Type 2 Diabetes Treatment

Type 2 Diabetes is a common type of diabetes. It is a disease that occurs when your blood glucose is too high. Blood glucose or blood sugar is the main source of energy and comes mainly from the food you eat.
A hormone made by the pancreas called insulin helps glucose get into your cells to be used for energy. Your body doesn’t produce enough insulin or doesn’t use it efficiently if you have type 2 diabetes. In this case, too much glucose remains in your blood and not enough reaches your cells.

Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes often develop slowly. You can be living with this disease for years and not know it. When symptoms are present, they may include:
- Unintended weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Increased hunger
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
- Areas of darkened skin, usually in the armpits and neck
- Slow-healing sores
- Frequent infections
Who Is At Risk Of Developing Type 2 Diabetes?
You are more likely to develop Type 2 Diabetes if you:
- Are obese or overweight
- Are older than 45
- Had gestational diabetes while pregnant
- Have high blood pressure
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Have pre-diabetes
Complications of High Blood Sugar Levels
Potential complications of high blood sugar levels from Type 2 diabetes can include:
- Heart disease
- Kidney disease
- Skin conditions
- Stroke
- Urinary tract infections and bladder infections
- Digestive problems
- Eye problems
- Hearing loss
- Liver problems, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Foot problems, including leg and foot ulcers
- Gum disease and other mouth problems
- Peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage)
- Sexual dysfunction
Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
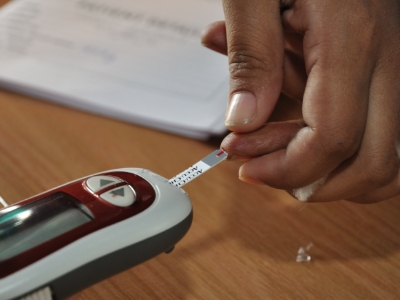
These steps will help keep your blood sugar level closer to normal, which can delay or prevent complications.
1. Healthy Eating
- Modest servings of low-fat dairy, low-fat meats, and fish
- Healthy cooking oils, such as olive oil or canola oil
- Fewer calories
- A regular schedule for meals and healthy snacks
- Fewer refined grains, starchy vegetables, and sweets
- Smaller portion sizes
- More high-fiber foods, such as fruits, nonstarchy vegetables, and whole grains
2. Physical Activity
Exercise is important for losing weight or maintaining a healthy weight. It also helps with regulating blood sugar levels.
- Aerobic exercise
- Resistance exercise
- Limit inactivity
3. Weight Loss
Blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, triglycerides, and blood pressure are better controlled with weight loss. Overweight people may notice improvements in these factors after losing as little as 5% of their body weight. As you lose weight, you will see a greater impact on your health and disease management.
4. Monitoring Your Blood Sugar
Your doctor will direct you on how often to check your blood sugar level to make sure you remain within your target range. You should keep a record of your measurements to share with your doctor.
5. Diabetes Medications
Diabetes medications that help lower insulin levels or insulin therapy may be prescribed by your doctor if diet and exercise are not sufficient to maintain your target blood sugar level. Diabetes medications that help lower insulin levels include the following.



