Vitiligo: Types, Causes, and Treatment
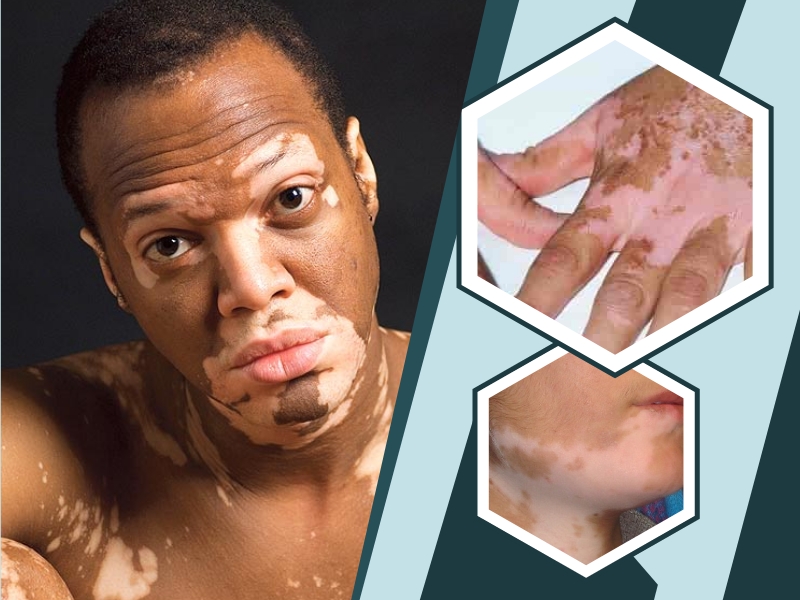
Vitiligo is a skin condition that causes the skin to lose its color. Smooth white areas appear on a person’s skin. If you have this condition, a place that has hair on your body may also turn white.
This skin disorder may have the signs and symptoms of:
- Patches of hair on your head or face turn prematurely gray or white.
- Patches of skin lose color including the eyes and/or the mucous membranes in your mouth or nose.
Vitiligo is not painful, but you can get painful sunburns on the lighter patches of the skin. You must protect yourself against the sun. Some people with this condition have reported having itchy skin sometimes.
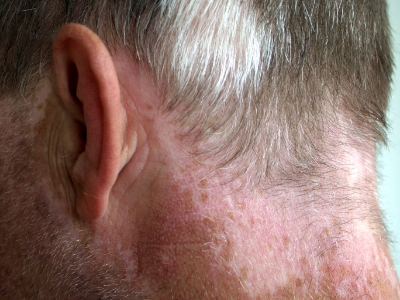
What are the types of Vitiligo?
Generalized: This is the most common type when macules appear in various places on the body.
- Segmental: This is limited to one side of the body or one area, such as the hands or face.
- Mucosal: This affects mucous membranes of the mouth and the genitals.
- Focal: This is a rare type wherein the macules are in a small area and do not spread in a certain pattern within one to two years.
- Trichome: This means that there is a white or colorless center, then an area of lighter pigmentation, and then an area of normally colored skin.
- Universal: This is another rare type of vitiligo, and one in which more than 80% of the skin of the body lacks pigment.
What causes Vitiligo?
The exact cause of Vitiligo is not completely understood, but these factors may play a role:
- Genetic factors: Certain factors that may increase the chance of getting vitiligo can be inherited. There are about 30% of vitiligo cases run in families.
- Neurogenic factors: A substance that is toxic to melanocytes may be released at nerve endings in the skin.
- Autoimmune disorder: The immune system of the affected person may develop antibodies that destroy melanocytes.
- Self-destruction: A defect in the melanocytes causes them to destroy themselves.
How is Vitiligo treated?
The goal of medical treatment is to create a uniform skin tone by either restoring color or eliminating the remaining color. Common treatments may include:

1. Camouflage Therapy
- The use of sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. The use of sunscreens minimizes tanning, thereby limiting the contrast between affected and normal skin.
- Hair dyes if vitiligo affects the hair.
- Depigmentation therapy with the drug monobenzone can be used if the disease is extensive. This medication is applied to pigmented patches of skin and will turn them white to match the areas of vitiligo.
2. Repigmentation Therapy
- Topical vitamin D analogs
- Topical immunomodulators such as calcineurin inhibitors
- Corticosteroids can be taken orally or topically. Results may take up to 3 months. The doctor will monitor the patient for any side effects, which can include skin thinning or striae if used for a prolonged period.
3. Light Therapy
- Narrowband ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) needs two to three treatment sessions per week for several months.
- Excimer lasers emit a wavelength of ultraviolet light close to that of narrow-band UVB.
- Combining oral psoralen and UVA (PUVA) is used to treat large areas of skin with vitiligo.
4. Surgery
- Autologous skin grafts: Skin is taken from one part of the patient and used to cover another part.
- Micropigmentation: A type of tattooing that is usually applied to the lips of people affected by vitiligo.
5. Medications



