Causes and Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer

Ovarian cancer is a malignant growth of cells within the ovaries. These cells reproduce rapidly, causing damage to healthy tissues.
There are two ovaries in the female reproductive system, one on either side of the uterus. Each ovary is about the size of an almond, and it produces eggs (ova) and hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. In most cases, ovarian cancer is treated with surgery and chemotherapy.
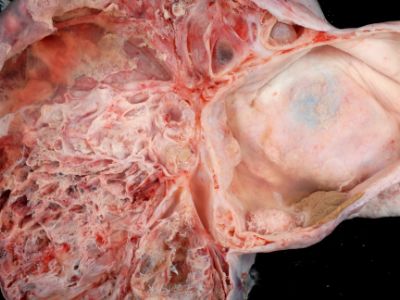
Cause of Ovarian Cancer
Scientists believe ovarian cancer is caused by cells located in or close to the ovaries that become mutated (changed). A cell’s DNA carries instructions for its function. Cancer cells grow and multiply rapidly when they are altered, forming a mass of cancer cells. At the same time, healthy cells die, cancer cells live on. Cancer cells can break off from an initial tumor and invade nearby tissues so they can spread to other parts of the body (metastasize).
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
As ovarian cancer develops, it may not cause any noticeable symptoms. This disease is usually attributed to other more common conditions when the symptoms occur. The symptoms of ovarian cancer may include:
- A frequent need to urinate
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation
- Back pain
- Fatigue
- Discomfort in the pelvic area
- Weight loss
- Quickly feeling full when eating
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
Risk Factors of Ovarian Cancer
Factors that increase your risk of ovarian cancer include:
- Being overweight or obese
- Older age
- Family history of ovarian cancer
- Inherited gene changes
- Endometriosis
- Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy
- Age when menstruation started and ended
Diagnosis for Ovarian Cancer
Tests and procedures used to diagnose ovarian cancer include:
- Blood tests
- Pelvic exam
- Imaging tests
- Genetic testing
- Surgery
Your doctor will assign a stage to your cancer once you’ve been diagnosed with ovarian cancer. The stages range from 1 to 4, which are often denoted with Roman numerals I to IV. The lowest stage indicates that the cancer is confined to the ovaries.
Prevent Ovarian Cancer
There are no exact ways how you can prevent ovarian cancer, but there may be ways to lessen your risk:
- Consider taking birth control pills. You may ask your doctor whether birth control pills may be right for you. Taking birth control pills reduces the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Discuss your risk factors with your doctor. If you have a family history of ovarian cancers, bring this up with your doctor. Your doctor can define what this may mean for your own risk of cancer. If you’re found to have a gene change that increases your risk of ovarian cancer, you may consider surgery to remove your ovaries to prevent cancer.
Treatment and Medication for Ovarian Cancer
Treatment of ovarian cancer usually involves a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. Other treatments may be used in certain situations.
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Hormone therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Supportive (palliative) care
Medications approved to use for the treatment of ovarian cancer include:
- Melphalan
- Lynparza (Olaparib)
- Olaparib
- Niraparib Tosylate Monohydrate
- Paclitaxel
- Bevacizumab
- Carboplatin



