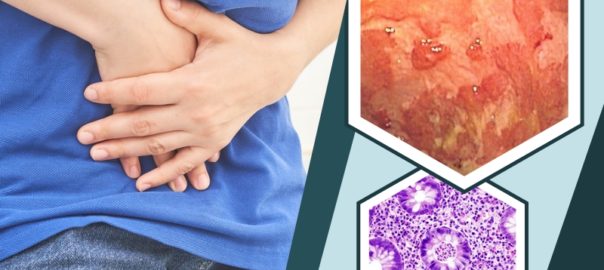
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic disorder of the digestive system that affects the large intestine. People with this condition experience abnormal inflammation which may result in open sores called ulcers inside the colon and rectum.
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis?
- Genetic Causes: In some families, ulcerative colitis is inherited. Researchers have identified genetic variations that may contribute to Ulcerative Colitis, but they are not sure exactly how these differences are linked directly to the disease.
- Overactive Intestinal Immune System: By attacking viruses, bacteria, and other threats, the immune system protects the body. These invaders are suspected of confusing the immune system and tricking it into launching an immune response against the lining of the large intestine, resulting in Ulcerative Colitis.
- Emotional Stress: Ulcerative colitis does not appear to be caused by this. Some studies suggest that it can cause Ulcerative Colitis flare-ups in some people who have already developed it.
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
- Abdominal cramps, discomfort or pain
- Persistent diarrhea with blood, pus, or mucus in the stool
- Urgent and loose bowel movements
- Bloody stool
- Nausea
- Weight loss
- Slowed or delayed growth in children
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Anemia due to excessive intestinal bleeding
Types of Ulcerative Colitis
Five types of Ulcerative Colitis are identified largely by where they are located in the body or their severity.
1. Ulcerative Proctitis
This is usually the mildest form of Ulcerative Colitis. It is limited to the rectum and rectal bleeding may be the only sign or symptom.
2. Proctosigmoiditis
This type affects the lower end of the colon along with the rectum and is sometimes called the sigmoid colon. Symptoms include abdominal cramps/pain and bloody diarrhea.
3. Left-Sided Colitis
This type causes cramps on the left side of the abdomen that affects the rectum and the portion of the colon on the left side of the body. Signs and symptoms include weight loss and bloody diarrhea.
4. Pancolitis
Pancolitis can affect the entire colon which causes multiple symptoms including major weight loss, bloody diarrhea, pain, abdominal cramps, and fatigue.
5. Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis
This condition is rare but affects the entire colon. Symptoms include pain, fever, and bloody diarrhea.
How To Diagnose Ulcerative Colitis?
To diagnose ulcerative colitis, doctors review your symptoms and medical and family history and perform a physical exam and tests. Medical tests may include stool tests, blood tests, and endoscopy of the large intestine.

Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis treatment usually involves either drug treatment or surgery.
1. Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Sulfasalazine
- Mesalamine
- Balsalazide
- Olsalazine
2. Corticosteroids
3. Immune System Suppressors
- Azathioprine
- Mercaptopurine
- Cyclosporine
- Tofacitinib
4. Biologics
- Infliximab
- Adalimumab
- Golimumab
- Vedolizumab
- Ustekinumab
5. Other Medications
- Loperamide
- Acetaminophen
Even when you are not experiencing symptoms, take your medication as prescribed. You may experience flare-ups if you skip the medications you’re supposed to take. The best way to manage ulcerative colitis is to follow your treatment plan and talk to your healthcare provider on a regular basis.