Does The Immune System Protect You From Cancer?
The immune system is the system in your body that fights off infection. Immunotherapy is a form of medical treatment that activates your immune system to help fight Cancer. There are many different types of immune cells in your body. Other cells fight different types of Cancer.
Does the Immune System Protect you from Cancer?
The immune system protects the body against illness and infection that bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites can cause. It is a collection of reactions and responses the body makes to damaged cells or diseases. It is sometimes called the immune response.
The immune system can help to fight Cancer. Some immune system cells can recognize cancer cells as abnormal and kill them. But this may not be enough to get rid of cancer altogether. Some treatments aim to use the immune system to fight Cancer.
There are two main parts of the immune system:
- The protection we have from birth (built-resistant protection)
- The security we develop after having certain diseases (acquired immunity)
Why Does the Immune System Kill Cancer?
Cancer avoids detection by the immune system and affects how the immune system works against other illnesses. Blood and bone marrow cancers, including lymphoma and most types of leukaemia, impact the immune system because bone marrow is where immune system cells are made. Specific treatments can also have an impact on cancer patients’ immunity.
What Stops Your Immune System From Killing Cancer Cells?
Cancer can weaken the immune system by spreading into the bone marrow. The bone marrow makes blood cells that help to fight infection. It often happens in leukaemia or lymphoma but can also occur with other cancers. Cancer can stop the bone marrow from making so many blood cells.
Specific cancer treatments can temporarily weaken the immune system. It is because they can cause a drop in the number of white blood cells made in the bone marrow. Cancer treatments that are more likely to weaken the immune system are:
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted cancer drugs
- Radiotherapy
- High dose of steroids
Why Doesn’t Immunotherapy Help With Cancer?
- Immunotherapy holds a lot of promise as a cancer treatment. Still, it can cause some problems.
- You might have a bad reaction. The area where the medication goes into your body could hurt, itch, swell, turn red, or get sore.
- There are side effects. Some types of immunotherapy rev up your immune system and make you feel like you have the flu, complete with fever, chills, and fatigue. Others could cause problems like swelling, weight gain from extra fluids, heart palpitations, a stuffy head, and diarrhoea. Most of the time, these ease up after your first treatment.
- It can harm organs and systems. Some drugs can cause your immune system to attack organs like your heart, liver, lungs, kidneys, or intestines.
- It isn’t a quick fix. In some cases, immunotherapy takes longer to work than other treatments. Your Cancer may not go away quickly.
- It doesn’t work for everyone. Immunotherapy works for less than half the people who try it. Many people only have a partial response. It means your tumour could stop growing or get smaller, but it doesn’t go away. Doctors aren’t sure yet why immunotherapy helps only some people.
- Your body could get used to it. Over time, immunotherapy may stop affecting your cancer cells. It means that even if it works at first, your tumour could start to grow again.
Recommended cancer medication that you can use:
- Bicalutamide – this drug is an oral medication that is in the class of medicines known as nonsteroidal antiandrogens. The drug is known to work by blocking the effect of androgen to stop the growth and spread of cancer cells. Androgen is a male hormone. Bicalutamide is recommended to take with other medication.
Can Men Have Breast Cancer?
What is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer forms in the cells of the breast but it can spread outside the breast through blood vessels and lymph vessels. It has two common kinds known as invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma. Invasive ductal carcinoma begins in the ducts and then grows outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. It can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body. Invasive lobular carcinoma begins in the lobules and then spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. They can also spread to other parts of the body.
What are the Symptoms of Breast Cancer?
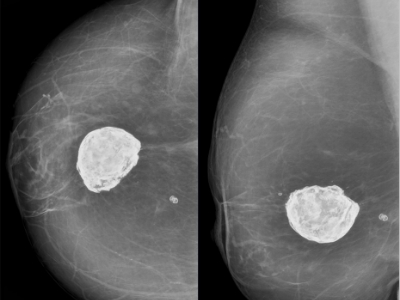
- A lump or thickening in the breast
- Changes in breast size and shape
- Changes in the physical appearance of the breast
- Changes to the skin over the breast, such as dimpling
- A newly inverted nipple
- Peeling, scaling, or crusting of the area surrounding the nipple or breast skin
- Flaking of the pigmented area of skin surrounding the nipple or breast skin
- Redness or pitting of the skin over your breast
Can Men Have Breast Cancer?
Male breast cancer is rare cancer that forms in the breast tissue of men. These are common in older men but do not mean it does not occur in the younger population. Though breast cancer is most commonly thought of as a disease that affects women, breast cancer does occur in males.
About 1 out of every 100 breast cancers diagnosed in the United States is found in a man. The most common type of breast cancer in men is infiltrating ductal cancer. It starts in the milk duct and spreads to nearby tissues. Other less-common types of breast cancer in men include inflammatory carcinoma and Paget disease of the nipple.
How to Diagnose Breast Cancer in Men?
Your doctor will assess the signs and symptoms as well as your medical history. During the visit, your doctor will do a clinical breast exam using his or her fingertips to examine your breasts and surrounding areas for lumps or other changes. Other diagnostic method includes:
- Imaging tests. Tests may include a breast X-ray or an ultrasound, which uses sound waves to create images and identify abnormal areas.
- Biopsy. It will help your doctor determine the type of cells involved in cancer, the aggressiveness of cancer, and whether the cancer cells have hormone receptors or other receptors that may influence your treatment options.
- Other tests. This includes a bone scan, CT scan, and or a PET scan to determine the extent of the affected part or if cancer already spread to other organs.
Treatment for Breast Cancer
Treatment for men’s and women’s breast cancer is similar. It involves killing or removing the affected cells of the breast. Male breast cancer treatment often involves surgery and may also include other treatments. Surgery may involve removing all of the breast tissue including the nipple and areola. Other surgical approaches will focus on removing a few lymph nodes for testing. f no cancer cells are found, there is a good chance that your breast cancer hasn’t spread beyond your breast tissue.
Radiation therapy may be used after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells in the breast, chest muscles, or armpit. Hormone therapy often involves medications that work in men. Chemotherapy is also recommended to remove affected cells using medication after surgery to kill any cancer cells that might have spread outside your breast. Chemotherapy may also be an option for men with advanced breast cancer.
Exemestane. It treats certain types of breast cancer. It also prevents cancer from returning after remission. It works by reducing the amount of estrogen the body makes and helps to slow or reverse the growth of these breast cancers. The dosage is based on your medical condition, response to treatment, and other medications you may be taking.




