Scabies: Everything You Need to Know
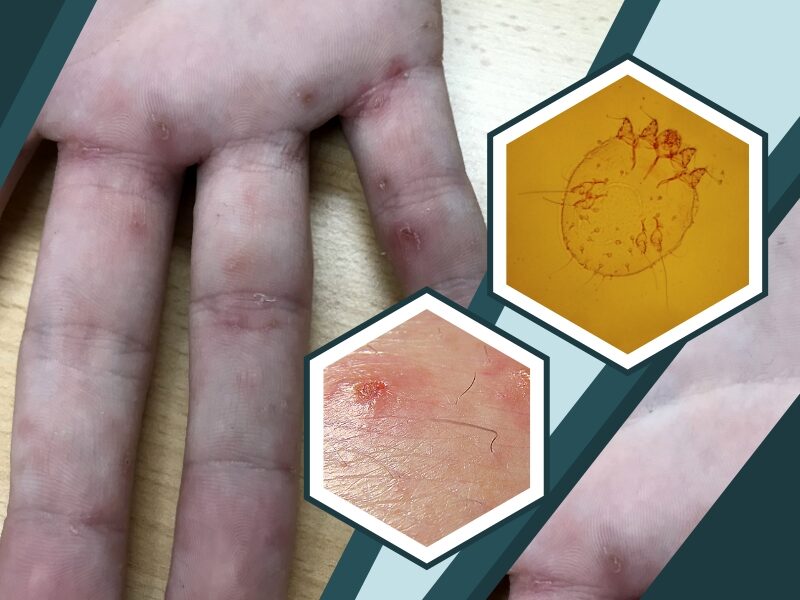
What is Scabies?
Scabies is an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite and affects people of all races. The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. It can spread rapidly under crowded conditions where close body and skin contact is frequent.
Symptoms
- Severe and usually worse itching especially at night
- Wavy and thin tunnels made up of tiny blisters
- Pimple-like skin rash
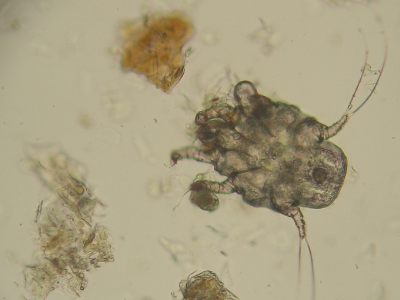
Causes
Scabies is caused by a tiny, eight-legged mite. Mites burrow just under the skin and lay eggs in tunnels. The eggs hatch and the mite larvae travel to the surface of the skin, where they mature. Once these mites have spread to other parts of your skin or to other people’s skin, they may multiply and become more widespread.
Allergic reactions to mite eggs, wastes, and eggs are responsible for itching. When people with scabies touch one another or share clothing or bedding, the mites can spread. A scabies-infected animal may cause brief itching if the mites get under the skin. But within a few days, the mite will die.
How Do Scabies Spread?
Scabies typically spread through prolonged, skin-to-skin contact that gives the mites time to crawl from one person to another. It also spread through shared personal items, such as bedding or towels, which may occasionally be blamed. Scabies can be passed easily between family members or sexual partners.
Different Types of Scabies
- Nodular. This type is more common among children. Even after the mites are gone, brown-red nodules may still be visible.
- Bullous. Adults with this type of scabies may mistake it for bullous pemphigoid, another skin blistering condition.
- Crusted. This type often happens in people with faulty immune systems. It tends to form crusted areas covering a large area of skin.
- Scalp. Psoriasis-like scales may appear on your scalp in this form.
How Long Does Scabies Last?
Scabies mites can live for 1 to 2 months in children and adults. When they are not on people, mites only survive for up to 72 hours. The itching and rash that scabies cause may initially become worse, but they will heal within four weeks.
Treatment
Ivermectin is an FDA-approved antiparasitic drug used to treat several neglected tropical diseases, including scabies. It improves the patient’s condition by killing the mites that cause the condition. Buy Ivermectin online and take them as prescribed by doctors.



