Nifedipine is a prescription calcium channel blocker used for:
- Lowering the blood pressure
- Prevention of rapid heart rhythm episodes
- Preventing angina pectoris or chest pain attack due to an increased workload of the heart or spasm of the coronary arteries
The short-acting tablet is used for:
- Treating Raynaud’s phenomenon, a condition where the blood vessels in the feet and hands go into spasm causing numbness, white and painful toes and fingers.
- Treating hiccups in palliative care
Non-FDA approved uses include:
- Postponing premature labor (off-label)
- Prevention of migraine headaches in adults
- Anal fissure
- Wound healing
- Ureteral stones as secondary therapy
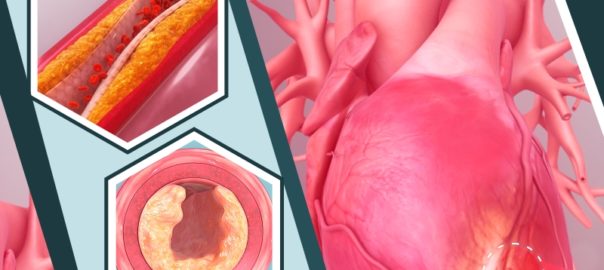
Nifedipine is mainly prescribed for the treatment of hypertension or high blood pressure. It’s a common condition but its long-term effect can cause serious medical conditions like heart problems and even death. Untreated high blood pressure can cause damages to the heart, blood vessels, kidneys and other organs of the body. Damages to these organs may cause heart disease, heart failure, heart attack, stroke, loss of vision, kidney failure and other problems. High blood pressure happens when blood pressure increases to an unhealthy level. You can get high blood pressure for years without any symptoms. It generally develops over years and affects nearly everyone. Fortunately, most high blood pressure can easily be detected.
It’s also used to treat two types of angina pectoris or chest pain: chronic stable angina and vasospastic angina. Angina pectoris is a type of chest discomfort due to coronary heart disease. It usually happens when one or more of the heart’s arteries is blocked or narrowed due to insufficient oxygen that it gets.
Nifedipine blocks the calcium channel found on the muscle cells in the walls of the arteries. This causes the walls to relax and widens. Relaxing the walls of the arteries reduces the resistance of the heart to pump blood around the body. This in return reduces the pressure in the blood vessels. Nifedipine helps control high blood pressure along with making a lifestyle change. These changes include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a diet that is low in salt and fat, exercising at least 30 minutes a day, using alcohol in moderation and not smoking.
Nifedipine also helps relax the peripheral arteries in the hands and feet which improve the circulation of blood in the fingers and toes. This helps relieve the symptoms of Raynaud’s phenomenon.
Why Buy Nifedipine?
Nifedipine is a potent calcium channel blocker that’s approved by the Food and Drug Administration for medical use in the United State since 1981. It’s listed as one of the safest and most effective medicines needed in the health system. It’s a generic medicine that works well in lowering the blood pressure and in preventing chest pain. It’s a first-choice treatment for high blood pressure and Prinzmetal angina for many people. Nifedipine prevents heart attack, stroke and heart-related chest pain when used regularly. Nifedipine is also available in several brand names in the market. However, the brand names cost much than the generic version.
How to Take Nifedipine?
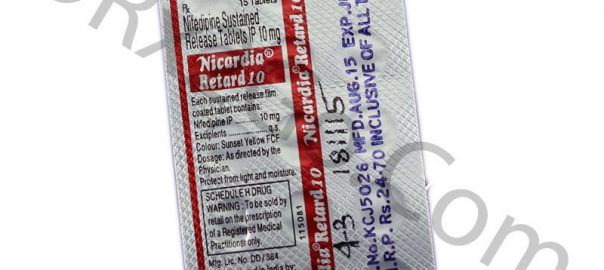
Your dose and the duration of your treatment depend on your condition. The typical recommended dose for treating angina pectoris is 10 mg to 20 mg three times a day. The maximum recommended dose is 180 mg a day. For hypertension, take 30 mg to 60 mg a day. Nifedipine comes in a tablet and capsule form for you to take by mouth. You can take it with or without food. Swallow the tablet whole with water.
The short-acting capsule takes effect as soon as the medicine is absorbed by the body and then tapers off. So you should take it three times a day. The long-acting tablet and capsule release the medicine steadily over the day. You need to take it once or two times a day.
What are the possible side effects of Nifedipine?
Nifedipine may cause unwanted side effects like any other medications and these may affect individuals in different ways. Contact your doctor right away if you have serious side effects like:
- Fainting
- Pounding or fast heartbeats
- Short breath
- Low blood pressure
- Swollen ankles due to fluid retention
- Swelling in the hands or feet
- numbness or tingly feeling
- Worsening angina
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes
- Chest pain, pain that spread to the arms or shoulder
- Nausea
- Sweating
- General ill feeling
- Visual disturbance
Less serious side effects are:
- Leg cramp
- Joint pain
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Sleep problems
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Itching, mild rashes
- Feeling tired
- Stomach pain
- Constipation
- Chills
- Migraine
- Nosebleed
- Urinating more than usual
Rare side effects are:
- Infertility in men
- Loss of appetite
- Enlargement of the gums
A very serious side effect is rare. However, if you will notice any serious side effects seek immediate medical attention.
Things to Remember
- Do not miss a dose. Stopping your medication can cause your blood pressure to go up suddenly which raises your risk of stroke and heart attack.
- Avoid grapefruit because it can make the effect of this medicine stronger.
- Nifedipine can make you feel dizzy or weary. Avoid drinking alcoholic beverages. When getting up from sitting or lying position, do it slowly
- In addition to taking your medication, making a lifestyle change can also control your blood pressur
- Do not take this to treat an angina attack that has started because it won’t work quickly enough.
- Have a regular blood sugar check-up because this medicine may affect the level of sugar in your blood.
- Tell your doctor if you are using this medication before having surgery.
- Do not use this if:
- You are having an ongoing angina attack because this drug doesn’t work that quickly compared with glyceryl trinitrate (GTN).
- You have had a recent heart attack
- You are allergic to any of the ingredients
- You have a liver problem, blockage in the stomach or intestines, ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease
- Use in a lower dose if:
- You are 65 years old and above
- You have a heart failure
- You have a severe liver problems
- You have a diabetes