What is Syphilis?
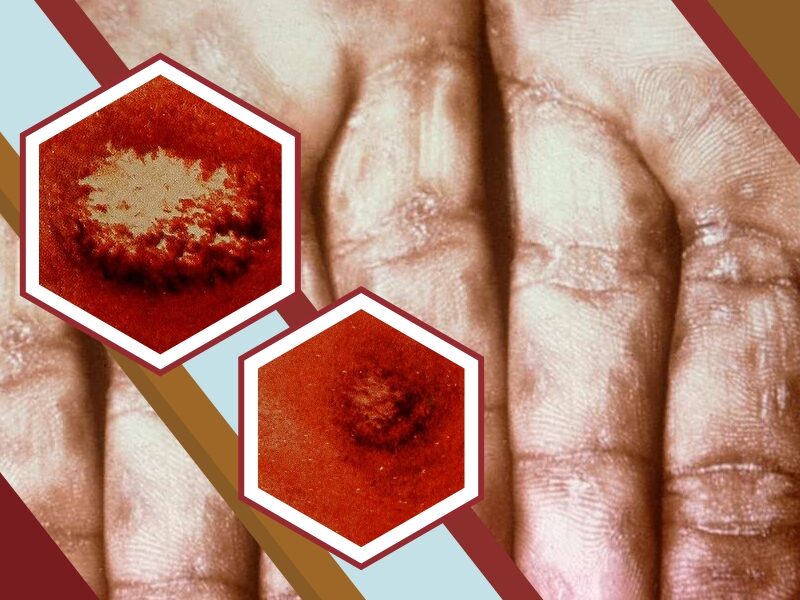
Syphilis is a bacterial infection typically spread by sexual contact. The infection starts as a painless sore in the genital, mouth, or rectum. Syphilis spreads from person to person through the skin or mucous membrane contact with these sores. The bacteria that cause this infection can remain inactive in the body for decades before becoming active again.
Symptoms of Syphilis
Symptoms depend on the stage of syphilis:
- Early or primary syphilis. People with primary syphilis get one or more sores called chancres. They are usually small, painless ulcers. The spots may appear on your genitals, anus, rectum, or in or around your mouth.
- Secondary syphilis. Typically, this stage begins 6 weeks to 6 months after exposure and lasts 1 to 3 months. People with secondary syphilis usually get rash on the palms of their hands and soles of their feet. They may also have different rashes on other parts of their body. Other symptoms include moist, wart-like lesions in the groin, white patches in the mouth, swollen lymph glands, fever, hair loss, and weight loss.
Syphilis Causes
Syphilis is caused by the bacteria treponema pallidum. Getting syphilis is as simple as touching someone with a sore from syphilis. Typically, the bacteria enter your body through your skin through cuts or through your mucous membranes during sexual activity.
How is Syphilis Transmitted?
Syphilis is transmitted is through direct contact with syphilitic chancres, or sores that may develop in the penis, anus, vagina, and mouth. Syphilis is primarily transmitted sexually. Note that you cannot get the infection by sharing a toilet, wearing another person’s clothing, or using other people’s eating utensils.
Stages of Syphilis Infection
- Primary syphilis. The first sign of syphilis is a small sore, called a chancre. The sore appears at the spot where the bacteria entered your body.
- Secondary syphilis. The rash may begin on your trunk and eventually cover your entire body within a few weeks of healing the original chancre. This rash is usually not itchy and may be accompanied by wartlike sores in your mouth or genital area.
- Latent syphilis. Syphilis moves from the secondary stage, when you have symptoms, to the hidden stage if you are not treated. Signs and symptoms may never return, or the disease may progress to the third stage.
- Tertiary syphilis. In the late stage, the disease may damage the brain, nerves, eyes, heart, blood vessels, liver, bones, and joints. These problems may occur many years after the original, untreated infection.
- Neurosyphilis. As soon as syphilis spreads, it can cause damage to the brain and nervous system, as well as to the eyes.
- Congenital syphilis. Babies born to syphilis-infected mothers can be infected through the placenta or during delivery. Congenital syphilis in newborns usually is not accompanied by symptoms, although it may cause a rash on the palms and soles of the feet.
Syphilis Risk Factors
- Unprotected sex
- Multiple sex partners
- HIV
- Man having sex with men
Treating and Curing Syphilis
Syphilis is curable with quick diagnosis and treatment. When treated too late, the infection can permanently damage the heart and brain. Doxycycline is a tetracyclic antibiotic that is used as a treatment medication for syphilis. This prevents the bacteria from multiplying and spreading to other parts of the tissue.



