Nociceptive Pain Caused By Injury
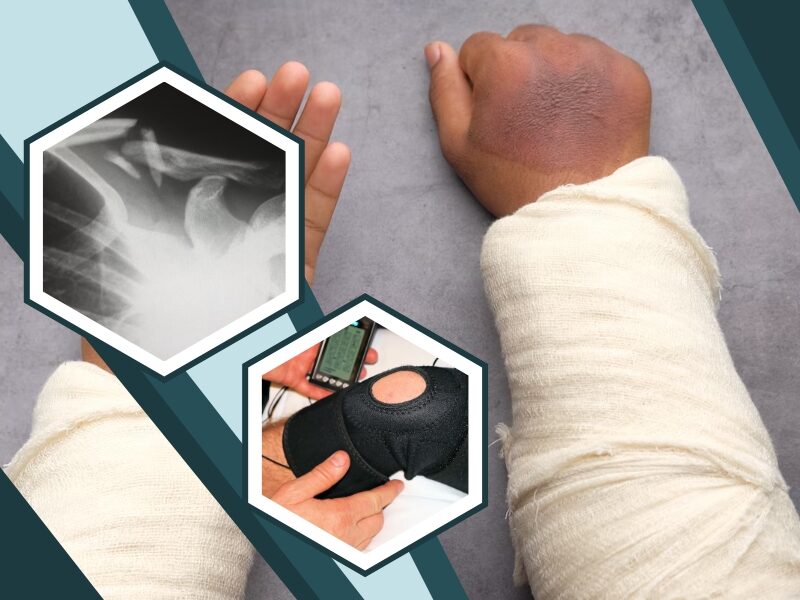
Nociceptive pain is discomfort due to your body’s response to damage to your tissues. Most pain you experience is nociceptive, commonly affecting your muscles, joints, and bones. Although it is sharp in nature, it goes away as soon as its underlying cause is healed.

Types of Nociceptive Pain
- Radicular pain. Radicular pain occurs when the nerve roots are irritated. It goes down your arm or leg through a nerve from the spinal cord. It causes numbness, weakness, and tingling or feelings of pins and needles, among other symptoms.
- Somatic pain. Somatic pain happens due to activated pain receptors in your tissues. This type of pain is often stimulated by movement. It’s usually localized. Headaches and cuts are both considered somatic pain.
- Visceral pain. Visceral pain happens due to the inflammation or injury of internal organs such as the heart. Visceral pain is often vague, occurs frequently, and feels like a deep ache or pressure.
Nociceptive vs. Neuropathic Pain
Neuropathic pain is linked with damage to the body’s neurological system, typically caused by an infection. It is generally described as shooting pain that travels along the nerve. On the other hand, nociceptive pain arises from actual or threatened damage to non-neural tissue due to the activation of the nociceptor.
What Does Nociceptive Pain Feel Like
Nociceptive pain feels sharp, aching, or throbbing. People commonly experience this condition in the musculoskeletal system. This includes the joints, muscles, skin, tendons, and bones. Left untreated, it can interfere with your daily life and make it difficult to move, causing mobility issues.
Examples of Nociceptive Pain

- Cuts
- Bruises
- Sprain
- Joint arthritis
- Crash injury
- Broken bones
- Joint damage caused by arthritis
- Damage or blockage in your internal organs and soft
- Cancer pain is also usually nociceptive
Treatment for Nociceptive Pain
Treatment for this condition involves treating the underlying condition or waiting for the injury to heal. A combination of pain management strategies such as physical therapy and medications also treats nociceptive pain. Doctors may also recommend prescription medications like opioids or antidepressants, depending on the severity of the condition.



