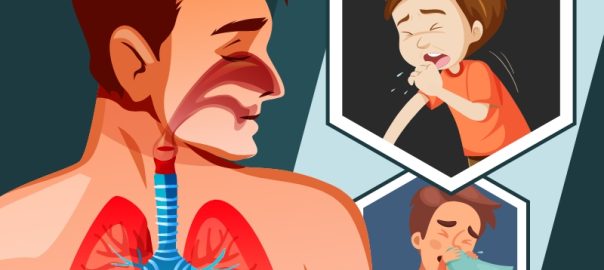
Sinusitis is an inflammation or swelling of the sinuses. The sinuses are four pairs of cavities in the head. These cavities are connected by narrow channels. A thin mucus drains from the sinuses into the nasal channels. The mucus keeps the nasal passages clean and free of bacteria. The sinuses are normally filled with air but can become blocked and filled with fluid. As a result, bacteria can grow and cause an infection.

What Are The Symptoms Of Sinusitis?
Common symptoms of sinusitis include:
- Tiredness
- Fever
- Postnasal drip
- Halitosis
- Cough
- Nasal discharge or stuffy nose
- Facial pressure, headache, and or pain in your teeth or ears
What Causes Sinusitis?
The sinuses can become inflamed and blocked by a virus, bacteria, or fungus. A few specific causes include:
- The common cold
- Polyps
- Nasal and seasonal allergies
- A weak immune system from illness or medications
- A deviated septum. The septum is the line of cartilage that divides your nose. A deviated septum means that it isn’t straight, so it is closer to the nasal passage on one side of your nose, causing a blockage.
Other causes may include:
- For infants and young children, spending time in daycares, using pacifiers, or drinking bottles while lying down could increase the chances of getting sinusitis.
- For adults, smoking increases the risks for sinus infections. You should stop if you smoke. Smoking is harmful to you and the people around you.
How to Diagnose Sinusitis?
You may be asked about your symptoms by your doctor. A physical exam will involve feeling for tender spots on your nose and face and examining your nose. Methods for diagnosing chronic sinusitis include:
- Imaging tests – this can show details of your sinuses and nasal area. These might pinpoint a deep inflammation or physical blockage that’s difficult to detect using an endoscope.
- Looking into your sinuses – a thin, flexible tube with a fiber-optic light inserted through your nose allows your doctor to see the inside of your sinuses. This can help your doctor see a deviated nasal septum, polyps, or tumors.
- An allergy test – a skin test is safe and quick and can help detect what allergen is responsible for your nasal flare-ups.
Treatment and Medication for Sinusitis
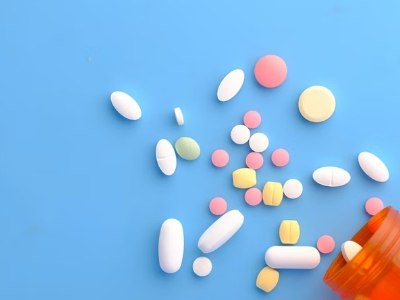
Sinusitis is treated in several ways, each depending on how severe the case of your condition is.
A simple sinusitis infection is treated with:
- Decongestants
- Cold and allergy medications
If symptoms of sinusitis don’t improve after 10 days, your doctor may prescribe:
- Antibiotics
- Oral or topical decongestants
- Intranasal steroid sprays
Long-term sinusitis may be treated by focusing on the underlying condition. This is usually treated with:
- Intranasal steroid sprays
- Topical antihistamine sprays or oral pills
- Leukotriene antagonists
Medications can be used for sinusitis: