Allergic Contact Dermatitis Demystified: Unveiling Causes, Symptoms, Triggers, Treatment, and Prevention
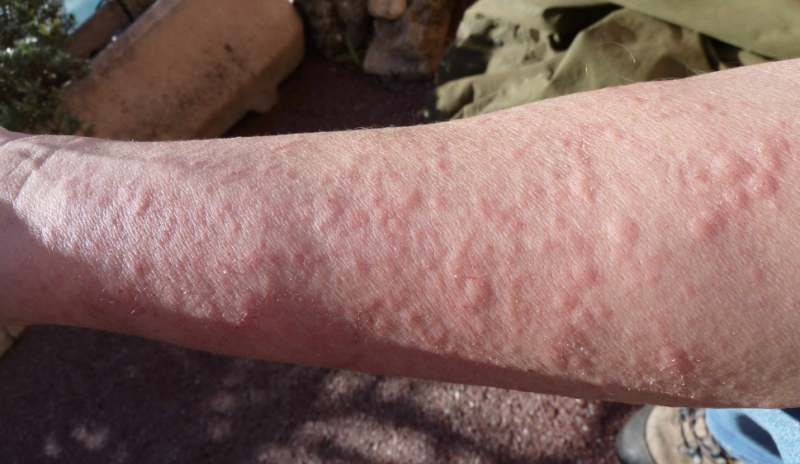
Allergic contact dermatitis is a prevalent skin condition characterized by an itchy rash. The itchy rash is caused by direct contact with a chemical or an allergic reaction to it. The rash is not contagious, but it can be exceedingly unpleasant.
Triggers may be due to a variety of factors, including cosmetics, scents, jewelry, and plants. The rash usually appears within days of being exposed.
What Causes Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis occurs due to exposure to substances. These substances can either irritate the skin or prompt an allergic response. They encompass a wide array of identified allergens and irritants.
Contact with Allergens: The primary cause of allergic contact dermatitis is direct contact with allergens. These allergens are typically substances found in everyday products. This includes fragrances, preservatives, metals (like nickel), and certain chemicals.
Immune Response: When the skin comes into contact with an allergen, the immune system is triggered to respond. This immune response leads to the development of inflammation and itchy rash.
What are the Symptoms of Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
Symptoms of this skin condition vary widely and may include:
- Skin Rash: Red, itchy rash at the site of allergen contact. This rash can vary in severity, from mild redness to extensive blistering.
- Itching and Discomfort: itchiness can be intense. This causes discomfort and potentially leads to scratching which can exacerbate the rash.
- Blisters and Swelling: In more severe cases, blisters may form. These blisters are accompanied by swelling. Blisters can rupture, leading to oozing and crusting of the affected skin.
What Triggers Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
Numerous substances can act as triggers for allergic contact dermatitis. These include:
- Cosmetics and Personal Care Products: Ingredients commonly found in cosmetics, skincare products, and toiletries can initiate allergic reactions.
- Metals: Certain metals, like nickel, can provoke skin reactions in susceptible individuals. These materials are often present in jewelry and clothing accessories.
- Topical Medications: Topical medications can cause allergic reactions when applied to the skin. This include antibiotic ointments.
- Cleaning Agents: Harsh cleaning agents and detergents can irritate the skin. This can potentially lead to allergic contact dermatitis.
Treatment and Medications for Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Managing allergic contact dermatitis involves several approaches to ease symptoms and promote healing:
- Avoidance of Allergens: Identifying and avoiding the allergens that trigger the condition is crucial. This requires:
- scrutiny of product labels
- making informed choices about personal care items and household products
- Topical Corticosteroids: For mild to moderate cases, OTC or prescription topical corticosteroids can be effective in reducing inflammation and alleviating itching.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: When corticosteroids are not suitable, topical calcineurin inhibitors may be used to manage inflammation.
- Oral Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines are often recommended to relieve itching and discomfort. This may be particularly helpful during acute flare-ups.
- Moisturizers: Regular application of moisturizers helps maintain skin hydration. This also reduces the risk of flare-ups.
How to Prevent Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
Prevention plays a crucial role in managing allergic contact dermatitis:
- Patch Testing: Patch testing can help identify specific allergens. This facilitates targeted allergen avoidance.
- Product Selection: Opt for products labeled as hypoallergenic and free from known allergens. It’s advisable to perform patch tests before using new products.
- Jewelry Choices: Choose jewelry made from hypoallergenic materials. This can help minimize exposure to potential allergens like nickel.
- Protective Measures: Wear protective gloves and clothing when handling potentially irritating substances. This help reduces skin contact and lowers the risk of triggering reactions.



