Dental Infections
A dental infection begins in a tooth or its supporting structures and may spread to surrounding tissues. Typically, dental infections are caused by bacteria invading the pulp and spreading to the surrounding tissues. Also, infections can affect the gums, causing gingivitis, which leads to periodontitis later on.
What Causes Dental Infections?
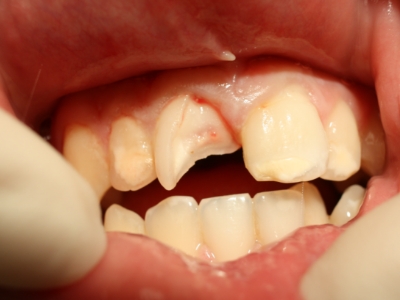
Anything that creates an opening for bacteria to get into the tooth or surrounding tissues can lead to dental infection. Causes may include:
- Broken, chipped, or cracked teeth: Bacteria can seep into any opening in a tooth and spread to the pulp.
- Severe tooth decay: A cavity, or tooth decay, is the destruction of the hard surfaces of the tooth. This occurs when bacteria break down sugars in food and drink that produce acid that attacks the enamel.
- Injury to the tooth: Trauma to a tooth can injure the inner pulp even if there’s no visible crack. The injury makes it susceptible to infection.
- Gum disease: It is an infection and inflammation of the tissues around the teeth. As gum disease progresses, the bacteria gain access to deeper tissues.
What Are The Symptoms Of Dental Infections?
If your tooth is infected, you may be:
- Radiating to the jawbone, neck, or ear
- Continuous or only when chewing
- Sharp or shooting
- Gnawing or throbbing
Other symptoms of infection include:
- Gum redness and swelling
- Foul-smelling breath
- Bitter taste in the mouth
- Tooth sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures
- Swollen area in the upper or lower jaw
- Loosening of the tooth
You may also experience generalized symptoms such as:
- Discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling
- Swollen neck glands
- Fever
Who Are At Risk Of Dental Infections?
You are more likely to develop dental infections if you:
- Smoke
- Have a weakened immune system
- Have poor dental hygiene
- Have dry mouth
How to Diagnose Dental Infections?
Along with examining the tooth and surrounding tissue for signs of infection, your dentist may:
- Recommend an X-ray: This helps detect sources of dental disease that may have led to the infection.
- Tap and press on your teeth: A tooth with an abscess is often sensitive to touch or pressure.
- Recommend a CT scan: If the infection has spread to other areas within the neck, this will help to identify the extent of the infection.
- Thermal tests: These tests will help your dentist know the health of your pulpal tissues.
What Are The Treatment And Medication For Dental Infections?
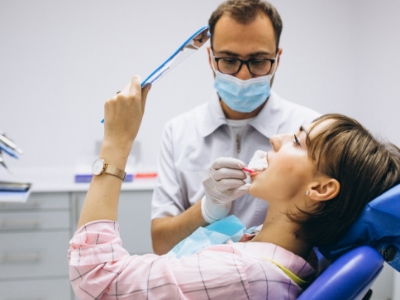
Treatment for dental infection may remove the infection and prevent complications. Treatment options include:
- Incision and drainage: Your dentist drains the pus from the abscess by making a small incision. It is sometimes necessary to place a small rubber drain to allow drainage.
- Tooth extraction: When a tooth cannot be saved, your dentist may have to extract it and allow pus to drain from the socket.
- Root canal: Your tooth is saved if you choose this option. During this procedure, the tooth’s infected inner pulp is removed and the space filled with the material to prevent another infection. Your restored tooth can last a lifetime if you care for it properly.
Medications usually used for the treatment of dental infection include:
Antibiotics
Pain Reliever



