 65 or over
- Wear artificial nails
- Have skin injury around the nail
- Have weakened immune system
- Wear closed shoes
- Have moist fingers or toes for an extended time
Fungal Nail Infection Symptoms
A spot of white or yellow may appear under your nail at first. This spreads over time and can cause your whole nail to turn white, yellow, green, or black.
- It may be difficult to trim the nail if it thickens.
- Nails may start to curl up or down or loosen from the nail bed.
- Your nail could become brittle and crumble.
- Your nail may become misshapen and may have a bad smell
Types of Fungal Nail Infections
- Distal or lateral subungual onychomycosis. This results from a fungus called a dermatophyte. You can get it in your fingernails or toenails.
- Proximal subungual onychomycosis. White spots appear first at the cuticle of the nail bed in the center. Infections with HIV, for instance, usually affect people with immune system problems.
- Candidal onychomycosis. Infections of the fingernails are usually caused by yeast. Nails damaged by an injury or another infection are more likely to suffer from this condition.
- White superficial onychomycosis. The condition is less common and affects the nail surface, mainly your toenails. It starts as white spots, which become powdery and cause the nail to crumble.
Fungal Nail Infections Treatment
- Oral antifungals. Fluconazole is an oral antifungal medication. It is indicated to treat fungal infections which can invade any part of the body including the nails. Buy Fluconazole here for the effective treatment of fungal nail infections.
- Laser or photodynamic therapy. Fungus-killing treatments using special light are being studied by doctors.
- Topical antifungals. You rub or brush these medicines onto your nails. Although they may work for mild infections, they can’t cure more serious ones because they don’t penetrate deep enough into the nail.
- Surgery. The doctor may remove your nail completely if other treatments don’t work and allow a healthy one to grow in its place.
Prevention
- Wash your hands and feet regularly. Dry well, apply an antifungal foot powder, and moisturize your nails.
- Cut nails straight across, smooth the edges with a file and file down thickened areas.
- Choose shoes made of materials that breathe.
- Discard old shoes or treat them with disinfectants or antifungal powders.
- Wear absorbent socks or change your socks throughout the day.
- If you have an athlete’s foot, treat it with an antifungal product.



