What Triggers Tonsillitis in Adults?
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils or the two oval-shaped pads of tissue at the back of the throat. It is not contagious, but most of the infections that cause tonsillitis are contagious.
What is the Cause of Tonsillitis in Adults?
Tonsillitis is most often caused by viruses and bacteria. Viruses that can cause tonsillitis are:
- Common cold viruses
- Herpes simplex virus
- Influenza virus
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Cytomegalovirus
- Adenovirus
- Measles virus

Can Tonsillitis Infect Other People?
Tonsillitis does not infect other people but the viruses that cause this condition are contagious. Bacterial tonsillitis spreads when a person has direct contact with the saliva or mucus of someone who already has the infection. Viral tonsillitis spreads through the surfaces. The most effective way to stop the spread of tonsillitis is by halting the spread of the pathogens that cause it.
How Serious is Tonsillitis in Adults?
Tonsilitis infections that are left untreated are serious and may lead to several complications. Seek immediate help if your tonsils have white pus-filled spots.
Tonsillitis Diagnosis

Your doctor will take several assessments and tests on your symptoms. Diagnosing tonsilitis includes:
- Examining your throat for redness, swelling, or white spots on your tonsils.
- Assess other symptoms such as a fever, cough, runny nose, rash, or stomachache.
- Look in your ears and nose for other signs of infection.
- Feel the sides of your neck to see if your lymph nodes are swollen and tender.
How Do You Treat Tonsillitis in Adults?
Homecare treatments are typical steps to manage tonsillitis. These include getting enough sleep, avoiding irritants, proper hydration, and taking a pain reliever. Antibiotics such as Amoxicillin are also helpful in treating bacterial tonsillitis. Buy Amoxicillin in your local pharmacy and complete the treatment period to successfully manage the condition.
Shingles: Risk factors and Prevention
Anyone who has ever had chickenpox has a high risk of shingles. In the United States, most adults had chickenpox when they were children, before the advent of the routine childhood vaccination that now protects against chickenpox.
Shingles is not a life-threatening condition, but they can be very throbbing. To prevent shingles, vaccines can help to lessen the risk. Early treatment can help shorten a shingles infection and lessen the chance of complications.
Symptoms of Shingles
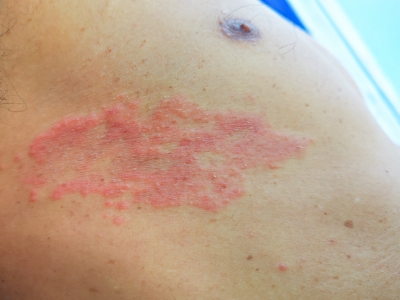
Symptoms of shingles usually affect only a small section of one side of your body. These symptoms may include:
- Fluid-filled blisters that break open and crust over
- Itching
- Pain, burning, numbness, or tingling
- A red rash that begins a few days after the pain
- Sensitivity to touch
Some people may also experience:
- Sensitivity to light
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Headache
When to see a doctor:
- You are 60 or older. Age significantly increases your risk of complications.
- The pain and rash occur near an eye. If left untreated, this infection can lead to permanent eye damage.
- You or someone in your family has a weakened immune system.
- The rash is widespread and painful.
Who Are At Risk Of Shingles?
Factors that may increase the risk of developing shingles include:
- Being older than 50 because shingle is most common in people older than 50. The risk increases with age.
- Having certain diseases that weaken your immune system can increase your risk of shingles.
- Undergoing cancer treatments. Chemotherapy and radiation can lower your resistance to diseases and may trigger shingles.
- Taking certain medications. Drugs designed to prevent the rejection of transplanted organs can increase your risk of shingles.
How To Prevent Shingles?
A shingles vaccine may help prevent shingles. The vaccine will likely lessen the course and severity of the disease and lessen your risk of postherpetic neuralgia.
The shingles vaccine is used only as a prevention strategy. It’s not intended to treat people who currently have the disease. Talk to your doctor about which option is appropriate for you.
Treatment for Shingles
Prompt treatment with prescription antiviral drugs can speed healing and lessen your risk of complications. The medication may include:
- Valacyclovir – this medicine is an antiviral drug that stops the growth of certain viruses. The viruses that cause these infections continue to live in the body even between outbreaks. The drug reduces the severity and length of these outbreaks. Valacyclovir helps the sores heal faster, keeps new sores from forming, and decreases pain and itching. This medication may also help reduce how long pain remains after the sores heal.
Shingles can cause severe pain, so your doctor also may prescribe:
- Capsaicin topical patch
- Anticonvulsants (Gabapentin (Neurontin)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline)
- Numbing agents (Lidocaine)
- Medications that contain narcotics (Codeine)
- An injection including corticosteroids and local anesthetics
Shingles generally last between two and six weeks. Most people get shingles only once, but it is possible to get it two or more times.
Types and Treatment of Candidiasis?
The treatments used for Candidiasis vary substantially and are based on the anatomic location of the infection, underlying disease and immune status, risk factors for infection, the specific species of Candida responsible for the infection, and, in some cases, the susceptibility of the Candida species to specific antifungal drugs.
What Causes Candidiasis?
Candida albicans (Monilia albicans) is a harmless yeast fungus that causes candidiasis. In healthy people, yeast is supposed to be present. However, chemotherapy or broad-spectrum antibiotics that suppress the bacterial flora present in the body may cause the fungus to multiply in the mouth or bowels. Candida infections may also be caused by other health conditions, such as pregnancy or diabetes.
Types of Candidiasis
There are several types of Candidiasis:
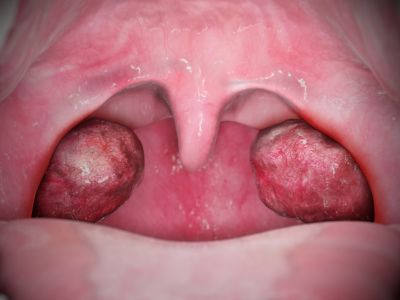
Thrush (Oropharyngeal Candidiasis)
When the candida yeast spreads in the mouth and throat, it can cause an infection called thrush. This type of Candidiasis is most common in newborns, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems. Symptoms of Thrush may include:
- Redness or soreness in the mouth and throat
- White or yellow patches on the tongue, lips, gums, the roof of the mouth, and inner cheeks
- Pain when swallowing, if it spreads to the throat
- Cracking at the corners of the mouth
Genital Yeast Infection (Genital Candidiasis)
This happens when too much yeast grows in the vagina. A yeast infection typically happens when the balance in the vagina changes. This can be caused by:
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- A weakened immune system
- Some medicines, including antibiotics and birth control pills
- Use of some douches, lubricants, vaginal sprays, or spermicides
- Wearing a wet bathing suit or workout clothes, or underwear that doesn’t breathe
Diaper Rash from Yeast Infection
Diaper rashes are usually caused by leaving a dirty or wet diaper on too long, but once your baby’s skin becomes irritated, infection becomes more likely. Check to see if their bottom is red and sensitive and if there’s a raised red border around the sores if their diaper rash doesn’t go away. Check for candidiasis with your pediatrician if this is the case. Antifungal creams can be applied to treat it. Preventing diaper rash and candidiasis starts with keeping your baby’s bottom clean and dry.
Invasive Candidiasis
If candida yeast enters the bloodstream, it can travel to the heart, brain, blood, eyes, and bones. This can cause a serious, life-threatening infection. Invasive Candidiasis happens most often in people who have recently been admitted to a hospital or live in a health care facility. The symptoms include fever and chills. Since it’s likely a person with this infection is already sick with another condition, it can be hard to diagnose.
Treatment for Candidiasis
When thinking about treatment for a yeast infection, it is important to know that there are many different types of yeast. Your healthcare provider may discuss different types of treatment depending on the type of yeast infection.
The most common medication recommended is:
- Clotrimazole Cream – this is an azole antifungal medication for topical treatment of tinea infections. Clotrimazole is also used for the treatment of athlete’s foot, otomycosis, and candidiasis. This prescription is more effective in the treatment of candidiasis because of its long-lasting residual effect after once-daily application.
Types Of Bacterial Infections
A bacterial infection is a proliferation of a harmful strain of bacteria on or inside the body. Several strains of bacteria are harmless, and some of them may even be beneficial to human health, such as those in the human gastrointestinal tract, which promote digestion and produce vitamins.
Bacteria are among the earliest known life forms on earth. There are thousands of different types of bacteria on every continent, and they live in every kind of environment. Some are airborne and others are mostly found in water, soil, plants, animals, and even people.
What are Bacterial Infections?
Bacterial infections are caused by the proliferation of a harmful strain of bacteria in the body. Infections can occur anywhere in the body. Meningitis, pneumonia, food poisoning, and meningitis are but a few of the diseases caused by bacteria.
- Bacteria come in three basic shapes: rod-shaped, spherical, or helical.
- Bacteria may also be classified as gram-positive or gram-negative: Gram-positive bacteria have a thick cell wall while gram-negative bacteria do not.
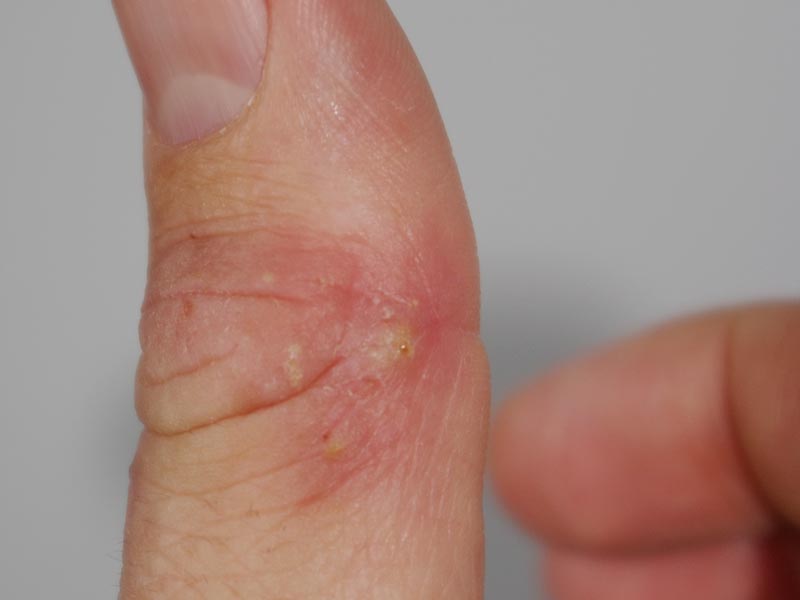
Types of Bacterial Infections
1. Bacterial Skin Infections
This infection is usually caused by gram-positive strains of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus or other organisms. Common bacterial skin infections include:
2. Foodborne Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are one cause of foodborne illnesses. Common symptoms may include abdominal pain, chills, fever, diarrhea, vomiting, and nausea. Poultry, eggs, fish, raw meat, and unpasteurized dairy products may harbor harmful bacteria that can cause illness. Unsanitary food preparation and handling can also encourage bacterial growth. Bacteria that cause food poisoning include:
- Vibrio
- Salmonella
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Escherichia coli
- Clostridium botulinum
- Campylobacter jejuni
3. Sexually Transmitted Bacterial Infections
There lots of sexually transmitted diseases are caused by harmful bacteria. At times, these infections are not linked with any symptoms but can still cause serious damage to the reproductive system. Common STDs caused by bacterial infections include:
4. Other Bacterial Infections
Harmful bacteria can affect almost any area of the body. Other types of bacterial infections include the following:

Treatment for Bacterial Infections
Antibiotics are medications that fight bacterial infections. They work by disrupting the processes necessary for bacterial cell growth and proliferation. It’s important to take antibiotics exactly as prescribed. Failure to do so could make a bacterial infection worse. Antibiotics don’t treat viruses, but they’re sometimes prescribed in viral illnesses to help prevent secondary bacterial infection.
The following are some of the antibiotics usually prescribed for bacterial infections:
NOTE: Overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to a rise in antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria are no longer sensitive to a medication that should eliminate an infection. For this reason, any of these medications should be taken as given.




