Urticaria: Causes, Symptoms, Triggers, Treatment, and Prevention
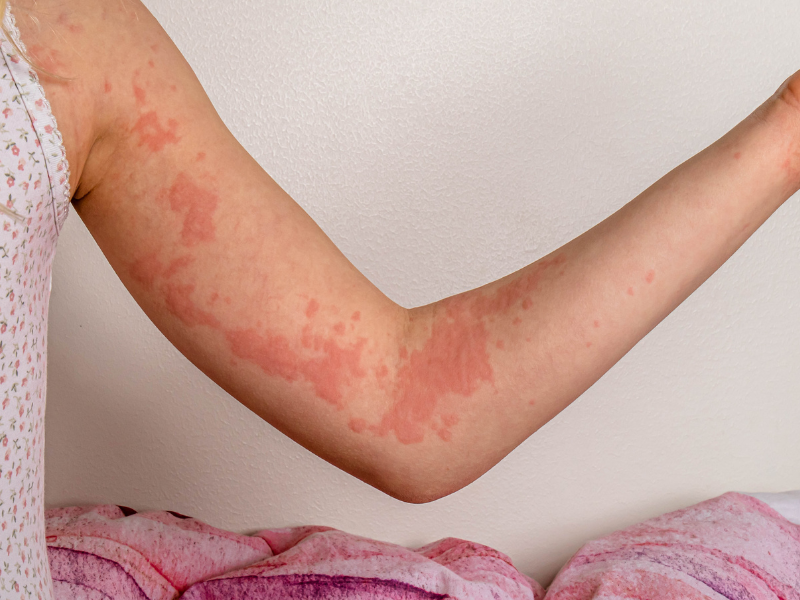
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by a very itchy skin rash. They are frequently caused by an allergic reaction to food or something you’ve touched. Hives can be short-lived (acute hives) or long-lasting (chronic hives). Antihistamines and steroids may be used as treatments.
What Causes Urticaria?
Urticaria can arise from a variety of factors, both allergic and non-allergic.
- Allergic Reactions: Urticaria often arises from allergens triggering an immune response. Substances like certain foods, medications, insect stings, and pollen can set off allergic urticaria.
- Physical Factors: Non-allergic triggers can lead to physical urticaria, such as:
- extreme temperatures
- pressure on the skin
- exercise
These factors prompt histamine release, causing hives.
- Autoimmune Factors: Chronic urticaria persist for over six weeks. This may result from autoimmune conditions and stress. Immune responses against the body’s tissues contribute to this form.
What are the Symptoms of Urticaria?
The hallmark symptom is the appearance of raised, red welts on the skin. These are often accompanied by intense itching.
- Welts on the Skin: These wheels vary in size and shape. They may merge, creating larger affected areas These welts are often accompanied by intense itching.
- Itching Sensation: Urticaria triggers a relentless itching sensation. This causes discomfort and sometimes affects sleep. Scratching can exacerbate the condition.
- Angioedema: In some cases, angioedema accompanies urticaria. This involves swelling in deeper skin layers. The swelling is typically found around the eyes, lips, and throat.
This condition can affect any part of the body. However, it commonly occurs on the arms, legs, back, and torso.
What Triggers Urticaria?
Identifying and avoiding triggers is a crucial step in managing urticaria.
- Dietary Triggers: Certain foods, such as shellfish, nuts, eggs, and dairy, can induce allergic urticaria.
- Medications: Medications like Aspirin, NSAIDs, and antibiotics can trigger hives as an allergic reaction.
- Environmental Factors: External triggers known to provoke urticarial outbreaks include:
- exposure to pollen
- latex
- animal dander
- insect stings
- Physical Factors: Physical triggers may include:
- pressure on the skin
- cold temperatures
- heat
- excessive sweating
Treatment and Medications for Urticaria
The treatment of urticaria depends on its underlying cause and severity.
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines effectively manage mild urticaria. It does this by blocking histamine, the primary allergic response chemical.
- Prescription Medications: For severe or chronic cases, stronger antihistamines, corticosteroids, leukotriene inhibitors, or immune modulators are recommended.
- Epinephrine: In cases of severe allergic reactions or angioedema, epinephrine injections can swiftly alleviate symptoms and prevent life-threatening complications.
How to Prevent Urticaria?
Complete prevention of urticaria may not always be possible. However, there are several measures that you can take to minimize the occurrence of outbreaks:
- Identify and Avoid Triggers: As mentioned earlier, identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial. Keeping a detailed diary of activities, foods, and environmental factors can help pinpoint potential triggers. This can also assist healthcare professionals in devising an effective management plan.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can bolster the immune system. It will also reduce the likelihood of urticarial outbreaks. These include exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing stress.
- Protect the Skin: When exposed to physical triggers like extreme temperatures or pressure, Wearing appropriate clothing and using skin protection measures can help prevent the development of wheals and itching.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration can help keep the skin healthy and resilient. This also reduces the risk of irritation and inflammation.
Urticaria, or hives, can be a bothersome and uncomfortable skin condition. By understanding its causes, symptoms, triggers, and available treatment options, those dealing with urticaria can better manage their condition and improve their quality of life.



