Athlete’s Foot
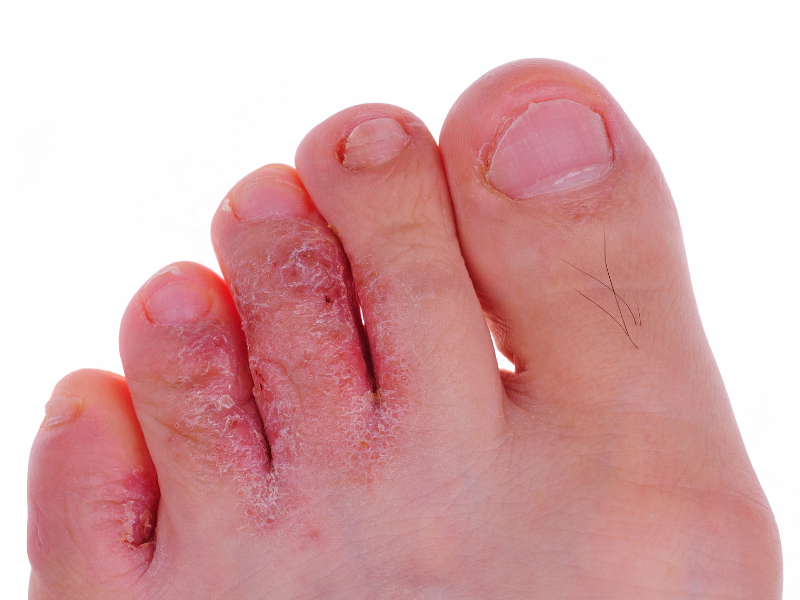
Athlete’s foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet, particularly between the area of the toes.
It is a contagious condition often characterized by burning, itching, and cracking of the skin. The infection can also cause the skin to become scaly, flaky, or cracked, and in some cases, it may lead to the formation of blisters or open sores.
While an athlete’s foot is typically not serious, it can cause discomfort and inconvenience if left untreated.
Causes of Athletes Foot
Athlete’s foot is caused by various types of fungi, including:
· Trichophyton
· Epidermophyton
The fungi that cause an athlete’s foot thrive in moist, warm, environments, making places like swimming pools, locker rooms, and saunas ideal breeding grounds for the infection.
Since it’s highly contagious, it can be spread through direct skin-to-skin contact or by coming into contact with contaminated surfaces, such as towels, socks, or shoes.
Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot
Athlete’s foot symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. In general, the infection causes the skin on the feet to become:
· Irritated with discoloration
· Stinging, burning, and itching sensation between the toes
· scaling or flaking
In more severe cases, the infection can spread to the toenails, causing them to become discolored, thick, and even crumble.
Is Athlete’s Foot Contagious?
An athlete’s foot can spread easily. Direct contact with contaminated surfaces or the sharing of objects like shoes, socks, or towels can both result in its spread from one person to another. Walking barefoot in public places where the fungi thrive also increases the risk of transmission.
Who Is at Risk?
While anyone can develop athlete’s foot, certain factors may increase the risk, including:
- Going barefoot in public spaces including swimming pools, gyms, and locker rooms
- Having a weakened immune system
- Wearing tight-fitting or poorly ventilated shoes
- Having sweaty feet
- Sharing personal items like towels or shoes with someone who has athlete’s foot
How Do You Get Athlete’s Foot?
Athlete’s foot is often contracted by coming into touch with the fungi that cause the condition. This can happen by walking barefoot in contaminated areas or sharing objects with an infected person. When the fungi penetrate the skin, they grow and create the typical symptoms of athlete’s foot.
How is it treated?
Over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal creams, ointments, gels, sprays, or powders can effectively treat athlete’s foot. These products contain:
· Clotrimazole
· Miconazole
· Tolnaftate
· terbinafine
These medications work by killing the fungi or preventing them from growing further. Prescription antifungal medications may be necessary in severe cases.
It is essential to finish the full course of medication to ensure that the infection is completely cleared up. Even if the symptoms go away, it is important to continue treatment to prevent the infection from returning.
How is it prevented?
Preventing an athlete’s foot involves taking steps to reduce the risk of exposure to the fungus that causes the infection. Here are some ways to prevent athlete’s foot:
- Wear flip-flops or sandals in public areas such as locker rooms, swimming pools, and communal showers.
- Keep the feet clean and dry, especially between the toes.
- Wear socks that wick moisture away from the feet.
- Alternate shoes and allow them to dry out completely before wearing them again.
- Avoid sharing towels, socks, or shoes with others.
- Use antifungal powder or spray on the feet and inside shoes to help prevent the growth of fungus.
Athlete’s foot is a contagious fungal infection of the feet that causes redness, itching, and burning. Prevention entails limiting fungus exposure, and treatment usually entails clearing the infection with antifungal drugs, either over-the-counter or prescription. Completing the entire course of medication is critical for a successful recovery.



