Genital Warts: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Genital warts are one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), HPV is the most common of all STIs. Everyone who is sexually active is vulnerable to complications of HPV, including genital warts.
What are Genital Warts?
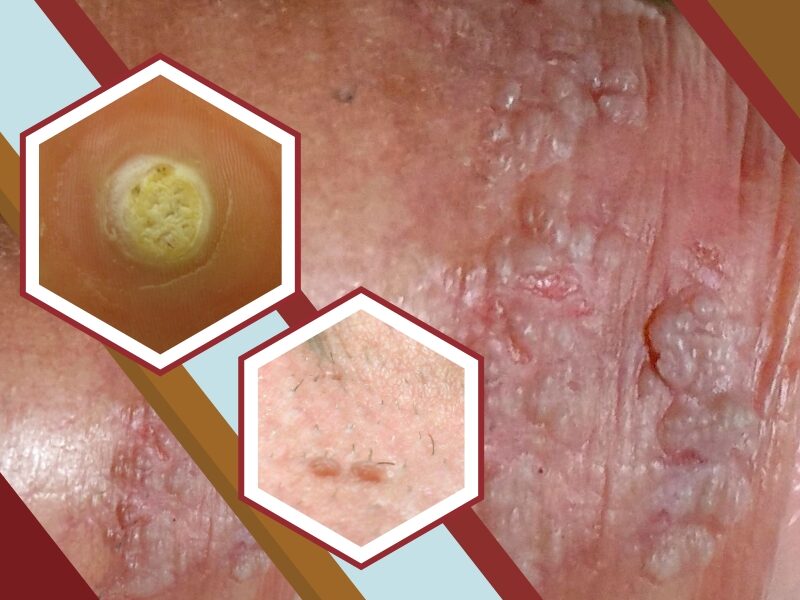
Genital warts are similar to common warts but are usually found around or in the vagina, cervix, penis, scrotum, rectum, or the area between the vagina and rectum. They are soft, fleshy, small growths on the skin.
This condition is more contagious, or more easily spread, than other warts. They are spread by skin-to-skin contact. They may spread to other nearby parts of the body and they may be passed from person to person by sexual activity. The warts are usually first seen 1 to 6 months after you have been infected with HPV. However, you can be infected with HPV without having any visible warts.
Signs and Symptoms
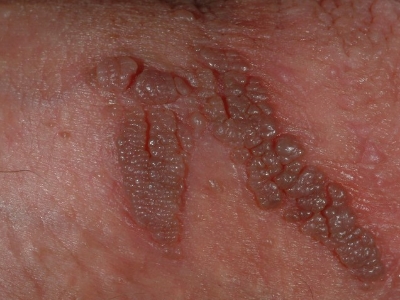
Genital warts are transmitted through sexual activity including oral, vaginal, and anal sex. You may not start to develop warts for several weeks or months after infection. It isn’t always visible to the human eye. They may be very small and the color of the skin or slightly darker. The top of the growths may resemble a cauliflower and may feel smooth or slightly bumpy to the touch. They may occur as a cluster of warts, or just one wart.
For people assigned male at birth, genital warts may appear in the following areas:
- Groin
- Thighs
- Penis
- Scrotum
- Inside or around the anus
For people assigned female at birth, these warts may appear:
- Outside of the vagina or anus
- On the cervix
- Inside of the vagina or anus
Genital warts may also appear on the lips, mouth, tongue, or throat of a person who has had oral sexual contact with a person who has HPV.
Even if you can’t see genital warts, they may still cause symptoms, such as:
- Vaginal discharge
- Itching
- Bleeding
- Burning
If genital warts spread or become enlarged, the condition can be uncomfortable or even painful.
What causes Genital Warts?
A genital wart appears on the skin around your genitals and anus. Certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) cause them. Some types of HPV can cause cancer, but those aren’t the same ones that result in genital warts.
HPV can be a challenging STD to understand. Most of the time, it will fade away on its own, but it is one of the most common STDs. Untreated high-risk HPV can sometimes develop into cancer. It is also possible to get warts on your vulva, vagina, cervix, rectum, anus, penis, or scrotum from other low-risk types of HPV. Genital warts are common. About 360,000 people get them each year.
Treatment and Management of Genital Warts

Depending on the severity, genital warts may disappear on their own, grow larger, or multiply. Genital warts can be removed in different ways. Getting rid of warts may require several treatments. Generally, an anesthetic will be administered first to numb the area being treated. Sexual contact should be avoided during treatment. Your healthcare provider may use one of these methods to treat genital warts:
- Freezing: During cryotherapy, your provider applies the liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy warts.
- Electrocautery: An electric current burns away warts.
- Laser treatment: A laser light destroys tiny blood vessels inside warts, cutting off their blood supply.
- Topical medicine: Once a week for several weeks, you apply a prescription chemical solution to warts. The chemical causes blisters to form under warts, stopping blood flow. In some cases, your provider may apply the solution.
- Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP): Your provider uses an electrically charged wire loop to remove warts. A provider may use this method to remove warts on a woman’s cervix.
- Topical TCA solution: Your provider may also provide a prescription for a topical medical when appropriate that patient self-administers at home for some weeks as directed.
- Surgery: Your provider may surgically cut out warts that are large or don’t respond to other treatments.
The recommended medicine for genital warts:
- Imiquimod Cream – this is a drug that is topically administered. Imiquimod is in a class of medications called immune response modifiers. It treats genital and anal warts by increasing the activity of the body’s immune system.



