Bronchitis
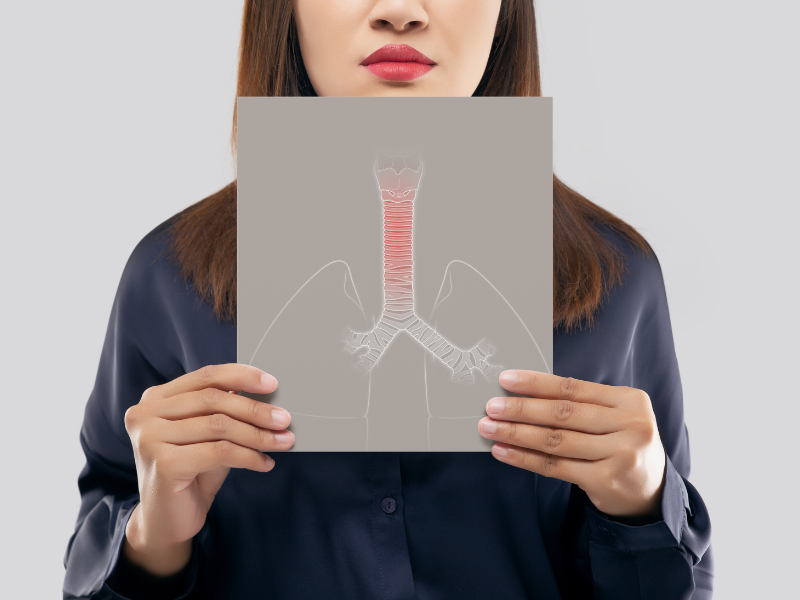
Bronchitis is a respiratory condition that affects the bronchial tubes, which are the air passages that connect the mouth and nose to the lungs. The condition is characterized by inflammation and swelling of the bronchial tubes, leading to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
Causes of Bronchitis
Viruses are typically responsible for bronchitis. It may occur during or following a cold or other respiratory infection. These viruses can irritate and inflame the bronchial tubes, leading to symptoms of bronchitis. Other causes may include:
- Bacterial infections: In some cases, bronchitis can be caused by a bacterial infection, such as pneumonia or bronchitis caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis (whooping cough).
- Irritants: Exposure to irritants can also cause bronchitis. This includes:
- Smoke
- Dust
- Fumes
- air pollution
- chemical gases
These irritants can damage the lining of the bronchial tubes and cause inflammation.
- Allergens: Allergens can also cause bronchitis in some individuals. This includes:
- Pollen
- Mold
- pet dander
Symptoms of Bronchitis
Bronchitis usually begins with a dry, irritating cough caused by inflammation of the bronchial tube lining. Other symptoms may include:
- Cough: A persistent cough is the most common symptom of bronchitis. The cough may be dry or may produce mucus or phlegm. Acute bronchitis can cause a cough that lasts 2 to 3 weeks.
- Wheezing: Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound that happens while you breathe, particularly during exhalation.
- Shortness of breath: Bronchitis can make it difficult to breathe, especially during physical activity.
- Chest tightness or pain: The inflammation and swelling of the bronchial tubes can cause chest tightness or pain.
- Fatigue: Bronchitis can cause fatigue and weakness. This can make it difficult to perform daily activities.
- Fever and chills: Bronchitis can occasionally cause fever and chills, especially if it is caused by a bacterial infection.
Treatment of Bronchitis
The treatment for bronchitis depends on the underlying cause of the condition.
Doctors will not prescribe antibiotics for virus-induced bronchitis.
Bronchitis caused by a viral infection will resolve on its own within a few weeks.
Several treatment options can ease bronchitis symptoms, including:
- Rest and fluids: Rest and staying hydrated can help your body fight off the virus that is causing your bronchitis.
- Pain relievers: OTC pain relievers can help alleviate fever, chest tightness, and pain. These are:
- Acetaminophen
- ibuprofen
- Cough suppressants: Cough suppressants can help reduce the frequency and severity of your cough.
- Bronchodilators: Bronchodilators help open up the airways and make it easier to breathe.
- Steroids: Steroids can help reduce inflammation in the bronchial tubes and ease symptoms.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed if your bronchitis is caused by a bacterial infection.
Prevention of Bronchitis
There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing bronchitis, including:
- Avoiding irritants and allergens
- Washing your hands regularly
- Getting vaccinated
- Quitting smoking
Risk Factors for Bronchitis
Individuals with an increased risk of acute bronchitis include:
- Older individuals
- Those exposed to irritating chemicals
- Young children
- Smokers
- Those with weakened immune systems
- Individuals with pre-existing lung conditions, like asthma
- Individuals who have not received vaccinations against influenza, whooping cough, or pneumococcal disease



