Genetic Ovarian Cancer

Genetic Ovarian Cancer diagnosis is considered when there are multiple cases of ovarian cancer on the same side of the family. The chance of having the disease increases in any of these situations:
- One or more women are diagnosed at age 45 or younger
- There are ovarian cancer in multiple generations on the same side of the family
- There is a history of ovarian cancer in the family
What Causes Genetic Ovarian Cancer?
The gene mutation is the most common cause of hereditary ovarian cancer. Mutations in other genes are also associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer, but scientists have not identified all of the genes involved.
Genes are instructions made from DNA that tell our cells how to function. Every cell in our body contains genes that decide and control how it functions, grows, and appears. Genes are duplicated in each person, one from the mother and one from the father.
Genes enable our cells to function normally. Occasionally, inherited genes may have small changes, known as mutations or alterations. The alteration or mutation of one of our genes can sometimes result in an increased risk of developing certain illnesses, compared to people who do not have the genetic change. The chances of passing on a gene mutation to a child are 50%.
Other Causes and Risk Factors
Risk factors for ovarian cancers in addition to genetic mutations include:
- Getting older
- Being obese or overweight
- Having children later or not at all
- Taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- Using fertility treatments
- Beginning menstruation early or before the age of 12
- Smoking
- Starting menopause later or after the age of 50
Diagnosis of Genetic Ovarian Cancer
People with new signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer lasting longer than 2 weeks must see a doctor for testing. These may include:
- Problems going to the bathroom, such as urgently or frequently needing the toilet
- Difficulty eating or feeling full too fast
- Pain in the stomach or pelvis
- Bloating
The doctor may use various tests to diagnose ovarian cancer including ultrasound, MRI scan, and CT scan. Diagnosis can also involve blood tests, colonoscopy, or biopsies. Early detection is vital to successfully treating ovarian cancer.
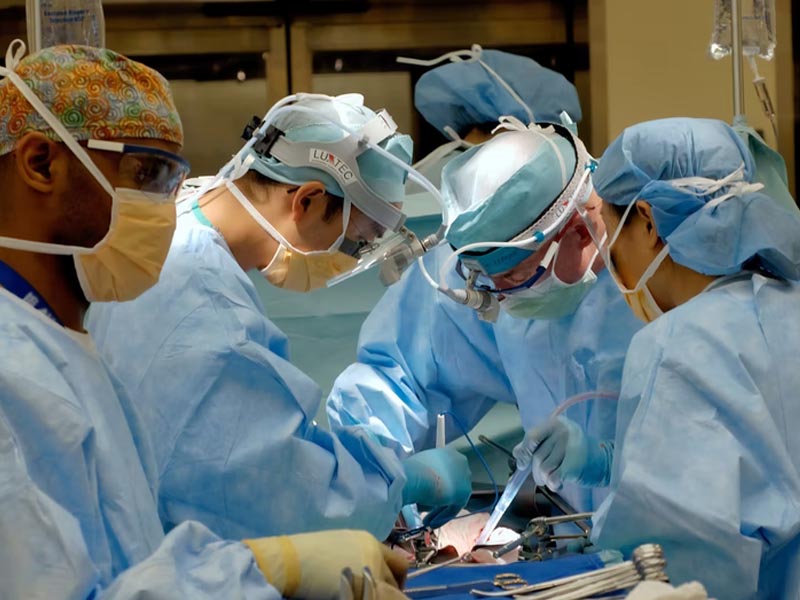
Treatment for Genetic Ovarian Cancer
Doctors will recommend treatment options based on the severity of cancer and the overall health of the patient. Ovarian cancer is usually treated with a combination of surgery to remove the cancerous tissue and chemotherapy to kill the remaining cancerous cells.
Targeted therapy is sometimes used by doctors. It involves identifying and attacking specific cancer cells with drugs. Chemotherapy typically causes more side effects.



