Diagnosis and Treatment of Lung Cancer

Lung cancer is the third most common cancer. This type of cancer occurs when cells divide in the lungs uncontrollably which causes tumors to grow. These can decrease a person’s ability to breathe and spread to other parts of the body. Cancer causes changes in the cells that are otherwise healthy. The cells grow too fast, without dying off.
There are two main types of lung cancer are small-cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. It depends on how they appear under a microscope. Anyone can develop lung cancer, but cigarette smoking and having exposure to smoke, inhaled chemicals, or other toxins can increase the risk.
Lung Cancer Symptoms
People with lung cancer may not have symptoms until a later stage. If symptoms do appear, they can resemble those of a respiratory. Some possible symptoms include:

- Shortness of breath and wheezing
- Chest pain
- A lingering cough that may start to get worse
- Swelling in the lymph nodes in the middle of the chest
- Frequent chest infections such as pneumonia or bronchitis
- Changes to a person’s voice
In time, a person may also experience more severe symptoms such as:
- Fatigue
- Appetite loss and weight loss
- Blood clots
- Coughing up blood
- Headache
- Bone pain and bone fractures
- Severe chest pain
Risks and Causes of Lung Cancer
A risk factor is anything that increases a person’s chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Different cancers have different risk factors. Some risk factors, like smoking, can be changed. Others, like a person’s age or family history, can’t be changed.
But having a risk factor, or even several does not mean that you will get the disease. Also, some people who get the disease may have few or no known risk factors.
Several risk factors can make you more likely to develop lung cancer. These factors are related to the risk of lung cancer in general:
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Exposure to asbestos and other carcinogens
- Exposure to radon gas
- Family history of lung cancer
- Previous radiation therapy
- Smoking
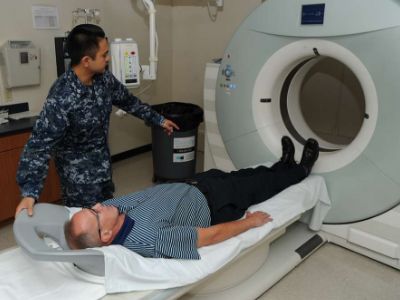
Lung Cancer Diagnosis
An annual lung cancer screening using low-dose CT scanning may be beneficial for people at increased risk of lung cancer. An elderly person who has smoked heavily for a long time or has given up smoking in the past 15 years is generally offered a lung cancer screening. Consult your doctor about your lung cancer risk. Depending on your risk, lung cancer screening might be of great help.
Lung Cancer Treatment
Your doctor will recommend a treatment plan based on your overall health, the type and stage of your cancer, and your preferences. In several cases, you may choose not to undergo treatment. For instance, you may feel that the side effects of treatment will outweigh the potential benefits. When that’s the case, your doctor may suggest comfort care to treat only the symptoms the cancer is causing, such as pain or shortness of breath.
Medication used for lung cancer treatment:
- Ondansetron – used to prevent nausea and vomiting following chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery. The medicine works by blocking one of the body’s natural substances (serotonin) that causes vomiting.



