Eczema
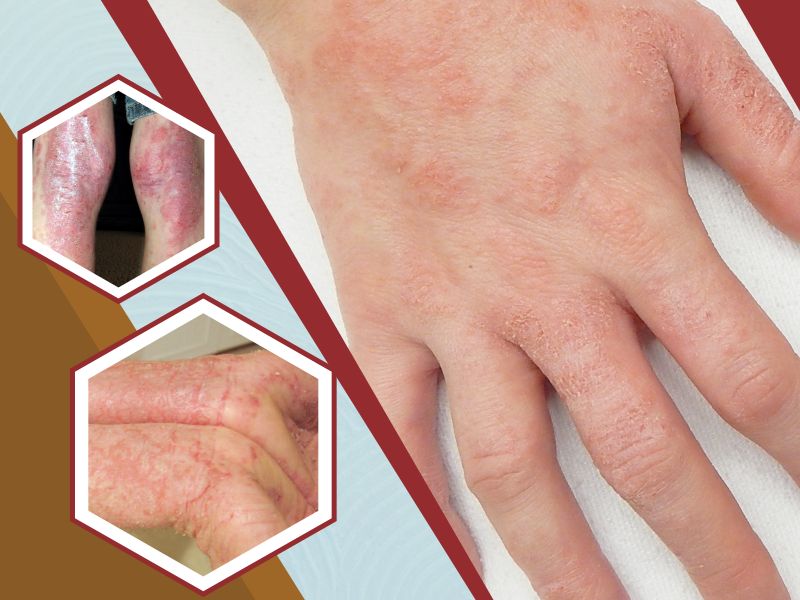
Eczema is a condition that causes the skin to become red and itchy. People of all ages can suffer from it. Eczema tends to flare periodically and is long-lasting. Hay fever and asthma are often associated with it.
Eczema has no known cure. Itching can be relieved and new outbreaks can be prevented by self-care measures and treatment. Avoiding harsh soaps, moisturizing your skin regularly, and applying medicated creams and ointments can help.
Causes of Eczema
Eczema is caused by a combination of immune system activation, genetics, environmental triggers, and stress.
- Stress levels can cause or worsen eczema.
- Your environment can also cause or worsen eczema. There is a lot in your environment that can irritate your skin.
- You are more likely to have eczema if there is a history of dermatitis in your family.
- If you have eczema, your immune system overreacts to small irritants. The overreaction can inflame your skin.
Risk Factors of Eczema
Risk factors that increase your chance of developing eczema include the following:
- Dry skin – having dry skin can be susceptible to inflammation. When you have less of that moisture barrier, your skin can become easily injured that resulting in inflammation and eczema.
- Sweating – your body’s sweat contains chemicals that are not as gentle as your skin’s natural moisture barrier. Excessive sweat that remains on your skin can become trapped moisture. This moisture can lead to skin irritation.
- Stress – Your hormones and immune system are affected by stress. Anywhere on your body, including on the surface of your skin, these effects can trigger an inflammatory response.
- Heat or cold – Excess cold or heat can be irritating to the surface of your skin.
Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema signs and symptoms differ from person to person. These signs and symptoms may include:
- Itching, which may be severe, especially at night
- Dry skin
- Thickened, cracked, scaly skin
- Sensitive and swollen skin from scratching
Diagnosis of Eczema
Your doctor will likely make a diagnosis by examining your skin and reviewing your medical history. They may also use patch testing or other tests to rule out other skin diseases or detect conditions that accompany your eczema.
Treatment and Medication for Eczema
Eczema can be persistent. You may need to try various treatments to control it. Even if treatment is successful, signs and symptoms may return.
Treatment should begin as soon as you recognize the condition. Your doctor may suggest one or more of these treatments if regular moisturizing and other self-care steps don’t help:
- Tacrolimus (Protopic) and Pimecrolimus (Elidel) – are creams that control itching and help repair the skin
- Antibiotic cream – to fight infection
- Prednisone – to control inflammation
- Dupilumab (Dupixent) – used to treat people with severe diseases who do not respond well to other treatment options



