Everyone experiences abdominal pain from time to time. Other terms to describe abdominal pain are stomachache, tummy ache, gut ache, and bellyache. The pain can be mild or severe. It may be continuous or come and go. Abdominal pain can be short-lived or occur over weeks, months, or years.
What Are Abdominal Cramps?

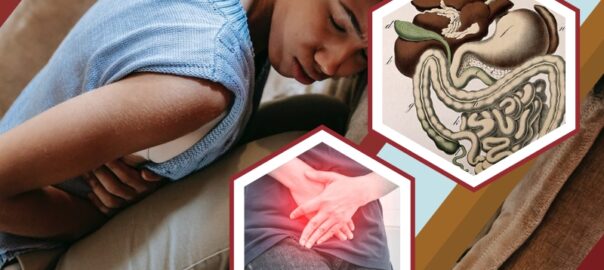
Abdominal pain is discomfort anywhere in your belly between your ribs and pelvis. We often think of abdominal pain as stomach pain or a stomachache, but the pain in your abdomen could be coming from other organs besides your stomach.
Your abdomen is home to your:
- Stomach
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
These are all organs in your digestive system. But pain can also be in your abdominal wall, the skin, and the muscles that make up the outer shell of your abdomen. And sometimes, the pain that you feel in your belly may be coming from somewhere else, like your chest, pelvis, or back.
Abdominal pain can take many forms and can mean many things. It may feel:
- Mild or severe
- Dull or sharp
- Burning or achy
- Crampy or colicky
- Constant or intermittent
- Localized or generalized
Ultimately, abdominal pain is a subjective symptom that only you can describe. Since your healthcare provider can’t measure it, it’s what you say it is. Your healthcare provider will always take your abdominal pain seriously.
What Are The Symptoms Of Abdominal Cramps?
Abdominal pain may take several different forms. In addition to how severe it is, abdominal pain can be as:
- Generalized Pain. It refers to pain felt in more than half of your abdominal area and is typical of stomach viruses, indigestion, or gas as the cause of your pain.
- Localized Pain. It refers to pain felt in just one area of your abdomen and is typical of a problem with an organ like your stomach, appendix, or gallbladder as the cause of your pain.
- Cramping. This type of pain comes and goes, or changes in severity or perceived position in your abdomen. Cramping is rarely severe and is typical of gas, passing a stool, or menstruation as the cause of your pain.
- Colicky Pain. Like cramping, this type of pain comes and goes but tends to be severe and starts and ends suddenly. It’s typical of kidney stones or gallstones as the cause of your pain.

It’s essential to call your doctor if your abdominal pain is so severe that you can’t move without feeling more pain or sit still in a comfortable position. Seek immediate medical attention if any of the following symptoms accompany your abdominal pain:
- Fever
- Bloody stool
- Nausea and vomiting that don’t resolve
- Weight loss
- Yellowish skin
- Abdomen very tender to touch
- Swollen abdomen
How to Treat Abdominal Pains?
The treatment of abdominal pain will depend on its underlying cause.
Mild abdominal pain may go away on its own within hours or days. Mild pain and related symptoms can also often treat with medicines from the pharmacy. Your pharmacist will be able to advise you on what type of product is best suited to your situation. It would be best not to use aspirin or anti-inflammatory medicines, such as ibuprofen, to treat abdominal pain other than period pain. These medicines may cause or irritate a stomach or bowel problem.
If you are treating mild abdominal pain with a known cause at home:
- Keep hydrated by drinking clear fluids; restrict alcohol, tea, and coffee
- Stay rested
- Use a hot water bottle or warm wheat pack on your abdomen
- Eat bland foods when you can start eating again, or as advised by your doctor
Medicine recommended to treat abdominal pain include:
- Baclofen is used to help relax specific muscles in your body. It relieves the spasms, cramping, and tightness of muscles caused by medical problems.
Does Abdominal Pain Need Treatment?
Abdominal pain has many possible causes. Some aren’t serious and get better independently in a few days. Others need more testing and treatment. If your pain continues or worsens, you need to be rechecked and may need more tests to determine what is wrong. You may need surgery to correct the problem.
Don’t ignore new symptoms, such as fever, nausea and vomiting, urination problems, worsening pain, and dizziness. These may be signs of a more severe problem. Your doctor may have recommended a follow-up visit in the next 8 to 12 hours. You may need more tests or treatment if you are not getting better.
The doctor has checked you carefully, but problems can develop later. If you notice any problems or new symptoms, get medical treatment immediately.