Insulin Resistance: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Causes, and Treatment
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance is when cells in your muscles, fat, and liver don’t respond well to insulin and can’t use glucose from your blood for energy. It may also include conditions like obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes. Insulin is a hormone released by the pancreas that tells your cells to open up to that sugar and convert it into energy.
When you eat food, your body converts that food into dietary sugars. The cells do not react with resistance, resulting in excessive sugar in the blood. Over time, the pancreas keeps trying to regulate the blood sugar, producing more and more insulin until it wears out and may not produce large amounts of insulin anymore. As a result, blood sugar levels increase to the point of being in the diabetic range.
Signs and Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
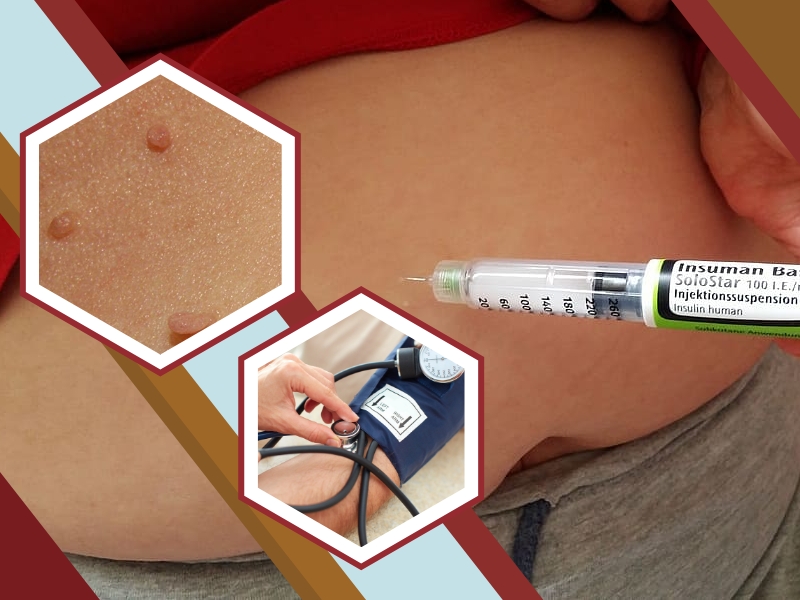
- A fasting triglyceride level over 150 mg/dL
- A HDL cholesterol level under 40 mg/dL in men and 50 mg/dL in women
- Skin tags
- A waistline over 40 inches in men and 35 inches in women
- Blood pressure readings of 130/80 or higher
- A fasting glucose level over 100 mg/dL
- Patches of dark, velvety skin
What are the Risk Factors of Insulin Resistance?
Anyone can develop insulin resistance temporarily or chronically. Over time, chronic insulin resistance can lead to pre-diabetes and then Type 2 diabetes if it’s not treated or can be treated. You are at risk if:

- You have obesity, or you are overweight, especially when the extra body weight is around the midriff
- You have a sedentary lifestyle
- You smoke or drink excessive amounts of alcoholic beverages
- You consume large amounts of alcohol, which can impact the liver
- You have sleep issues
- Having high cholesterol levels
- Having high blood pressure
How Common is Insulin Resistance?
The best way to measure the prevalence of insulin resistance is through the number of prediabetes cases. More than 84 million adults in the United States have prediabetes. That’s about 1 out of every 3 adults.
This condition may progress to type 2 diabetes if you do not change how you eat and exercise. Your blood sugar levels will rise until you have prediabetes. It causes your pancreas to use extra insulin to make up for it. It will work for a while, and your blood sugar levels will stay normal.
How is Insulin Resistance Diagnosed?
Doctors usually request more than one of these tests to ensure an accurate diagnosis. Several tests can help diagnose prediabetes and diabetes:
- An A1C test measures a person’s average blood sugar level over the previous 3 months.
- Fasting blood glucose test: A doctor checks glucose levels after an individual refrains from eating or drinking for 8 hours.
- Random glucose test involves a medical professional checking blood glucose levels at some point during the day.
How to Prevent Insulin Resistance?

- Factors such as genetic and family history are not preventable. Ensure to visit your doctor for further recommendations. Here are some tips to prevent the condition:
- Manage your weight or quit smoking to prevent heart disease and stroke. Experts say that up to 50% of people with prediabetes can prevent the onset of diabetes through such measures.
- According to the CDC, if a person with overweight or obesity loses 5 to 7% of their body weight, this can significantly reduce their risk of developing diabetes.
- Exercise can also help. Muscles become more sensitive to insulin after exercise, helping the body reverse insulin resistance.
Medication Used For Insulin Resistance
Pioglitazone. It enhances the transcription of insulin-responsive genes and improves the entry of glucose into muscles and fats. It can also be used as monotherapy along with diet and exercise in mild cases and to supplement insulin in advanced cases.



