Obesity: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
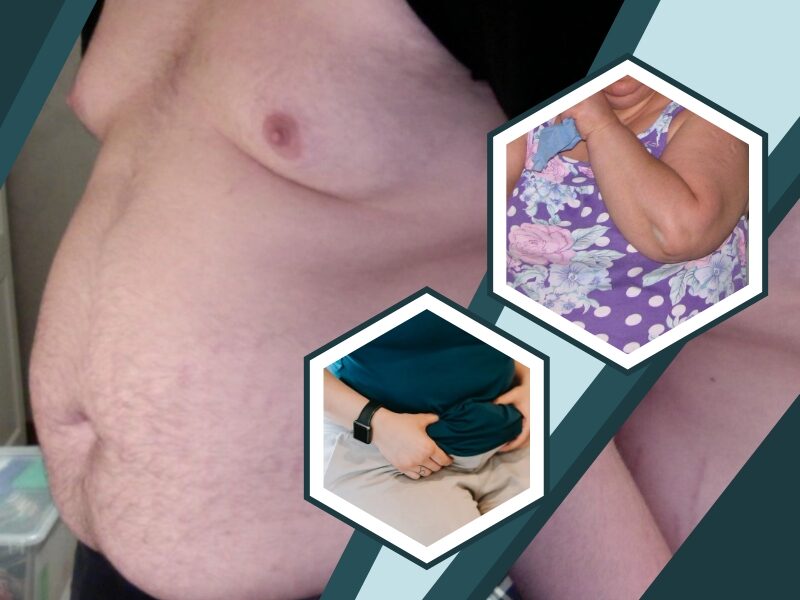
Obesity is a complex disease involving an excessive amount of body fat. It isn’t just a cosmetic concern. It’s a medical problem that increases the risk of other diseases and health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. There are many reasons why some people have difficulty losing weight. Usually, obesity results from inherited, physiological and environmental factors, combined with diet, physical activity, and exercise choices.
What is Obesity?
Overweight and obesity are defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a health risk. A body mass index (BMI) over 25 is considered overweight, and over 30 is obese. The issue has grown to epidemic proportions, with over 4 million people dying each year as a result of being obese in 2017 according to the global burden of disease.
Obesity is one side of the double burden of malnutrition and today more people are obese than underweight. Once considered a problem only in high-income countries, overweight and obesity are now dramatically on the rise in low- and middle-income countries, particularly in urban settings. The vast majority of overweight or obese children live in developing countries, where the rate of increase has been more than 30% higher than that of developed countries.

Signs and Symptoms
The most obvious symptom is the increase in weight therefore the symptoms that may be presented arise from this increase in weight that, among others, other symptoms may include:
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Back and joint pains
- Excessive sweating
- Intolerance to heat
- Infections in skin folds
- Fatigue
- Depression
- The feeling of shortness of breath
The main signs also derive from the magnitude of the excess weight, the most common:
- Acanthosis nigricans is a skin disorder characterized by the presence of hyperkeratosis and hyperpigmentation in the skin folds and armpits.
- Stretch marks due to distension and rupture of the elastic fibers of the skin or vinous in the case of obesity due to endocrinological alteration.
- Swelling and varicose veins in the lower limbs.
- Waist circumference greater than 94 cm in men and 88 cm in women.
- High blood pressure level > 140/90 mmHg.
- Body Mass Index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2.
What Causes Obesity?
Several factors can play a role in gaining and retaining excess weight. These include diet, lack of exercise, environmental factors, and genetics.
- Food and Activity. People gain weight when they eat more calories than they burn through activity. This imbalance is the greatest contributor to weight gain.
- Genetics. Research shows that genetics plays a role in obesity. Genes can directly cause obesity in such disorders as Prader-Willi syndrome.
- Health Conditions and Medications. Some hormone problems may cause overweight and obesity, such as underactive thyroid, Cushing syndrome, and polycystic ovary syndrome. Certain medicines also may cause weight gain, including some corticosteroids, antidepressants, and seizure medicines.
- Stress, Emotional Factors, and Poor Sleep. Some people eat more than usual when they are bored, angry, upset, or stressed.

Treatment and Management of Obesity
The best way to treat obesity is to eat a healthy, reduced-calorie diet, and exercise regularly. To do this you should:
- Eat slowly and avoid situations where you know you could be tempted to overeat
- Eat a balanced, calorie-controlled diet as recommended by your GP or weight loss management health professional
- Take up activities such as fast walking, jogging, swimming, or tennis for 150 to 300 minutes a week
- Join a local weight loss group
You may also benefit from receiving psychological support from a trained healthcare professional to help change the way you think about food and eating. If lifestyle changes alone don’t help you lose weight, a medication called orlistat may be recommended. If taken correctly, this medication works by reducing the amount of fat you absorb during digestion. Your GP will know whether Orlistat is suitable for you.
The drug is used with an individualized low-calorie, low-fat diet, and exercise program to help people lose weight. Orlistat is in a class of medications called lipase inhibitors. It works by preventing some of the fat in foods eaten from being absorbed in the intestines.
In rare cases, weight loss surgery may be recommended.



