Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Causes, and Treatment
What is Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome?
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome is a rare condition that causes tumors to grow in your intestine or pancreas. Tumors or gastrinomas release hormones that trigger your stomach to produce gastric acid. Too much production may lead to ulcers and other complications which may also include cancerous tumors.

Signs and Symptoms of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
- Diarrhea
- Stomach pain
- Aching and burning discomfort in the upper abdomen
- Heartburn
- Nausea and vomiting
- Burping
- Acid reflux
- Unexplained weight loss
- Bleeding in the digestive tract
- Loss of appetite
Seek immediate help if you have aching or burning pain in your upper belly that does not go away with medications. Conditions associated with nausea, vomiting, and persistent diarrhea may need immediate medical attention.
What Causes Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome?
The exact specific cause of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is unknown. But the pattern of events that occurs in this condition typically follows the same sequence. The syndrome begins when one or more tumors form in your pancreas or a part of the duodenum or the section connected to your stomach. Sometimes the tumors form at other sites, such as the lymph nodes next to your pancreas.
Your pancreas sits behind and below your stomach. It makes enzymes that are needed for digesting food. Digestive juices from the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder mix in the duodenum. This is where most of your digestion happens.
The tumors that occur with this condition are made up of cells that secrete large amounts of the hormone gastrin. High gastrin production causes the stomach to make far too much acid. The excess acid then leads to peptic ulcers and sometimes to diarrhea. Besides causing excess acid production, the tumors are often cancerous and may affect the liver and other nearby organs.
What are the Risk Factors of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome?
Anyone is at risk of this condition but people with the condition may have a genetic problem known as multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1). Children of adults with MEN1 are at a greater risk of getting the disease. This is common in men from 30 to 50 years old. Ensure to seek immediate help if you experience persistent symptoms of ZES.
How to Diagnose Zollinger Ellison Syndrome?
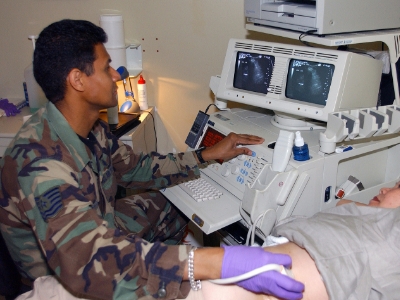
Your doctor will assess your symptoms and review your medical history. To diagnose ZES, your doctor will run some blood tests to see through your gastrin levels. Other diagnostic method includes:
- Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Tissue samples may be removed to examine gastrin-producing tumors. This test can determine whether the stomach is making high levels of gastric acid.
- Endoscopic ultrasound. This procedure uses an endoscope to spot tumors in your stomach, duodenum, and pancreas. This test also requires fasting after midnight and sedation.
- Imaging tests. One test is a nuclear scan called somatostatin receptor scintigraphy. This test uses radioactive tracers to help locate tumors. Other helpful imaging tests include ultrasound, computerized tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and Ga-DOTATATE PET-CT scanning.
Treatment, Management, and Prevention of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
The goal of the treatment is to focus on managing the hormone-secreting tumors as well as the ulcer they cause. The treatment of tumors includes an operation to remove the gastrinomas. If you have just one tumor, your provider may be able to remove it surgically. But surgery may not be an option if you have many tumors or tumors that have spread to your liver. Risks associated with surgery include infection, pain, and blood loss. Talk to your doctor to understand your risks.
Medication Used for Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Ranitidine. This drug blocks gastric secretion and treats conditions like hypersecretory conditions like ZES. Ranitidine counteracts the effects of gastrin. Medicines known as proton pump inhibitors are the first line of treatment. These are effective medicines for controlling acid production in ZES. Continue taking this medication throughout the treatment course to ensure recovery.



